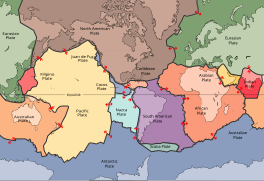
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift, an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called tectonics. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons.

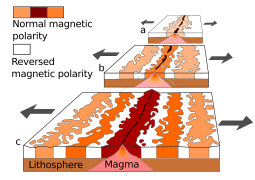
Seafloor spreading, or seafloor spread, is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
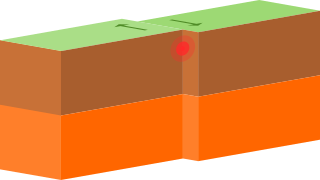
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a strike-slip fault that also forms a plate boundary.

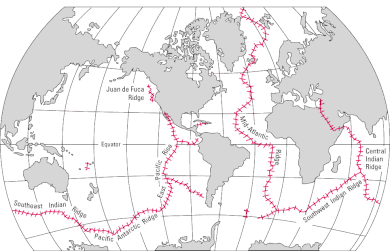
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts, which eventually become rift valleys. Most active divergent plate boundaries occur between oceanic plates and exist as mid-oceanic ridges.

A convergent boundary is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types.

Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust overlies the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere.
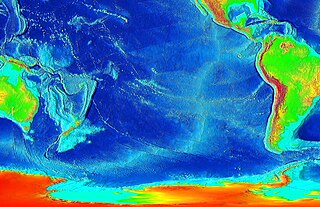
The East Pacific Rise (EPR) is a mid-ocean rise, at a divergent tectonic plate boundary, located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific plate to the west from the North American plate, the Rivera plate, the Cocos plate, the Nazca plate, and the Antarctic plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55°S130°W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) trending west-south-west towards Antarctica, near New Zealand. Much of the rise lies about 3,200 km (2,000 mi) off the South American coast and reaches a height about 1,800–2,700 m (5,900–8,900 ft) above the surrounding seafloor.
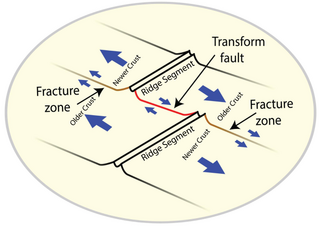
A fracture zone is a linear feature on the ocean floor—often hundreds, even thousands of kilometers long—resulting from the action of offset mid-ocean ridge axis segments. They are a consequence of plate tectonics. Lithospheric plates on either side of an active transform fault move in opposite directions; here, strike-slip activity occurs. Fracture zones extend past the transform faults, away from the ridge axis; are usually seismically inactive, although they can display evidence of transform fault activity, primarily in the different ages of the crust on opposite sides of the zone.
Marine geology or geological oceanography is the study of the history and structure of the ocean floor. It involves geophysical, geochemical, sedimentological and paleontological investigations of the ocean floor and coastal zone. Marine geology has strong ties to geophysics and to physical oceanography.

The supercontinent cycle is the quasi-periodic aggregation and dispersal of Earth's continental crust. There are varying opinions as to whether the amount of continental crust is increasing, decreasing, or staying about the same, but it is agreed that the Earth's crust is constantly being reconfigured. One complete supercontinent cycle is said to take 300 to 500 million years. Continental collision makes fewer and larger continents while rifting makes more and smaller continents.

A back-arc basin is a type of geologic basin, found at some convergent plate boundaries. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones, with many found in the western Pacific Ocean. Most of them result from tensional forces, caused by a process known as oceanic trench rollback, where a subduction zone moves towards the subducting plate. Back-arc basins were initially an unexpected phenomenon in plate tectonics, as convergent boundaries were expected to universally be zones of compression. However, in 1970, Dan Karig published a model of back-arc basins consistent with plate tectonics.

The Izu–Bonin–Mariana (IBM) arc system is a tectonic plate convergent boundary in Micronesia. The IBM arc system extends over 2800 km south from Tokyo, Japan, to beyond Guam, and includes the Izu Islands, the Bonin Islands, and the Mariana Islands; much more of the IBM arc system is submerged below sealevel. The IBM arc system lies along the eastern margin of the Philippine Sea plate in the Western Pacific Ocean. It is the site of the deepest gash in Earth's solid surface, the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench.

The Aegir Ridge is an extinct segment of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in the far-northern Atlantic Ocean. It marks the initial break-up boundary between Greenland and Norway, along which seafloor spreading was initiated at the beginning of the Eocene epoch to form the northern Atlantic Ocean. Towards the end of the Eocene, the newly forming Kolbeinsey Ridge propagated northwards from Iceland, splitting the Jan Mayen Microcontinent away from the Greenland plate. As the Kolbeinsey Ridge formed, so activity on the Aegir Ridge reduced, ceasing completely at the end of the Oligocene epoch when the Kolbeinsey Ridge reached the Jan Mayen fracture zone.

Kenneth Craig Macdonald is an American oceanographer and marine geophysicist born in San Francisco, California, in 1947. As of 2018 he is professor emeritus at the Department of Earth Science and the Marine Sciences Institute at the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB). His work focuses on the tectonics and geophysics of the global mid-oceanic ridge including its spreading centers and transform faults, two of the three types of plate boundaries central to the theory of plate tectonics. His work has taken him to the north and south Atlantic oceans, the north and south Pacific oceans, the Indian Ocean, the Red Sea and the Sea of Cortez, as well as to the deep seafloor on over 50 dives in the research submersible ALVIN. Macdonald has participated in over 40 deep sea expeditions, and was chief- or co-chief scientist on 31 expeditions.
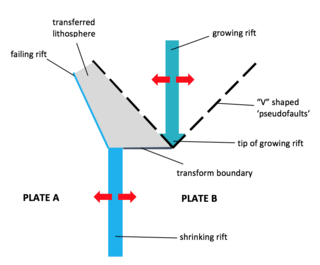
A propagating rift is a seafloor feature associated with spreading centers at mid-ocean ridges and back-arc basins. They are more commonly observed on faster rate spreading centers. These features are formed by the lengthening of one spreading segment at the expense of an offset neighboring spreading segment. Hence, these are remnant features produced by migration of the tip of a spreading center. In other words, as the tip of a spreading center migrates or grows, the plate itself grows at the expense of the shrinking plate, transferring lithosphere from the shrinking plate to the growing plate.
Ridge push is a proposed driving force for plate motion in plate tectonics that occurs at mid-ocean ridges as the result of the rigid lithosphere sliding down the hot, raised asthenosphere below mid-ocean ridges. Although it is called ridge push, the term is somewhat misleading; it is actually a body force that acts throughout an ocean plate, not just at the ridge, as a result of gravitational pull. The name comes from earlier models of plate tectonics in which ridge push was primarily ascribed to upwelling magma at mid-ocean ridges pushing or wedging the plates apart.
The depth of the seafloor on the flanks of a mid-ocean ridge is determined mainly by the age of the oceanic lithosphere; older seafloor is deeper. During seafloor spreading, lithosphere and mantle cooling, contraction, and isostatic adjustment with age cause seafloor deepening. This relationship has come to be better understood since around 1969 with significant updates in 1974 and 1977. Two main theories have been put forward to explain this observation: one where the mantle including the lithosphere is cooling; the cooling mantle model, and a second where a lithosphere plate cools above a mantle at a constant temperature; the cooling plate model. The cooling mantle model explains the age-depth observations for seafloor younger than 80 million years. The cooling plate model explains the age-depth observations best for seafloor older that 20 million years. In addition, the cooling plate model explains the almost constant depth and heat flow observed in very old seafloor and lithosphere. In practice it is convenient to use the solution for the cooling mantle model for an age-depth relationship younger than 20 million years. Older than this the cooling plate model fits data as well. Beyond 80 million years the plate model fits better than the mantle model.

The plate theory is a model of volcanism that attributes all volcanic activity on Earth, even that which appears superficially to be anomalous, to the operation of plate tectonics. According to the plate theory, the principal cause of volcanism is extension of the lithosphere. Extension of the lithosphere is a function of the lithospheric stress field. The global distribution of volcanic activity at a given time reflects the contemporaneous lithospheric stress field, and changes in the spatial and temporal distribution of volcanoes reflect changes in the stress field. The main factors governing the evolution of the stress field are:
- Changes in the configuration of plate boundaries.
- Vertical motions.
- Thermal contraction.
Intraplate volcanism is volcanism that takes place away from the margins of tectonic plates. Most volcanic activity takes place on plate margins, and there is broad consensus among geologists that this activity is explained well by the theory of plate tectonics. However, the origins of volcanic activity within plates remains controversial.
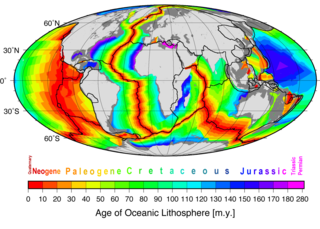
Marine geophysics is the scientific discipline that employs methods of geophysics to study the world's ocean basins and continental margins, particularly the solid earth beneath the ocean. It shares objectives with marine geology, which uses sedimentological, paleontological, and geochemical methods. Marine geophysical data analyses led to the theories of seafloor spreading and plate tectonics.