Related Research Articles

A debit card, also known as a check card or bank card, is a payment card that can be used in place of cash to make purchases. The card usually consists of the bank's name, a card number, the cardholder's name, and an expiration date, on either the front or the back. Many of the new cards now have a chip on them, which allows people to use their card by touch (contactless), or by inserting the card and keying in a PIN as with swiping the magnetic stripe. These are similar to a credit card, but unlike a credit card, the money for the purchase must be in the cardholder's bank account at the time of the purchase and is immediately transferred directly from that account to the merchant's account to pay for the purchase.

Mastercard Inc. is the second-largest payment-processing corporation worldwide. It offers a range of payment transaction processing and other related-payment services. Its headquarters are in Purchase, New York. Throughout the world, its principal business is to process payments between the banks of merchants and the card-issuing banks or credit unions of the purchasers who use the Mastercard-brand debit, credit and prepaid cards to make purchases. Mastercard has been publicly traded since 2006.

A giro transfer, often shortened to giro, is a payment transfer from one current bank account to another bank account and initiated by the payer, not the payee. The debit card has a similar model. Giros are primarily used in Europe; although electronic payment systems exist in the United States, it is not possible to perform third-party transfers with them. In the European Union, there is the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA), which allows electronic giro or debit card payments in euros to be executed to any euro bank account in the area.

Visa Debit is a major brand of debit card issued by Visa in many countries around the world. Numerous banks and financial institutions issue Visa Debit cards to their customers for access to their bank accounts. In many countries the Visa Debit functionality is often incorporated on the same plastic card that allows access to ATM and any domestic networks like EFTPOS or Interac.
A payment system is any system used to settle financial transactions through the transfer of monetary value. This includes the institutions, payment instruments such as payment cards, people, rules, procedures, standards, and technologies that make its exchange possible. A common type of payment system, called an operational network, links bank accounts and provides for monetary exchange using bank deposits. Some payment systems also include credit mechanisms, which are essentially a different aspect of payment.

UnionPay, also known as China UnionPay or by its abbreviation, CUP or UPI internationally, is a Chinese state-owned financial services corporation headquartered in Shanghai, China. It provides bank card services and a major card scheme in mainland China. Founded on 26 March 2002, China UnionPay is an association for China's banking card industry, operating under the approval of the People's Bank of China. It is also an electronic funds transfer at point of sale (EFTPOS) network, and the only interbank network in China that links all the automatic teller machine (ATMs) of all banks throughout the country. UnionPay cards can be used in 181 countries and regions around the world.

Payment cards are part of a payment system issued by financial institutions, such as a bank, to a customer that enables its owner to access the funds in the customer's designated bank accounts, or through a credit account and make payments by electronic transfer with a payment terminal and access automated teller machines (ATMs). Such cards are known by a variety of names including bank cards, ATM cards, client cards, key cards or cash cards.
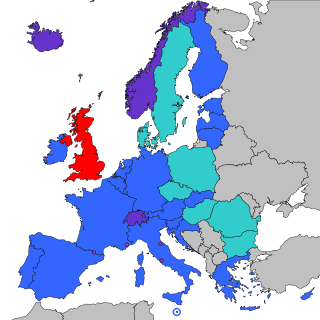
The Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) is a payment integration initiative of the European Union for simplification of bank transfers denominated in euro. As of 2020, there were 36 members in SEPA, consisting of the 27 member states of the European Union, the four member states of the European Free Trade Association, and the United Kingdom. Some microstates participate in the technical schemes: Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City.

An ATM card is a dedicated payment card card issued by a financial institution which enables a customer to access their financial accounts via its and others' automated teller machines (ATMs) and, in some countries, to make approved point of purchase retail transactions. ATM cards are not credit cards or debit cards, however most credit and debit cards can also act as ATM cards and that is the most common way that banks issue cards since the 2010s.
An interbank network, also known as an ATM consortium or ATM network, is a computer network that enables ATM cards issued by a financial institution that is a member of the network to be used to perform ATM transactions through ATMs that belong to another member of the network.

The Malaysian Electronic Payment System (MEPS) is an interbank network service provider in Malaysia. In August 2017, MEPS merged with Malaysian Electronic Clearing Corporation Sdn Bhd (MyClear) to form Payments Network Malaysia Sdn Bhd (PayNet).
ATM usage fees are the fees that many banks and interbank networks charge for the use of their automated teller machines (ATMs). In some cases, these fees are assessed solely for non-members of the bank; in other cases, they apply to all users. There is usually a higher fee for use of White-label ATMs rather than bank owned ATMs.

Multibanco is a portuguese interbank network. It is the largest interbank network in Portugal owned and operated by SIBS , that links the ATMs of 27 banks in Portugal, totaling 12,700 machines as of December 2014. The bank members of Multibanco control the SIBS. Multibanco is a fully integrated interbank network. One of the most notable characteristics of Multibanco is the wide range of services that can be utilised through its machines.

EUFISERV is a European interbank network connecting the ATMs of savings banks in Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland. It is the largest and the only international credit union-owned interbank network in Europe.

girocard is an interbank network and debit card service connecting virtually all German ATMs and banks. It is based on standards and agreements developed by the German Banking Industry Committee.
V Pay is a Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) debit card for use in Europe, issued by Visa Europe. It uses the EMV chip and PIN system and can be co-branded with various national debit card schemes such as the German Girocard or Italy's PagoBancomat.
Vocalink is a payment systems company headquartered in the United Kingdom, created in 2007 from the merger between Voca and LINK. It designs, builds and operates the UK payments infrastructure, which underpins the provision of the Bacs payment system and the UK ATM LINK switching platform covering 65,000 ATMs and the UK Faster Payments systems.

Bancomat is an Italian interbank network for cash withdrawals widely used in Italy. It was first introduced in 1983 for use with automated teller machines.

SIA S.p.A. is an Italian company operating in the area of ICT, providing services to the banking and finance sector in addition to platforms for financial markets and e-payment services.

The European Payments Initiative (EPI), previously known as the Pan-European Payments System Initiative (PEPSI), is a European Central Bank-backed payment-integration initiative aiming to create a pan-European payment system and interbank network to rival Mastercard and Visa, and eventually replace national European payment schemes such as France's Carte Bancaire and Germany's Girocard.
References
- 1 2 "Payments Competition In The World of High Risk Payment Processing". EMB. March 24, 2017.
- ↑ Press release, card-alliance.eu. (November 2007) Retrieved 2008-08-04. Archived February 20, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ SEPA for cards on way to reality in Europe. (23 May 2007) atmarketplace.com. Retrieved 2008-08-04.
- ↑ About Archived 2008-11-21 at the Wayback Machine , EUFISERV official site]
- ↑ Tumpel-Gugerell, Gertrude, Member of the Executive Board of the ECB Colloquium. (February 13, 2007) The European Central Bank's view on SEPA [ permanent dead link ] bancaditalia.it Retrieved 2008-08-04.
- ↑ Kenny, Peter. (June 21, 2007)Banks announce low overseas debit withdrawal Archived 2008-08-21 at the Wayback Machine thriftyscot.co.uk. Retrieved 2008-08-04.
- ↑ Wissenbach, Ilona. (June 20, 2007) European banks agree corssborder Mastercard rival Reuters. Retrieved 2008-08-04.
- ↑ Debit cards: pressure continues for third scheme in Europe (2007) European Card Review. Retrieved 2008-08-04 Archived July 26, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 3 ""PaySys SEPA Newsletter - Jan. 2008"" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-01-24. Retrieved 2010-08-15.
- 1 2 IT, Corporate Center-Research. "Globale Suche". Deutsche Bank Research.
- ↑ PayFair news Archived 2010-08-16 at the Wayback Machine , "22 Sept 2009 - EasyCash, key PayFair partner in Germany" Bergisch Gladbach
- 1 2 "PROJET MONNET - Une vingtaine de banques européennes prévoient de créer un nouveau système de cartes bancaires en Europe", press release, 6. May 2010
- ↑ "A grand scheme" Archived 2011-07-20 at the Wayback Machine , Interview with EAPS board chairman Ugo Bechis, by Ronan McCaughey, 1. January 2010
- 1 2 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2010-08-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2010-08-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - 1 2 "Infobrief SEPA – Euro-Zahlungsverkehr - Nr.12" [ permanent dead link ], May 2010
- ↑ "SEPA for cards: more than a symbol of SEPA’s success", Speech by Gertrude Tumpel-Gugerell, Member of the Executive Board of the ECB, at the Monnet Symposium organised by The Monnet Project, Madrid, 5 May 2010