
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine.

Methylecgonine cinnamate is a natural tropane alkaloid found within the coca plant. Its more common name, cinnamoylcocaine, reflects its close structural similarity to cocaine. It is said to be pharmacologically inactive. But some studies funded by anti-drug agencies imply that it is active when smoked. Furthermore, the discovery of differing impurity products yielding methylecgonine cinnamate in confiscated cocaine have led enforcing agencies to postulate that illicit manufacturers have changed their oxidation procedures when refining cocaine from a crude form. Methylecgonine cinnamate can dimerize to the truxillic acid derivative truxilline. It is notable that methylecgonine cinnamate is given in patents of active cocaine analogue structures.

Erythroxylum coca is one of two species of cultivated coca.
Tropane is a nitrogenous bicyclic organic compound. It is mainly known for a group of alkaloids derived from it, which include, among others, atropine and cocaine. Tropane alkaloids occur in plants of the families Erythroxylaceae and Solanaceae.

Hydroxytropacocaine is a tropane alkaloid found in Erythroxylum coca.
The name Catuaba is used for the infusions of the bark of a number of trees native to Brazil. The most widely used barks are derived from the trees Trichilia catigua and Erythroxylum vaccinifolium. Other catuaba preparations use the bark of trees from the following genera or families: Anemopaegma, Ilex, Micropholis, Phyllanthus, Secondatia, Tetragastris and species from the Myrtaceae.

Erythroxylum (Erythroxylon) is a genus of tropical flowering plants in the family Erythroxylaceae. Many of the approximately 200 species contain the drug cocaine; Erythroxylum coca, a native of South America, is the main commercial source of cocaine and of the mild stimulant coca tea. Another species, Erythroxylum vaccinifolium is used as an aphrodisiac in Brazilian drinks and herbal medicine.

Erythroxylaceae is a family of flowering trees and shrubs consisting of 4 genera and 271 species. The four genera are AneulophusBenth., ErythroxylumP.Browne, NectaropetalumEngl., and PinacopodiumExell & Mendonça. The best-known species are the coca plants, including the species Erythroxylum coca, the source of the drug cocaine.

Erythroxylum australe is a shrub or small tree in the Malpighiales, endemic to northern Australia. The plant is known by a variety of names including Brigalow erythroxylon shrub and dogwood.
Otto Eugen Schulz was a German botanist, born in Berlin. He was the brother of botanist Roman Schulz (1873-1926).

Xenohyla truncata, the Izecksohn's Brazilian treefrog, is a species of frugivorous tree frog in the family Hylidae. It is endemic to the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.

Catuabines are a group of tropane alkaloids, isolated from Erythroxylum vaccinifolium, which are used in the preparation of the drug Catuaba. While catuabine A, B and C were isolated and characterized by Graf and Lude, catuabine D was recently isolated by Zanolari et al. The catuabines are not known to have any physiological effects, this is in contrast to cocaine, which is an active constituent of another species, Erythroxylum coca.
Erythroxylum pacificum is a species of plant in the Erythroxylaceae family. It is endemic to Peru.
Erythroxylum ruizii is a species of plant in the Erythroxylaceae family. It is endemic to Ecuador. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests.
Erythroxylum sechellarum is a species of plant in the Erythroxylaceae family. It is endemic to Seychelles.
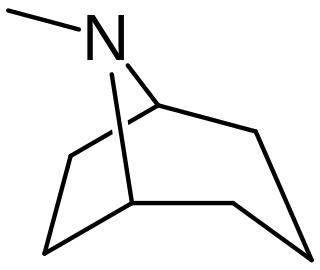
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic [3.2.1] alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Some tropane alkaloids have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants.
Methylecgonone reductase (EC 1.1.1.334, MecgoR (gene name)) is an enzyme with systematic name ecgonine methyl ester:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Coca alkaloids are the alkaloids found in the coca plant, Erythroxylum coca. They are predominantly of either the pyrrolidine or the tropane types.

Erythroxylum vaccinifolium is a flowering plant species in the genus Erythroxylum.

Psychoactive plants are plants, or preparations thereof, that upon ingestion induce psychotropic effects. As stated in a reference work:
Psychoactive plants are plants that people ingest in the form of simple or complex preparations in order to affect the mind or alter the state of consciousness.











