Related Research Articles

The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 km2 (41,100,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World.

The Norwegian Sea is a marginal sea in the Atlantic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea.

North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) is a deep water mass formed in the North Atlantic Ocean. Thermohaline circulation of the world's oceans involves the flow of warm surface waters from the southern hemisphere into the North Atlantic. Water flowing northward becomes modified through evaporation and mixing with other water masses, leading to increased salinity. When this water reaches the North Atlantic it cools and sinks through convection, due to its decreased temperature and increased salinity resulting in increased density. NADW is the outflow of this thick deep layer, which can be detected by its high salinity, high oxygen content, nutrient minima, high 14C/12C, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
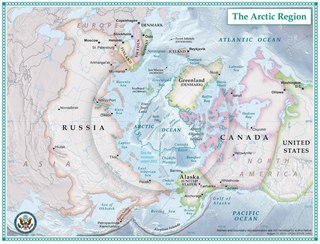
The Arctic is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada, Denmark (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States (Alaska). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places.

The Gakkel Ridge is a mid-oceanic ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is located in the Eurasian Basin of the Arctic Ocean, between Greenland and Siberia, and has a length of about 1,800 kilometers. Geologically, it connects the northern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge with the Laptev Sea Rift.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.
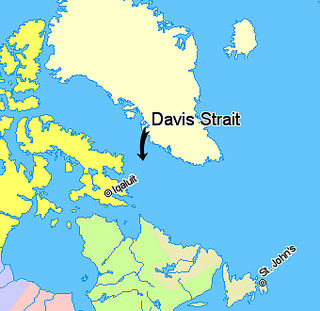
Davis Strait is a northern arm of the Atlantic Ocean that lies north of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. To the north is Baffin Bay. The strait was named for the English explorer John Davis (1550–1605), who explored the area while seeking a Northwest Passage. By the 1650s it was used for whale hunting.

The Labrador Sea is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, and northeast. It connects to the north with Baffin Bay through the Davis Strait. It is a marginal sea of the Atlantic.

The East Greenland Current (EGC) is a cold, low-salinity current that extends from Fram Strait (~80N) to Cape Farewell (~60N). The current is located off the eastern coast of Greenland along the Greenland continental margin. The current cuts through the Nordic Seas and through the Denmark Strait. The current is of major importance because it directly connects the Arctic to the Northern Atlantic, it is a major contributor to sea ice export out of the Arctic, and it is a major freshwater sink for the Arctic.

The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the Atlantic Ocean. However, definitions of the Arctic Ocean and its seas tend to be imprecise or arbitrary. In general usage the term "Arctic Ocean" would exclude the Greenland Sea. In oceanographic studies the Greenland Sea is considered part of the Nordic Seas, along with the Norwegian Sea. The Nordic Seas are the main connection between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans and, as such, could be of great significance in a possible shutdown of thermohaline circulation. In oceanography the Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas are often referred to collectively as the "Arctic Mediterranean Sea", a marginal sea of the Atlantic.

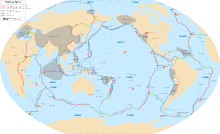
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about 2,600 meters (8,500 ft) and rises about 2,000 meters (6,600 ft) above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean ridges. Mid-ocean ridges around the globe are linked by plate tectonic boundaries and the trace of the ridges across the ocean floor appears similar to the seam of a baseball. The mid-ocean ridge system thus is the longest mountain range on Earth, reaching about 65,000 km (40,000 mi).

The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is the zonally integrated component of surface and deep currents in the Atlantic Ocean. It is characterized by a northward flow of warm, salty water in the upper layers of the Atlantic, and a southward flow of colder, deep waters that are part of the thermohaline circulation. These "limbs" are linked by regions of overturning in the Nordic and Labrador Seas and the Southern Ocean, although the extent of overturning in the Labrador Sea is disputed. The AMOC is an important component of the Earth's climate system, and is a result of both atmospheric and thermohaline drivers. Model projections suggest that the strength of the AMOC is “very likely” to decrease over the course of the 21st century due to climate change, which is likely to have an impact on weather patterns and sea level. Paleoclimate reconstructions and some models also raise the possibility of an AMOC collapse, which would likely affect the weather and climate system. This makes the AMOC an important climate indicator to monitor. Modern measurements of the AMOC are supported by the RAPID array, which is able to directly measure the strength of AMOC overturning directly as well as water characteristics such as temperature and salinity.

The North Atlantic Igneous Province (NAIP) is a large igneous province in the North Atlantic, centered on Iceland. In the Paleogene, the province formed the Thulean Plateau, a large basaltic lava plain, which extended over at least 1.3 million km2 (500 thousand sq mi) in area and 6.6 million km3 (1.6 million cu mi) in volume. The plateau was broken up during the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean leaving remnants preserved in north Ireland, west Scotland, the Faroe Islands, northwest Iceland, east Greenland, western Norway and many of the islands located in the north eastern portion of the North Atlantic Ocean. The igneous province is the origin of the Giant's Causeway and Fingal's Cave. The province is also known as Brito–Arctic province and the portion of the province in the British Isles is also called the British Tertiary Volcanic Province or British Tertiary Igneous Province.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.

The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the nation of Kalaallit Nunaat (Greenland).

Volcanism of Northern Canada has produced hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations across Northern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Northern Canada has a record of very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions.
The Greenland Plate is a supposed tectonic plate bounded to the west by Nares Strait, a probable transform fault; on the southwest by the Ungava transform underlying Davis Strait; on the southeast by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge; and the northeast by the Gakkel Ridge, with its northwest border still being explored. The Greenland craton is made up of some of the oldest rocks on Earth. The Isua greenstone belt in southwestern Greenland contains the oldest known rocks on Earth dated at 3.7–3.8 billion years old.
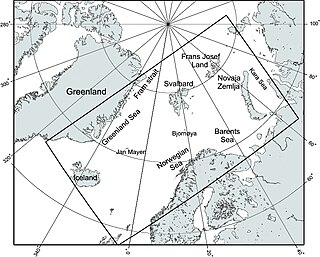
The Nordic Seas are located north of Iceland and south of Svalbard. They have also been defined as the region located north of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge and south of the Fram Strait-Spitsbergen-Norway intersection. Known to connect the North Pacific and the North Atlantic waters, this region is also known as having some of the densest waters, creating the densest region found in the North Atlantic Deep Water. The deepest waters of the Arctic Ocean are connected to the worlds other oceans through Nordic Seas and Fram Strait. There are three seas within the Nordic Sea: Greenland Sea, Norwegian Sea, and Iceland Sea. The Nordic Seas only make up about 0.75% of the World's Oceans. This region is known as having diverse features in such a small topographic area, such as the mid oceanic ridge systems. Some locations have shallow shelves, while others have deep slopes and basins. This region, because of the atmosphere-ocean transfer of energy and gases, has varying seasonal climate. During the winter, sea ice is formed in the western and northern regions of the Nordic Seas, whereas during the summer months, the majority of the region remains free of ice.
The South Greenland Triple Junction was a geologic triple junction in the North Atlantic Ocean that divided the North American, Greenland and Eurasian plates. It existed during the Paleogene and consisted of the Mid-Labrador and Mid-Atlantic ridges. The triple junction became extinct when seafloor spreading along the Mid-Labrador Ridge ceased during the Eocene.
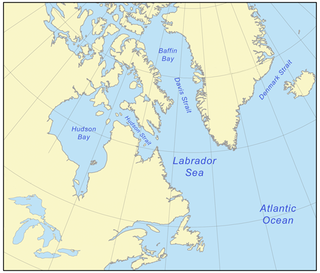
The Canadian Arctic Rift System is a major North American geological structure extending from the Labrador Sea in the southeast through Davis Strait, Baffin Bay and the Arctic Archipelago in the northwest. It consists of a series of interconnected rifts that formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Extensional stresses along the entire length of the rift system have resulted in a variety of tectonic features, including grabens, half-grabens, basins and faults.
References
- ↑ Oakey, Gordon N.; Stephenson, Randell (2008). "Crustal structure of the Innuitian region of Arctic Canada and Greenland from gravity modelling: implications for the Palaeogene Eurekan orogen". Geophysical Journal International . Royal Astronomical Society. 173 (3): 1041. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03784.x . ISSN 0956-540X.
- ↑ Herman, Yvonne (1974). Marine Geology and Oceanography of the Arctic Seas. Springer-Verlag. p. 92. ISBN 978-3-642-87413-0.
- ↑ Litvin, V. M. (1984). The Morphostructure of the Atlantic Ocean Floor: Its Development in the Meso-Cenozoic. Dordrecht, Holland: D. Reidel Publishing Company. p. 29. ISBN 978-94-009-6247-7.