
Diatoms are a major group of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes.

The order Pennales is a traditional subdivision of the heterokont algae known as diatoms. The order is named for the shape of the cell walls of pennate diatoms, which are elongated in valve view. The valves may be linear or oval in shape, and usually bear bilaterally symmetrical ornamental patterns. These patterns are composed of a series of transverse lines that can appear as rows of dots when viewed with an optical microscope. Some pennate diatoms also exhibit a fissure along their longitudinal axis. This is known as a raphe, and is involved in gliding movements made by diatom cells; motile diatoms always possess a raphe.

The Coscinodiscophyceae are a class of diatoms. They are similar to the Centrales, a traditional, paraphyletic subdivision of the heterokont algae known as diatoms. The order is named for the shape of the cell walls of centric diatoms, which are circular or ellipsoid in valve view. The valves often bear radially symmetrical ornamental patterns that can appear as dots when viewed with an optical microscope. Some also bear spines on their valves, which may either increase cell surface area and reduce sinking, or act as a deterrent to zooplankton grazers. Unlike pennate diatoms, centric diatoms never have a raphe.
In certain species of diatoms, auxospores are specialised cells that are produced at key stages in their cell cycle or life history. Auxospores typically play a role in growth processes, sexual reproduction or dormancy.

Chaetocerotaceae is a diatom family (Bacillariophyta). This family comprise the three genera Attheya T. West, Bacteriastrum Shadbolt and Chaetoceros Ehrenberg. Chaetoceros is perhaps the largest and most species rich genus of marine planktonic diatoms. The taxonomic status within Chaetocerotaceae at present is somewhat unclear.

Chaetoceros is probably the largest genus of marine planktonic diatoms with approximately 400 species described, although many of these descriptions are no longer valid. It is often very difficult to distinguish between different Chaetoceros species. Several attempts have been made to restructure this large genus into subgenera and this work is still in progress. However, most of the effort to describe species has been focused in boreal areas, and the genus is cosmopolitan, so there are probably many tropical species still undescribed. Some species are known from the fossil record, from the Quaternary of Sweden. It is the type genus of its family.
Craticula is a genus of diatom that lies on or in the top layers of sediments in the freshwater to brackish water environments it inhabits. In addition to frustule morphology the genus differs from closely related species by its sexual reproduction and movement in response to light.
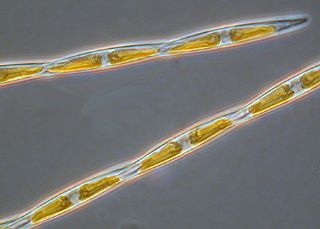
Pseudo-nitzschia is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of Pseudo-nitzschia occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health.
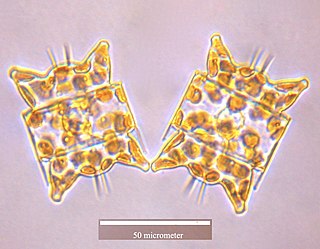
Odontella aurita is a diatom and the type species of genus Odontella. The easiest way to identify this species is by recognizing the very distinct shape of the cells belonging to this genus. Odontella aurita is cultivated industrially for human consumption due to its ability to produce up to 28% of its total lipids as Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). PUFAs such as EPA are known to provide a variety of health benefits in humans, and are commonly obtained by fish oil. However, with the increasing concern of over-exploited fisheries, microalgae are a promising source of PUFAs as they can be grown year-round and their fatty acid profile and content are easily manipulated by growth conditions.

Amphora is a major genus of marine and freshwater diatoms. With over 1000 species, it is one of the largest genera of diatoms. These diatoms are recognized by their strongly dorsiventral frustules, which means that their ridges lie close to the ventral margin of the valve, and their girdle is much wider on the dorsal side.
Eugene F. Stoermer was a leading researcher in diatoms, with a special emphasis on freshwater species of the North American Great Lakes. He was a professor of biology at the University of Michigan School of Natural Resources and Environment.

The Cymbellaceae are a diatom family in the order Cymbellales.

Ditylum brightwelli is a species of cosmopolitan marine centric diatoms. It is a unicellular photosynthetic autotroph that has the ability to divide rapidly and contribute to spring phytoplankton blooms.
Navicula cari is a species of algae in the genus Navicula. Navicula cari occur in eutrophic waters.
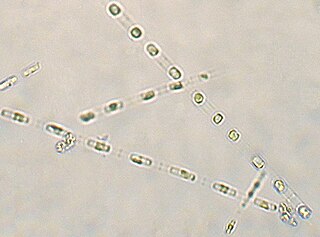
Skeletonema is a genus of diatoms in the family Skeletonemataceae. It is the type genus of its family. The genus Skeletonema was established by R.K. Greville in 1865 for a single species, S. barbadense, found in the Barbados deposit [Jung 2009]. These diatoms are photosynthetic organisms, meaning they obtain carbon dioxide from their surrounding environment and produce oxygen along with other byproducts. Reproduce sexually and asexually [Guiry 2011]. Skeletonema belong to the morphological category referred to as centric diatoms. These are classified by having valves with radial symmetry and the cells lack significant motility [Horner 2002]. Skeletonema are cylindrical shaped with a silica frustule. Cells are joined by long marginal processes to form a filament [Horner 2002]. Their length ranges from 2-61 micrometers, with a diameter ranging from 2-21 micrometers [Hasle 1997]. They are found typically in the neritic zone of the ocean and are highly populous in coastal systems [Jung 2009]. The genus is considered cosmopolitan, showing a wide range of tolerance for salinity and temperature [Hasle 1973]. For example, they have been found in various aquatic environments such as brackish or freshwater. Skeletonema are found worldwide excluding Antarctic waters [Hevia-Orube 2016]. Some harmful effects these diatoms may have on an ecosystem are attributed to large blooming events which may cause hypoxic events in coastal systems. Additionally, they are known to cause water discoloration [Kraberg 2010].

Biddulphiaceae is a family of diatom in the order Biddulphiales. The Biddulphiaceae are distinguished from the Eupodiscaceae by their pseudocelli, where the Eupodiscaceae have fully developed ocelli. Both families commonly inhabit the littoral zone of the ocean, close to the shore. Sixteen species of Biddulphiaceae are found on the west coast of India.
Luticola is a genus of marine diatoms.
Stauroneis is a genus of diatoms (Bacillariophyta) with species that occur in fresh and marine water.
Cyclotella is a genus of diatoms often found in oligotrophic environments, both marine and fresh water. It is in the family Stephanodiscaceae and the order Thalassiosirales. The genus was first discovered in the mid 1800s and since then has become an umbrella genus for nearly 100 different species, the most well-studied and the best known being Cyclotella meneghiniana. Despite being among the most dominant genera in low-productivity environments, it is relatively understudied.

Diatoms belong to a large group called the heterokonts, which include both autotrophs such as golden algae and kelp; and heterotrophs such as water moulds. The classification of heterokonts is still unsettled: they may be designated a division, phylum, kingdom, or something intermediate to those. Consequently, diatoms are ranked anywhere from a class, usually called Diatomophyceae or Bacillariophyceae, to a division (=phylum), usually called Bacillariophyta, with corresponding changes in the ranks of their subgroups.











