Related Research Articles

The Tuath(a) Dé Danann, also known by the earlier name Tuath Dé, are a supernatural race in Irish mythology. They are thought to represent the main deities of pre-Christian Gaelic Ireland. The Tuatha Dé Danann constitute a pantheon whose attributes appeared in a number of forms throughout the Celtic world.

In Irish mythology, Nuada or Nuadu, known by the epithet Airgetlám, was the first king of the Tuatha Dé Danann. He is also called Nechtan, Nuadu Necht and Elcmar, and is the husband of Boann. He is mostly known from the tale in which he loses his arm or hand in battle, and thus his kingship, but regains it after being magically healed by Dian Cécht. Nuada is thought to have been a god and is related to the British and Gaulish god Nodens, who is associated with hunting and fishing. His Welsh equivalent is Nudd or Lludd Llaw Eraint.
In Irish mythology, Bodb Derg or Bodhbh Dearg was a son of Eochaid Garb or the Dagda, and the Dagda's successor as King of the Tuatha Dé Danann.

The Fomorians are a supernatural race in Irish mythology. They are often portrayed as hostile and monstrous beings who come from under the sea or the earth. Later, they were portrayed as giants and sea raiders. They are enemies of Ireland's first settlers and opponents of the Tuatha Dé Danann, the other supernatural race in Irish mythology. However, their relationship with the Tuath Dé is complex; some of their members intermarry and have children. The Fomorians have thus been likened to the jötnar of Norse mythology and the Titans of Greco-Roman mythology.

Nemed or Nimeth is a character in medieval Irish legend. According to the Lebor Gabála Érenn, he was the leader of the third group of people to settle in Ireland: the Muintir Nemid, Clann Nemid or "Nemedians". They arrived thirty years after the Muintir Partholóin, their predecessors, had died out. Nemed eventually dies of plague and his people are oppressed by the Fomorians. They rise up against the Fomorians, attacking their tower out at sea, but most are killed and the survivors leave Ireland. Their descendants become the Fir Bolg and the Tuatha Dé Danann.

In medieval Irish myth, the Fir Bolg are the fourth group of people to settle in Ireland. They are descended from the Muintir Nemid, an earlier group who abandoned Ireland and went to different parts of Europe. Those who went to Greece became the Fir Bolg and eventually return to Ireland, after it had been uninhabited for many years. After ruling it for some time and dividing the island into provinces, they are overthrown by the invading Tuatha Dé Danann.
Ogma is a god from Irish and Scottish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, he is often considered a deity and may be related to the Gallic god Ogmios. According to the Ogam Tract, he is the inventor of Ogham, the script in which Irish Gaelic was first written.
Tailtiu or Tailltiu is the name of a presumed goddess from Irish mythology. The goddess's name is linked to Teltown in Co. Meath, site of the Óenach Tailten. A legendary dindsenchas "lore of places" poem relates a myth connecting the presumed goddess Tailtiu with the site. However, linguistic analysis of the name reveals that Tailtiu as a place-name derives from a loan word of Brythonic origin represented by the Welsh telediw "well formed, beautiful." The mythological character of Tailtiu likely derives her name from the place-name.
In the Mythological Cycle of early Irish literature, Midir or Midhir was a son of the Dagda of the Tuatha Dé Danann. After the Tuatha Dé were defeated by the Milesians, he lived in the sidh of Brí Léith. The name Midir may come from the old Irish word for a judge, midithir.
Eochaid or Eochaidh is a popular medieval Irish and Scottish Gaelic name deriving from Old Irish ech, horse, borne by a variety of historical and legendary figures.
In Irish mythology Fintan mac Bóchra, known as "the Wise", was a seer who accompanied Noah's granddaughter Cessair to Ireland before the deluge. Bóchra may be his mother, or may be a poetic reference to the sea.

Cath Maige Tuired is the name of two saga texts of the Mythological Cycle of Irish mythology. It refers to two separate battles in Connacht: the first in the territory of Conmhaícne Cúile Tuireadh near Cong, County Mayo, the second near Lough Arrow in County Sligo. The two texts tell of battles fought by the Tuatha Dé Danann, the first against the Fir Bolg, and the second against the Fomorians.

The Mythological Cycle is a conventional division within Irish mythology, concerning a set of tales about the god-like peoples said to have arrived in five migratory invasions into Ireland and principally recounting the doings of the Tuatha Dé Danann. It is one of the four major cycles of early Irish literary tradition, the others being the Ulster Cycle, the Fenian Cycle and the Cycles of the Kings.
In Irish mythology Fodbgen or Odbgen son of Sengann of the Fir Bolg became High King of Ireland when he overthrew his cousin Rinnal son of Genann. It is said that before his time there were no knots in trees.
In Irish mythology Sreng was a champion of the Fir Bolg or Men of Bolg. Armed with an iron club or mace, he faced Nuada, king of the Tuatha Dé Danann in the first Battle of Magh Tuiredh, and with one great blow he cut off half his shield and severed Nuada's arm at the shoulder.
In Irish mythology Tuan mac Cairill was a recluse who retains his memories from his previous incarnations, going back to Antediluvian age. Initially a follower of Partholon, he alone survived the plague, or the Flood, that killed the rest of his people. Through a series of animal transformations he survived into Christian times, and, in conversation with St. Finnian of Moville told a brief history of himself and of Ireland from his people onward to the coming of St. Patrick.
Cairbre Cinnchait or Caitchenn was, according to medieval Irish legend and historical tradition, a High King of Ireland. There is considerable differences in the sources over his ancestry and his place in the traditional sequence of High Kings.
Rudraige, son of Dela, of the Fir Bolg was the legendary second High King of Ireland, succeeding his brother Sláine.
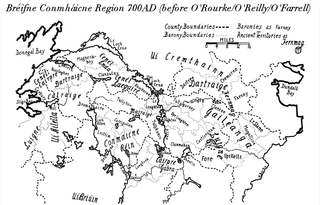
The Masraige were a semi-legendary Fir Bolg tribe inhabiting Magh Slécht in County Cavan, Ireland. They were also called Masragii, Masraide, Masraidhe, Masruidhe, Mascraide, Masree, Macraighe or Mascraidhe. The name can be translated as "Beautiful/Fine-Looking/Handsome Folk", from Old Irish mass "fine, becoming, beautiful, handsome" and raige "pre-Gaelic tribe".
References
- Lebor Gabála Érenn
- Annals of the Four Masters
- Seathrún Céitinn's Foras Feasa ar Érinn