
Balanoglossus is a genus of ocean-dwelling acorn worms. It has zoological importance because, being hemichordates, they are an "evolutionary link" between invertebrates and vertebrates. Balanoglossus specimens are deuterostomes, and resemble the sea squirts in that they possess branchial openings, or "gill slits". They have notochords and stomochords but no dorsal nerve cord.

Eusynstyela is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Ceramaster is a genus of cushion stars in the family Goniasteridae. The species in this genus have no arms. They live in deeper waters than most sea stars.

Stolidobranchia is an order of tunicates in the class Ascidiacea. The group includes both colonial and solitary animals. They are distinguished from other tunicates by the presence of folded pharyngeal baskets. This provides the etymology of their name: in ancient Greek, στολίς, ίδος means the "fold" of a cloth. Stolidobranchian sea squirts are also characterized by the complete absence of an abdomen. The abdominal organs of other tunicates are instead located to one side of the pharyngeal basket in this group.
Kikutaro Baba was a Japanese malacologist. He was the leading researcher on sea slugs and bubble snails, opisthobranch gastropod mollusks in Japan.

Eubranchus is a genus of aeolid nudibranch in the family Eubranchidae.

BQ-123, also known as cyclo(-D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu-), is a cyclic pentapeptide that was first isolated from a fermentation broth of Streptomyces misakiensis in 1991. NMR studies indicate that the polypeptide backbone consists of a type II beta turn and an inverse gamma turn. The side-chains adopt different orientations depending on the solvent used. The proline carbonyl oxygen atom located at the onset of a beta turn is a sodium ion binding site. It has a high affinity for sodium ions and can coordinate up to three of them. Studies have shown that BQ123 is effective in reversing Ischemia-induced acute renal failure, and it has been suggested that this might be because BQ123 increases reabsorption of sodium ions in the proximal tubule cells.
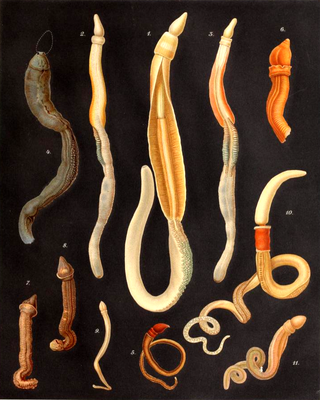
Ptychoderidae is a family of acorn worms.

Aspidosiphonidae is a family of peanut worms. It is the only family in the monotypic order Aspidosiphonida, which is in the class Phascolosomatidea.

Amphiroa is a genus of thalloid red algae under the family Corallinaceae.
Marginodostomia is a genus of very small sea snails, pyramidellid gastropod mollusks or micromollusks.

Sybrida is a genus of snout moths.

Polycarpa is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Styelidae is a family of ascidian tunicates.

Solanderia is the sole genus of hydrozoans in the monotypic family Solanderiidae. They are commonly known as tree hydroids or sea fan hydroids.
Gynandrocarpa is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.
Polyandrocarpa is a genus of ascidian tunicates within the family Styelidae.
Leostyletus is a genus of sea slugs, specifically of aeolid nudibranchs.
Kitasatospora misakiensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Kitasatospora which has been isolated from soil in Japan. Kitasatospora misakiensis produces tubermycin A, tubermycin B, misakimycin and the endothelin receptor antagonist BE-18257B.
Roseivirga misakiensis is a Gram-negative, aerobic and slightly curved-rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Roseivirga which has been isolated from coastal surface water of Misaki in Japan.












