Eutropis ashwamedhi, also known commonly as the Ashwamedh supple skink or Ashwamedha writhing skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to India.
The Allapalli grass skink or Schmidt's mabuya is a species of skink found in India.
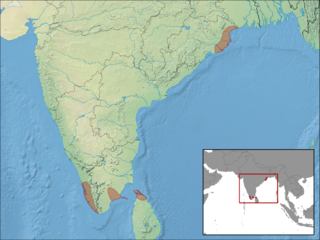
Eutropis bibronii, also known commonly as Bibron's mabuya, Bibron's skink, and the seashore skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to India and Sri Lanka.

Eutropis clivicola, known as Inger's mabuya or mountain skink, is a species of skink found in India (Kerala). It was first formally described in 1984 as Mabuya clivicola.
Eutropis dawsoni, also known as Gans's mabuya and Gans's grass skink, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the southern Western Ghats, India.
Blanford's mabuya ( is a species of skink found in peninsular India.

The bronze grass skink, bronze mabuya or speckled forest skink, is a species of skink found in South and Southeast Asia. It is a common, but shy, ground-dwelling species that is active both day and night.

Eutropis multifasciata, commonly known as the East Indian brown mabuya, many-lined sun skink, many-striped skink, common sun skink or (ambiguously) as golden skink, is a species of skink.

Sharma's mabuya is a species of skinks found in India. It was described by Sharma (1969) from hills south of Vijaypuri on the right bank of the river Krishna in Andhra Pradesh.

Eutropis rugifera, variously known as Nicobar Island skink or rough-scaled sun skink, is a species of skink from southeastern Asia.

Eutropis trivittata is a species of skink found in India.

Eutropis is a genus of skinks belonging to the subfamily Mabuyinae. For long, this genus was included in the "wastebin taxon" Mabuya; it contains the Asian mabuyas. They often share their habitat with the related common skinks (Sphenomorphus), but they do not compete significantly as their ecological niches differ. This genus also contains the only member of the subfamily to occur in Australasia, the many-lined sun skink, whose wide range includes New Guinea.

Eutropis longicaudata, the longtail mabuya or long-tailed sun skink, is a species of skink. It is found in southern China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Peninsular Malaysia.
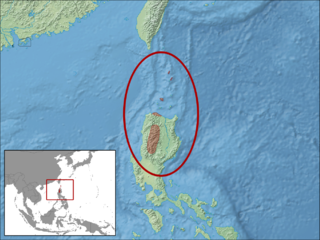
The Luzon montane mabouya is a species of skink found in Luzon in the Philippines.
The Sapa mabouya is a species of skink found in Vietnam.

Eutropis cumingi, also known commonly as Cuming's eared skink, Cuming's mabouya, and Cuming's mabuya, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the Philippines.
Eutropis darevskii, also known commonly as Darevsy's mabouya, Darevsky's mabuya, and Darevsky's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Vietnam.

The six-striped mabouya is a species of skink found in Mindanao in the Philippines.
Brown's mabuya is a species of skink found in Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
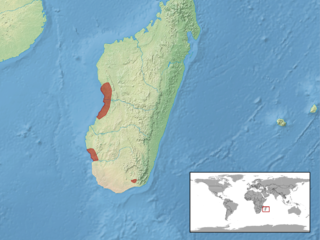
Trachylepis dumasi is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.













