Electranet is a proposed smart electric grid which would allow people to sell electricity into the grid without any artificial caps. It was proposed in an op-ed article Al Gore wrote in a "My Turn" column for Newsweek in 2006. [1]
Like the internet, which widely distributed information, the Electranet would allow homeowners and small businesses to operate small generating power facilities and contribute to local and regional energy needs by selling power into the grid at a rate that is determined by free market forces. Like the internet, which led to a surge of productivity, the Electranet's distributed generation model is hoped to lead to innovative power generation through alternative sources and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Electranet advocates predict that as more people participate in the Electranet, the cost of electricity will continue to go down until it becomes free.[ citation needed ]
In a 2006 speech to NYU, [2] Al Gore advocated deploying an Electranet as one way to reduce global warming, as well as reduce the cost of energy, by dropping the barriers to entry for average citizens to actively participate in the business of harnessing and distributing power. Al Gore frequently notes that "a lot of energy is all around us. Instead of having the sun bake us in the summer, why not gather that energy", he asks. "Why not collect from road surfaces, roofs, any painted surfaces and more?"
Al Gore has also said that "once there is a convenient way to sell energy into the grid, not only will homeowners be compelled to hop onto the grid and supply energy, but there will also be a brand new market to develop and then sell all sorts of energy gathering devices and technologies, such as solar paint, solar fabrics, thin films for windows, micro windmills, and more."
Al Gore mentioned the Electranet idea in his congressional Global Warming Testimony on March 21, 2007.
Electranet advocates predict that just like data on the internet, energy itself, including what is necessary for electric cars, will continue to be more economical as more people get onto the smart grid and supply power, and as more and more efficient technologies are developed for gathering the abundant energy around us. It is reasonable to imagine a day when there is no actual cost for driving, per mile, for energy, because of the abundance of energy coming from the Electranet.
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to as distributed energy resources (DER).

Net metering is an electricity billing mechanism that allows consumers who generate some or all of their own electricity to use that electricity anytime, instead of when it is generated. This is particularly important with renewable energy sources like wind and solar, which are non-dispatchable. Monthly net metering allows consumers to use solar power generated during the day at night, or wind from a windy day later in the month. Annual net metering rolls over a net kilowatt-hour (kWh) credit to the following month, allowing solar power that was generated in July to be used in December, or wind power from March in August.

Microgeneration is the small-scale production of heat or electric power from a "low carbon source," as an alternative or supplement to traditional centralized grid-connected power.

The Edison Electric Institute (EEI) is an association that represents all U.S. investor-owned electric companies.

Load balancing, load matching, or daily peak demand reserve refers to the use of various techniques by electrical power stations to store excess electrical power during low demand periods for release as demand rises. The aim is for the power supply system to have a load factor of 1.

According to preliminary data from the US Energy Information Administration, renewable energy accounted for about 12.6% of total primary energy consumption and about 19.8% of the domestically produced electricity in the United States in 2020.

A smart grid is an electrical grid which includes a variety of operation and energy measures including:

A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system's overall performance and include an integrated battery.

Electricity pricing can vary widely by country or by locality within a country. Electricity prices are dependent on many factors, such as the price of power generation, government taxes or subsidies, CO
2 taxes, local weather patterns, transmission and distribution infrastructure, and multi-tiered industry regulation. The pricing or tariffs can also differ depending on the customer-base, typically by residential, commercial, and industrial connections.
Unified National Smart Grid as well as Unified Solar is a proposal for a nationally interconnected grid relying on a backbone of electric power transmission lines linking the US' local grids that have been upgraded to smart grids. Europe's analogous project is sometimes referred to as the SuperSmart Grid.
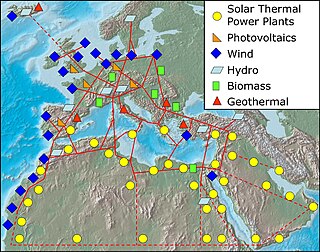
A super grid or supergrid is a wide-area transmission network, generally trans-continental or multinational, that is intended to make possible the trade of high volumes of electricity across great distances. It is sometimes also referred to as a "mega grid". Super grids typically are proposed to use high-voltage direct current (HVDC) to transmit electricity long distances. The latest generation of HVDC power lines can transmit energy with losses of only 1.6% per 1,000 km.

Solar power in California includes utility-scale solar power plants as well as local distributed generation, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics. It has been growing rapidly because of high insolation, community support, declining solar costs, and a Renewable Portfolio Standard which requires that 33% of California's electricity come from renewable resources by 2020, and 60% by 2030. Much of this is expected to come from solar power via photovoltaic facilities or concentrated solar power facilities.

Net metering is a policy by many states in the United States designed to help the adoption of renewable energy. Net metering was pioneered in the United States as a way to allow solar and wind to provide electricity whenever available and allow use of that electricity whenever it was needed, beginning with utilities in Idaho in 1980, and in Arizona in 1981. In 1983, Minnesota passed the first state net metering law. As of March 2015, 44 states and Washington, D.C. have developed mandatory net metering rules for at least some utilities. However, although the states' rules are clear, few utilities actually compensate at full retail rates.

EPB of Chattanooga, formerly known as the Electric Power Board of Chattanooga, is an American electric power distribution and telecommunications company owned by the city of Chattanooga, Tennessee. EPB serves nearly 180,000 homes and businesses in a 600-square mile area in the greater Chattanooga area and Hamilton County. In 2010, EPB was the first company in the United States to offer 1 Gbit/s high-speed internet over a fiber optic network, over 200 times faster than the national average. As a result, Chattanooga has been called "Gig City" and held up as a national model for deploying the world's fastest internet and the most advanced Smart Grid electric distribution system in the United States. On October 15, 2015, Chattanooga implemented the world's first community-wide 10-gig Internet service.

A grid-connected photovoltaic system, or grid-connected PV system is an electricity generating solar PV power system that is connected to the utility grid. A grid-connected PV system consists of solar panels, one or several inverters, a power conditioning unit and grid connection equipment. They range from small residential and commercial rooftop systems to large utility-scale solar power stations. When conditions are right, the grid-connected PV system supplies the excess power, beyond consumption by the connected load, to the utility grid.

Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or biomass, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power.

Solar power in Connecticut makes Connecticut the second state in the US to reach grid parity, after Hawaii, due to the high average cost of electricity. Installing solar panels for a home provides an estimated 15.6% return on investment.
The UCLA Smart Grid Energy Research Center (SMERC), located on the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) campus, is an organization focused on developing the next generation of technologies and innovation for tSmartGrid. Partnerships with government, technology providers, DOE research labs and universities, utilities, policymakers, and electric vehicle and appliance manufacturers provide SMERC with diverse capabilities and exceptional, mature leadership.
Home energy storage devices store electricity locally, for later consumption. Electrochemical energy storage products, also known as "Battery Energy Storage System", at their heart are rechargeable batteries, typically based on lithium-ion or lead-acid controlled by computer with intelligent software to handle charging and discharging cycles. Companies are also developing smaller flow battery technology for home use. As a local energy storage technologies for home use, they are smaller relatives of battery-based grid energy storage and support the concept of distributed generation. When paired with on-site generation, they can virtually eliminate blackouts in an off-the-grid lifestyle.
Net metering in New Mexico is a set of state public policies that govern the relationship between solar customers and electric utility companies.