Related Research Articles
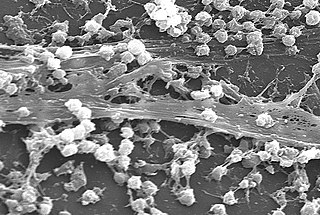
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes".
The class Flavobacteriia is composed of a single order of environmental bacteria. According to Bernardet et al., Flavobacteriia are Gram-negative aerobic rods, 2–5 μm long, 0.3–0.5 μm wide, with rounded or tapered ends that are motile by gliding, yellow colonies on agar, decompose several polysaccharides but not cellulose, G+C contents of 32–37%, and are widely distributed in soil and fresh and seawater habitats. In particular, Flavobacteriia are prominent members of marine biofilms. The type species Flavobacterium aquatile was isolated from a well in Kent, England.
Hyphomicrobium nitrativorans is a bacterium from the genus of Hyphomicrobium which was isolated from biofilm at the Montreal Biodome in Canada.
Psychroserpens is a Gram-negative and strictly aerobic bacteria genus from the family of Flavobacteriaceae.
Nocardioides salsibiostraticola is a Gram-positive, aerobic, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Nocardioides which has been isolated from biofilm from coastal seawater from the Norwegian Sea.
Dokdonia donghaensis is a strictly aerobic, gram-negative, phototrophic bacterium that thrives in marine environments. The organism can grow at a broad range of temperatures on seawater media. It has the ability to form biofilms, which increases the organism’s resistance to antimicrobial agents, such as tetracycline.
Chelatococcus caeni is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped and motile bacterium from the genus of Chelatococcus which has been isolated from biofilm reactor sludge in Korea.
Costertonia is a mesophilic genus of bacteria from the family of Flavobacteriaceae with one known species. The genus Costertonia is named after the American microbiologist J.W. Costerton.
Pseudogracilibacillus marinus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, endospore-forming, aerobic and motile bacterium from the genus of Pseudogracilibacillus which has been isolated from biofilm from seawater.
Diaphorobacter polyhydroxybutyrativorans is a Gram-negative, facultatively aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Diaphorobacter which has been isolated from biofilm from a denitrifying reactor in Beijing in China. Diaphorobacter polyhydroxybutyrativorans has the ability to degrade poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate).
Rhodanobacter is a Gram-negative and non-motile genus of Proteobacteria.
Rhodanobacter thiooxydans is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Rhodanobacter which has been isolated from biofilm from Daejon in Korea.
Metallibacterium is a Gram-negative genus of Proteobacteria from the family of Rhodanobacteraceae with one known species. Metallibacterium scheffleri has been isolated from acidic biofilm from a pyrite mine from the Harz Mountain in Germany.
Cribrihabitans marinus is a Gram-negative bacterium from the genus of Cribrihabitans which has been isolated from biofilm from a marine recirculating aquaculture system in Tianjin in China.
Epibacterium multivorans is an aerobic bacteria bacterium from the genus of Epibacterium which has been isolated from seawater from the beach of Malvarrosa in Spain.
Epibacterium mobile is a bacterium from the genus of Epibacterium.
Limimaricola hongkongensis is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, short rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Limimaricola which has been isolated from biofilm from Hong Kong.
Shimia marina is a bacterium from the genus of Shimia which has been isolated from biofilm from a coastal fish farm from Tongyeong in Korea.
Kopriimonas is a genus of bacteria from the family of Kopriimonadaceae. Kopriimonas byunsanensis has been isolated from a marine biofilm.
Polaribacter septentrionalilitoris is a species of Gram-negative, non-motile temperate marine bacteria, traits typical of members of the genus Polaribacter. This strain was originally isolated from the biofilm of a stone collected at Nordstrand, which is a tiny peninsula on the German portion of the North Sea. Lab culture tests have found it to be mesophilic in nature. Colonies of this strain are pigmented bright yellow when grown on agar. It also demonstrates robust growth on hypersaline agar. Its type strain is ANORD1T.
References
- 1 2 Parte, A.C. "Epibacterium". LPSN .
- 1 2 3 4 "Epibacterium scottomollicae". www.uniprot.org.
- ↑ "Details: DSM-25328". www.dsmz.de.
- ↑ Vandecandelaere, I; Nercessian, O; Segaert, E; Achouak, W; Faimali, M; Vandamme, P (December 2008). "Ruegeria scottomollicae sp. nov., isolated from a marine electroactive biofilm". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 58 (Pt 12): 2726–33. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65843-0 . PMID 19060048.