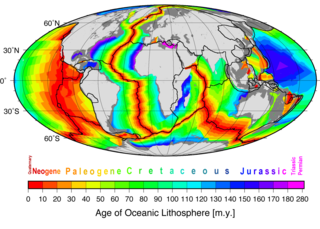
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.

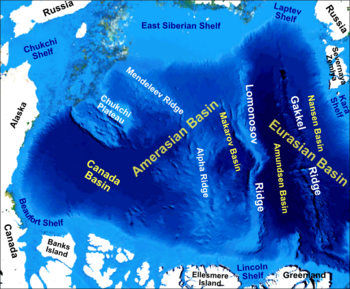
The Gakkel Ridge is a mid-oceanic ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is located in the Eurasian Basin of the Arctic Ocean, between Greenland and Siberia, and has a length of about 1,800 kilometers. Geologically, it connects the northern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge with the Laptev Sea Rift.
In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, ocean basins are large geologic basins that are below sea level.

A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about 2,600 meters (8,500 ft) and rises about 2,000 meters (6,600 ft) above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin.

Lincoln Sea is a body of water in the Arctic Ocean, stretching from Cape Columbia, Canada, in the west to Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland, in the east. The northern limit is defined as the great circle line between those two headlands. It is covered with sea ice throughout the year, the thickest sea ice in the Arctic Ocean, which can be up to 15 m (49 ft) thick. Water depths range from 100 m (330 ft) to 300 m (980 ft). Water and ice from Lincoln Sea empty into Robeson Channel, the northernmost part of Nares Strait, most of the time.

The Lomonosov Ridge is an unusual underwater ridge of continental crust in the Arctic Ocean. It spans 1,800 kilometres (1,100 mi) between the New Siberian Islands over the central part of the ocean to Ellesmere Island of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The ridge divides the Arctic Basin into the Eurasian Basin and the Amerasian Basin. The width of the Lomonosov Ridge varies from 60 to 200 kilometres. It rises 3,300 to 3,700 metres above the 4,200-metre (13,800 ft) deep seabed. The minimum depth of the ocean above the ridge is less than 400 metres (1,300 ft). Slopes of the ridge are relatively steep, broken up by canyons, and covered with layers of silt.

Litke Deep is an oceanic trench in the Arctic Ocean. The deepest point, also referred to as Litke Deep is 5,449 m (17,877 ft) below sea level.

The Alpha Ridge is a major volcanic ridge under the Arctic Ocean between the Canada Basin and the Lomonosov Ridge. It was active during the formation of the Amerasian Basin. It was discovered in 1963. The highest elevation is about 2,700 m over the ocean floor. It is 200 to 450 km wide. The Alpha Ridge, Lomonosov Ridge, and Nansen-Gakkel Ridge are the three major ranges that divide the Arctic Ocean floor, running generally parallel to each other.

The Siberian Shelf is a coastal shelf in the Arctic Ocean and is the largest continental shelf of the Earth, a part of the continental shelf of Russia. It extends from the continent of Eurasia in the general area of North Siberia into the Arctic Ocean. It stretches to 1,500 kilometers (930 mi) offshore. It is relatively shallow, with average depth of 100 m. A number of islands are within the shelf, including the Wrangel Island, Novaya Zemlya, and the New Siberian Islands.
The continental shelf of Russia is a continental shelf adjacent to the Russian Federation. Geologically, the extent of the shelf is defined as the entirety of the continental shelves adjacent to Russia's coast. In international law, however, the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea more narrowly defines the extent of the shelf as the seabed and subsoil of the submarine areas over which a state exercises sovereign rights.

The Amerasia Basin, or Amerasian Basin, is one of the two major basins from which the Arctic Ocean can be subdivided. The triangular-shaped Amerasia Basin broadly extends from the Canadian Arctic Islands to the East Siberian Sea, and from Alaska to the Lomonosov Ridge. The basin can be further subdivided based on bathymetric features; these include the Canada Basin, the Makarov Basin, the Podvodnikov Basin, the Alpha-Mendeleev Ridge, and the Chukchi Plateau.
The Molloy Deep is a bathymetric feature in the Fram Strait, within the Greenland Sea east of Greenland and about 160 km west of Svalbard. It is the location of the deepest point in the Arctic Ocean. The Molloy Deep, Molloy Hole, Molloy Fracture Zone, and Molloy Ridge were named after Arthur E. Molloy, a U.S. Navy research scientist who worked in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic Oceans in the 1950s-1970s.

The Arctic Basin is an oceanic basin in the Arctic Ocean, consisting of two main parts separated by the Lomonosov Ridge, a mid-ocean ridge between north Greenland and the New Siberian Islands. It is bordered by the continental shelves of Eurasia and North America.

The South American–Antarctic Ridge or simply American-Antarctic Ridge is the tectonic spreading center between the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate. It runs along the sea-floor from the Bouvet Triple Junction in the South Atlantic Ocean south-westward to a major transform fault boundary east of the South Sandwich Islands. Near the Bouvet Triple Junction the spreading half rate is 9 mm/a (0.35 in/year), which is slow, and the SAAR has the rough topography characteristic of slow-spreading ridges.
The Laptev Sea Rift is a divergent tectonic plate boundary between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate located on the Arctic Ocean coast of northeastern Siberia in Russia. The Laptev Sea Rift is the continuation of the Gakkel Ridge into the continental crust of Siberia. It starts offshore in the continental shelf and continues onshore to a point located in the Chersky Range where the boundary motion changes from extension to compression.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.

The Fram Strait is the passage between Greenland and Svalbard, located roughly between 77°N and 81°N latitudes and centered on the prime meridian. The Greenland and Norwegian Seas lie south of Fram Strait, while the Nansen Basin of the Arctic Ocean lies to the north. Fram Strait is noted for being the only deep connection between the Arctic Ocean and the World Oceans. The dominant oceanographic features of the region are the West Spitsbergen Current on the east side of the strait and the East Greenland Current on the west.

The Transpolar Drift Stream is a major ocean current of the Arctic Ocean, transporting sea ice from the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea towards Fram Strait. Drift experiments with ships such as the Fram or the Tara expedition showed that the drift takes between two and four years.

The Amundsen Basin, with depths up to 4.4 km (2.7 mi), is the deepest abyssal plain in the Arctic Ocean, and contains the geographic North Pole. The Amundsen Basin is embraced by the Lomonosov Ridge and the Gakkel Ridge. It is named after the polar researcher Roald Amundsen. Together with the Nansen Basin, the Amundsen Basin is often summarized as Eurasian Basin.

The Nansen Basin is an abyssal plain with water-depths of around 3 km in the Arctic Ocean and part of the Eurasian Basin. It is named after Fridtjof Nansen. The Nansen Basin is bounded by the Gakkel Ridge on the one side and by the Barents Sea continental shelf on the other.