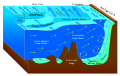
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection.

The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths". Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud.
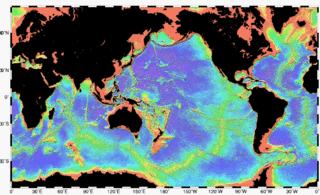
Bathymetry is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors, lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago.

The seabed is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.

A survey vessel is any type of ship or boat that is used for underwater surveys, usually to collect data for mapping or planning underwater construction or mineral extraction. It is a type of research vessel, and may be designed for the purpose, modified for the purpose or temporarily put into the service as a vessel of opportunity, and may be crewed, remotely operated, or autonomous. The size and equipment vary to suit the task and availability.

The National Oceanography Centre Southampton (NOCS) is a centre for research, teaching, and technology development in Ocean and Earth science. NOCS was created in 1995, jointly between the University of Southampton and the UK Natural Environment Research Council and is located within the port of Southampton at a purpose-built dockside campus with modern facilities. In 2010 the university and NERC components demerged, and the NERC-managed component became the National Oceanography Centre. The two components of NOCS continue close collaboration through the jointly run Graduate School, shared research facilities and laboratories, complementary research groups, and many joint research grants and publications. The university component “Ocean and Earth Science, National Oceanography Centre Southampton” (OES) is part of the Faculty of Environmental and Life Sciences, (FELS). It was ranked 46th in the world for Earth and Marine Sciences by the QS World University Rankings in 2019.

Underwater acoustics is the study of the propagation of sound in water and the interaction of the mechanical waves that constitute sound with the water, its contents and its boundaries. The water may be in the ocean, a lake, a river or a tank. Typical frequencies associated with underwater acoustics are between 10 Hz and 1 MHz. The propagation of sound in the ocean at frequencies lower than 10 Hz is usually not possible without penetrating deep into the seabed, whereas frequencies above 1 MHz are rarely used because they are absorbed very quickly.

Scientific diving is the use of underwater diving techniques by scientists to perform work underwater in the direct pursuit of scientific knowledge. The legal definition of scientific diving varies by jurisdiction. Scientific divers are normally qualified scientists first and divers second, who use diving equipment and techniques as their way to get to the location of their fieldwork. The direct observation and manipulation of marine habitats afforded to scuba-equipped scientists have transformed the marine sciences generally, and marine biology and marine chemistry in particular. Underwater archeology and geology are other examples of sciences pursued underwater. Some scientific diving is carried out by universities in support of undergraduate or postgraduate research programs, and government bodies such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency and the UK Environment Agency carry out scientific diving to recover samples of water, marine organisms and sea, lake or riverbed material to examine for signs of pollution.

Deep-sea exploration is the investigation of physical, chemical, and biological conditions on the ocean waters and sea bed beyond the continental shelf, for scientific or commercial purposes. Deep-sea exploration is an aspect of underwater exploration and is considered a relatively recent human activity compared to the other areas of geophysical research, as the deeper depths of the sea have been investigated only during comparatively recent years. The ocean depths still remain a largely unexplored part of the Earth, and form a relatively undiscovered domain.

Gelatinous zooplankton are fragile animals that live in the water column in the ocean. Their delicate bodies have no hard parts and are easily damaged or destroyed. Gelatinous zooplankton are often transparent. All jellyfish are gelatinous zooplankton, but not all gelatinous zooplankton are jellyfish. The most commonly encountered organisms include ctenophores, medusae, salps, and Chaetognatha in coastal waters. However, almost all marine phyla, including Annelida, Mollusca and Arthropoda, contain gelatinous species, but many of those odd species live in the open ocean and the deep sea and are less available to the casual ocean observer. Many gelatinous plankters utilize mucous structures in order to filter feed. Gelatinous zooplankton have also been called Gelata.
Sediment Profile Imagery (SPI) is an underwater technique for photographing the interface between the seabed and the overlying water. The technique is used to measure or estimate biological, chemical, and physical processes occurring in the first few centimetres of sediment, pore water, and the important benthic boundary layer of water. Time-lapse imaging (tSPI) is used to examine biological activity over natural cycles, like tides and daylight or anthropogenic variables like feeding loads in aquaculture. SPI systems cost between tens and hundreds of thousands of dollars and weigh between 20 and 400 kilograms. Traditional SPI units can be effectively used to explore continental shelf and abyssal depths. Recently developed SPI-Scan or rSPI (rotational SPI) systems can now also be used to inexpensively investigate shallow (<50m) freshwater, estuarine, and marine systems.

The box corer is a marine geological sampling tool for soft sediments in lakes or oceans. It is deployed from a research vessel with a wire and suitable for any water depth. It is designed for a minimum of disturbance of the sediment surface by bow wave effects which is important for quantitative investigations of the benthic micro- to macrofauna, geochemical processes, sampling of bottom water or sedimentology.
Acoustic seabed classification is the partitioning of a seabed acoustic image into discrete physical entities or classes. This is a particularly active area of development in the field of seabed mapping, marine geophysics, underwater acoustics and benthic habitat mapping. Seabed classification is one route to characterizing the seabed and its habitats. Seabed characterization makes the link between the classified regions and the seabed physical, geological, chemical or biological properties. Acoustic seabed classification is possible using a wide range of acoustic imaging systems including multibeam echosounders, sidescan sonar, single-beam echosounders, interferometric systems and sub-bottom profilers. Seabed classification based on acoustic properties can be divided into two main categories; surficial seabed classification and sub-surface seabed classification. Sub-surface imaging technologies use lower frequency sound to provide higher penetration, whereas surficial imaging technologies provide higher resolution imagery by utilizing higher frequencies.
The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT) program is a long-term oceanographic study based at the University of Hawaii at Manoa. In 2015, the American Society for Microbiology designated the HOT Program's field site Station ALOHA a "Milestone in Microbiology", for playing "a key role in defining the discipline of microbial oceanography and educating the public about the vital role of marine microbes in global ecosystems."
The benthic boundary layer (BBL) is the layer of water directly above the sediment at the bottom of a body of water. Through specific sedimentation processes, certain organisms are able to live in this deep layer of water. The BBL is generated by the friction of the water moving over the surface of the substrate, which decrease the water current significantly in this layer. The thickness of this zone is determined by many factors, including the Coriolis force. The benthic organisms and processes in this boundary layer echo the water column above them.

BENGAL was the acronym of the research project High-resolution temporal and spatial study of the BENthic biology and Geochemistry of a north-eastern Atlantic abyssal Locality. The project was funded through the EC MAST III program from 1996 to 1998.

A cabled observatory is a seabed oceanographic research platform connected to land by cables that provide power and communication. Observatories are outfitted with a multitude of scientific instruments that can collect many kinds of data from the seafloor and water column. By removing the limitations of undersea power sources and sonar or RF communications, cabled observatories allow persistent study of underwater phenomena. Data from these instruments is relayed to a land station and data networks, such as Ocean Networks Canada, in real time.
Neocalanus cristatus is a species of copepod found primarily in the northern Pacific.
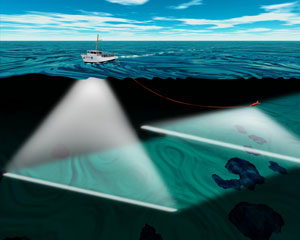
An underwater survey is a survey performed in an underwater environment or conducted remotely on an underwater object or region. Survey can have several meanings. The word originates in Medieval Latin with meanings of looking over and detailed study of a subject. One meaning is the accurate measurement of a geographical region, usually with the intention of plotting the positions of features as a scale map of the region. This meaning is often used in scientific contexts, and also in civil engineering and mineral extraction. Another meaning, often used in a civil, structural, or marine engineering context, is the inspection of a structure or vessel to compare actual condition with the specified nominal condition, usually with the purpose of reporting on the actual condition and compliance with, or deviations from, the nominal condition, for quality control, damage assessment, valuation, insurance, maintenance, and similar purposes. In other contexts it can mean inspection of a region to establish presence and distribution of specified content, such as living organisms, either to establish a baseline, or to compare with a baseline.

Underwater exploration is the exploration of any underwater environment, either by direct observation by the explorer, or by remote observation and measurement under the direction of the investigators. Systematic, targeted exploration is the most effective method to increase understanding of the ocean and other underwater regions, so they can be effectively managed, conserved, regulated, and their resources discovered, accessed, and used. Less than 10% of the ocean has been mapped in any detail, less has been visually observed, and the total diversity of life and distribution of populations is similarly obscure.