
The dwarf sperm whale is a sperm whale that inhabits temperate and tropical oceans worldwide, in particular continental shelves and slopes. It was first described by biologist Richard Owen in 1866, based on illustrations by naturalist Sir Walter Elliot. The species was considered to be synonymous with the pygmy sperm whale from 1878 until 1998. The dwarf sperm whale is a small whale, 2 to 2.7 m and 136 to 272 kg, that has a grey coloration, square head, small jaw, and robust body. Its appearance is very similar to the pygmy sperm whale, distinguished mainly by the position of the dorsal fin on the body–nearer the middle in the dwarf sperm whale and nearer the tail in the other.

The Cyclopteridae are a family of marine fishes, commonly known as lumpsuckers or lumpfish, in the order Scorpaeniformes. They are found in the cold waters of the Arctic, North Atlantic, and North Pacific oceans. The greatest number of species are found in the North Pacific. The family name Cyclopteridae derives from the Greek words κύκλος (kyklos), meaning "circle", and πτέρυξ (pteryx), meaning "wing" or "fin", in reference to the circle-shaped pectoral fins of most of the fish in this family.

Channa is a genus of predatory fish in the family Channidae, commonly known as snakeheads, native to freshwater habitats in Asia. This genus contains about 50 scientifically described species. The genus has a wide natural distribution extending from Iraq in the west, to Indonesia and China in the east, and parts of Siberia in the Far East. A particularly high richness of species exists in Myanmar (Burma) and northeastern India, and many Channa species live nowhere else. In contrast, a few widespread species have been introduced to several regions outside their natural range, where they often become invasive. The large and medium-sized Channa species are among the most common staple food fish in several Asian countries, and they are extensively cultured. Apart from their importance as a food fish, snakeheads are consumed in some regions as a traditional medicine for wound healing and reducing postoperative pain and discomfort, and collected for the international aquarium pet trade.

Dwarf snakehead is a term coined by aquarists to describe a group of Channa snakehead fishes growing to about 25 cm (10 in) maximum. They are found in freshwater habitats in South and Southeast Asia, and southern China.

Danio is a genus of small freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae found in South and Southeast Asia, commonly kept in aquaria. They are generally characterised by a pattern of horizontal stripes, rows of spots or vertical bars. Some species have two pairs of long barbels. Species of this genus consume various small aquatic insects, crustaceans and worms.

Cephaloscyllium is a genus of catsharks, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, commonly known as swellsharks because of their ability to inflate their bodies with water or air as a defense against predators. These sluggish, bottom-dwelling sharks are found widely in the tropical and temperate coastal waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. They have stocky, spindle-shaped bodies and short, broad, and flattened heads. The mouth is capacious, containing many small teeth and lacking furrows at the corners. The two dorsal fins are placed far back on the body, with the first much larger than the second. Different species have various color patterns of saddles, blotches, reticulations, and/or spots. The largest members of the genus can grow over 1 m (3.3 ft) in length. Swellsharks prey on a variety of fishes and invertebrates, and are oviparous, with females producing egg capsules in pairs. They are harmless and have been deemed of having no commercial value.

Dendrochirus brachypterus, the dwarf lionfish, short-finned turkeyfish, shortspine rockcod or shortspine scorpionfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and lionfishes. It is found in the Indo-Pacific. It is sometimes found in the aquarium trade.
Anatoly Petrovich Andriyashev was a Soviet and Russian ichthyologist, marine biologist, and zoogeographist, notable for his studies of marine fauna of the Arctic and the Northern Pacific.

Eumicrotremus is a genus of lumpfishes native to the northern oceans. The name for this genus comes from the Greek roots eu meaning "good", mikros meaning "small" or "little", and trema meaning "hole".

Lethotremus is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cyclopteridae, the lumpfishes or lumpsuckers. This genus is found in the northern Pacific Ocean. Following a 2017 taxonomic review by Lee et al., the species Lethotremus awae was reclassified as a species of Eumicrotremus, leaving the genus monotypic with Lethotremus muticus as its only species. Also known as the docked snailfish, is a species of lumpfish native to the Northeast Pacific. It is known from the Bering Sea and the Aleutian Islands, where its range extends to Unimak Pass, and it occurs at a depth range of 58 to 330 m. It is a benthic species that reaches 11.5 cm in total length. It can be found on substrates of mud, rock, or gravel, and it is currently the only known species of Lethotremus, following a reclassification of the second described species in the genus as Eumicrotremus awae.

The Pacific spiny lumpsucker is a species of bony fish in the family Cyclopteridae.
Eumicrotremus andriashevi, also known as the pimpled lumpsucker, is a species of lumpfish native to the Arctic and North Pacific. In addition to the Arctic Ocean, it may be found in the Chukchi and Bering Seas, where it occurs at a depth range of 20 to 83 m. It is a small bottom-dwelling fish that reaches 4.8 cm in standard length.

Eumicrotremus spinosus, commonly known as the Atlantic spiny lumpsucker, is a species of lumpfish native to the Arctic and North Atlantic.
Eumicrotremus jindoensis is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific, where it may be found off the coast of the Korean Peninsula and in the Yellow Sea. It occurs at a depth range of 20 to 30 metres, and it reaches 2.5 centimetres (1 in) SL. This species was described in 2017 as part of a review of "dwarf" species of Eumicrotremus, which reclassified the species then known as Lethotremus awae as a member of Eumicrotremus in addition to describing another similarly small new species, known as Eumicrotremus uenoi.

Eumicrotremus pacificus, sometimes known as the spotted lumpsucker or the balloon lumpfish, is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific. It can be found in the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan, the East China Sea, and the Pacific Ocean off Hokkaido and the Kuril Islands. It may be confused with the closely related Eumicrotremus orbis, which overlaps with E. pacificus in range, although E. pacificus is larger, reaching 20 cm (7.9 inches) TL. This fish is generally yellow to orange in color with small dark spots and its tubercles are usually smaller and less pronounced than E. orbis, giving it a less spiny appearance.
Eumicrotremus schmidti is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific. It is a demersal fish known only from the northern Sea of Okhotsk, where it is found at a depth range of 20 to 143 m. Specimens of E. schmidti were once attributed to the related species E. andriashevi, which does not inhabit the Sea of Okhotsk. This species was first formally described in 1955 by the Soviet ichthyologists Georgii Ustinovich Lindberg and Marina Iosifovna Legeza with its type locality given as Penzhinskaya Bay in the Sea of Okhotsk in Russia. The identity of the person honoured in the specific name was not given by Lindberg and Legeza but it is likely to be Petr Yulievich Schmidt, a Russian ichthyologist.

Eumicrotremus taranetzi is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific. It is known from the Bering Sea, the Kuril Islands, the Sea of Okhotsk, and the Sea of Japan. It is a small demersal fish that reaches 5.9 cm SL.
Eumicrotremus uenoi is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific. It is found off the Korean Peninsula and Japan, where it occurs at a depth range of 90 to 100 m. It is a very small demersal fish, reaching 2 cm SL. The species was named after Dr. Tatsuji Ueno, formerly of the Hokkaido Fisheries Experimental Station, in honor of his work with the systematics of Cyclopteridae, the lumpfishes. It was described in 2017 following a taxonomic review of "dwarf" lumpfishes that also resulted in the description of Eumicrotremus jindoensis and the reclassification of the species Lethotremus awae as Eumicrotremus awae.
Eumicrotremus tokranovi is a species of lumpfish native to the Northwest Pacific, and one of two species some authorities place in the genus Microancathus. It is known from the Kuril Islands. It is distinguished from the closely related E. fedorovi by a taller body and flatter and less developed bone plaques. FishBase does not recognize the genus Microancathus,. This species was described by the Russian ichthyologist Olga Stepanovna Voskoboinikova in 2015 in the proposed new genus, Microancathus and the reclassification of M. fedorovi in that genus. Catalog of Fishes does not recognize the new genus and classifies this species in Eumicrotremus. The specific name honors the ichthyologist Alexei Mikhailovich Tokranovof the Kamchatka Branch of the Pacific Institute of Geography and the Far East Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
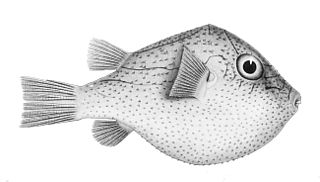
Canthigaster investigatoris is a species of pufferfish in the family Tetraodontidae. It is an oviparous demersal species known only from Indonesia. It may occur as far down as 101 m (331 ft).














