Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to as distributed energy resources (DER).
Energy demand management, also known as demand-side management (DSM) or demand-side response (DSR), is the modification of consumer demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and behavioral change through education.

Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) describes a system in which plug-in electric vehicles, such as battery electric vehicles (BEV), plug-in hybrids (PHEV) or hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV), communicate with the power grid to sell demand response services by either returning electricity to the grid or by throttling their charging rate. V2G storage capabilities can enable EVs to store and discharge electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, with output that fluctuates depending on weather and time of day.
A microgrid is a decentralized group of electricity sources and loads that normally operates connected to and synchronous with the traditional wide area synchronous grid (macrogrid), but can also disconnect to "island mode" — and function autonomously as physical or economic conditions dictate.
A virtual power plant (VPP) is a cloud-based distributed power plant that aggregates the capacities of heterogeneous distributed energy resources (DER) for the purposes of enhancing power generation, as well as trading or selling power on the electricity market. Examples of virtual power plants exist in the United States, Europe, and Australia.
ENTSO-E, the European Network of Transmission System Operators, represents 43 electricity transmission system operators (TSOs) from 36 countries across Europe, thus extending beyond EU borders. ENTSO-E was established and given legal mandates by the EU's Third Package for the Internal energy market in 2009, which aims at further liberalising the gas and electricity markets in the EU.

A smart grid is an electrical grid which includes a variety of operation and energy measures including smart meters, smart appliances, renewable energy resources, and energy efficient resources. Electronic power conditioning and control of the production and distribution of electricity are important aspects of the smart grid.
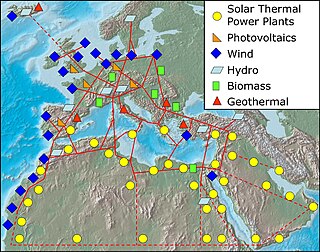
The SuperSmart Grid (SSG) is a hypothetical wide area electricity network connecting Europe with northern Africa, the Middle East, Turkey and the IPS/UPS system of CIS countries. The system would unify super grid and smart grid capabilities into a comprehensive network. There are no planned locations for infrastructure or schedule explicitly for the SSG; the name is used to discuss the economic and technological feasibility of such a network and ways that it might gain political support.

An electrical grid, electric grid or power grid, is an interconnected network for delivering electricity from producers to consumers. It consists of:

A super grid or supergrid is a wide-area transmission network that makes it possible to trade high volumes of electricity across great distances. It is sometimes also referred to as a "mega grid". Super grids can support a global energy transition by smoothing local fluctuations of wind energy and solar energy. In this context they are considered as a key technology to mitigate global warming. The latest generation of High-voltage direct current (HVDC) power lines can transmit energy with losses of only 1.6% per 1000 km.
Support for the smart grid in the United States became federal policy with passage of the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007. The law set out $100 million in funding per fiscal year from 2008–2012, established a matching program to states, utilities and consumers to build smart grid capabilities, and created a Grid Modernization Commission to assess the benefits of demand response and to recommend needed protocol standards. The law also directed the National Institute of Standards and Technology to develop smart grid standards, which the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) would then promulgate through official rulemakings.
The North Sea Offshore Grid, officially the North Seas Countries Offshore Grid Initiative (NSCOGI), was a collaboration between EU member-states and Norway to create an integrated offshore energy grid which links wind farms and other renewable energy sources across the northern seas of Europe. It is one of several proposed European super grid schemes. Since 2016, the cooperation has been integrated into the new Political Declaration on energy cooperation between the North Seas Countries.
Although there is no standard global definition, the European Technology Platform SmartGrids defines smart grids as electricity networks that can intelligently integrate the behaviour and actions of all users connected to it – generators, consumers and those that do both – in order to efficiently deliver sustainable, economic and secure electricity supplies.
The term Smart Grid is most commonly defined as an electric grid that has been digitized to enable two way communication between producers and consumers. The objective of the Smart Grid is to update electricity infrastructure to include more advanced communication, control, and sensory technology with the hope of increasing communication between consumers and energy producers. The potential benefits from a Smart Grid include increased reliability, more efficient electricity use, better economics, and improved sustainability.
The term Smart Grid has describes a next-generation electric power system that is classified by the increased use of communication and information technology in the generation, delivery, and consumption of electrical energy. For individual consumers, smart grid technology offers more control over electricity consumption. Typically, the goal is greater overall energy efficiency.

IEEE Smart Grid is an initiative launched by IEEE to help provide expertise and guidance for individuals and organizations involved in the modernization and optimization of the power grid, better known as the "smart grid". IEEE Smart Grid encompasses an array of activities, including development of new smart grid-related standards, best practices, publications, and conferences and educational opportunities.
The UCLA Smart Grid Energy Research Center (SMERC), located on the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) campus, is an organization focused on developing the next generation of technologies and innovation for the SmartGrid. Partnerships with government, technology providers, DOE research labs and universities, utilities, policy makers, and electric vehicle and appliance manufacturers provide SMERC with diverse capabilities and exceptional, matured leadership.
Open energy system models are energy system models that are open source. However, some of them may use third party proprietary software as part of their workflows to input, process, or output data. Preferably, these models use open data, which facilitates open science.

Rajit Gadh is a Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science and the founding director of the UCLA Smart Grid Energy Research Center (SMERC), the UCLA Wireless Internet for Mobile Enterprise Consortium (WINMEC), and the Connected and Autonomous Electric Vehicles Consortium (CAEV).
Open energy system database projects employ open data methods to collect, clean, and republish energy-related datasets for open use. The resulting information is then available, given a suitable open license, for statistical analysis and for building numerical energy system models, including open energy system models. Permissive licenses like Creative Commons CC0 and CC BY are preferred, but some projects will house data made public under market transparency regulations and carrying unqualified copyright.





