Nature reserves

Six marine areas in the German EEZ are designated as Naturschutzgebiet (nature reserves): [5]
- Borkum-Riffgrund
- Doggerbank
- Fehmarnbelt
- Kadetrinne
- Pommersche Bucht
- Sylter Außenriff – Östliche Deutsche Bucht
The Federal Republic of Germany declared the entry into force of the convention with effect from 1 January 1995, the establishment of a German Exclusive Economic Zone in the North and Baltic Seas. [1] The relevant German legal provisions that are applicable within the exclusive economic zone include the Maritime Task Act (Seeaufgabengesetz) from 1965, the Maritime Facilities Act (Seeanlagengesetz) from 2017, before that the Sea Facilities Ordinance (Seeanlagenverordnung) since 1997, the Federal Mining Act (Bundesberggesetz) and the Regional Planning Act (Raumordnungsgesetz).
The German EEZ has an area of 32,982 km2. 70% of the EEZ is the entire German North Sea area and about 29% is the entire German Baltic Sea area. [2]
Driven by the approval process for planned Offshore-Windparks, a spatial planning plan issued by the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure came into force for the North Sea area on 26 September 2009, for the much smaller Baltic Sea area on 19 December 2009. [3] For the German exclusive economic zone, Germany has reported ten Natura 2000 areas to the EU Commission. [4]

Six marine areas in the German EEZ are designated as Naturschutzgebiet (nature reserves): [5]
In 2014, Germany and the Kingdom of the Netherlands resolved part of a centuries-old border dispute [6] regarding the exact location of the border in the Dollart Bay. [7] [8]

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind.

The Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution is Germany's federal domestic intelligence agency. Together with the Landesämter für Verfassungsschutz (LfV) at the state level, the federal agency is tasked with intelligence-gathering on efforts against the liberal democratic basic order, the existence and security of the federation or one of its states, and the peaceful coexistence of peoples; with counter-intelligence; and with protective security and counter-sabotage. The BfV reports to the Federal Ministry of the Interior and tasks and powers are regulated in the Bundesverfassungsschutzgesetz. The President is Thomas Haldenwang; he was appointed in 2018.
The United States has land borders with only Canada and Mexico, both of them long. It has maritime boundaries with many countries due to its extensive exclusive economic zone (EEZ). All of its maritime borders with Canada are at least partially disputed, and its territorial claims on three Caribbean islands are disputed.
Germany is a country in Central and Western Europe that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and is seventh-largest country by area in the continent. The area of Germany ranked 63rd and covers 357,600 km2 (138,070 sq mi), consisting of 349,250 km2 (134,846 sq mi) of land and 8,350 km2 (3,224 sq mi) of waters, smaller than Japan but larger than Republic of the Congo.
The Polish exclusive economic zone has an area of 30,533 km2 (11,789 sq mi) within the Baltic Sea.

This division of Germany into major natural regions takes account primarily of geomorphological, geological, hydrological, and pedological criteria in order to divide the country into large, physical units with a common geographical basis. Political boundaries play no part in this, apart from defining the national border.
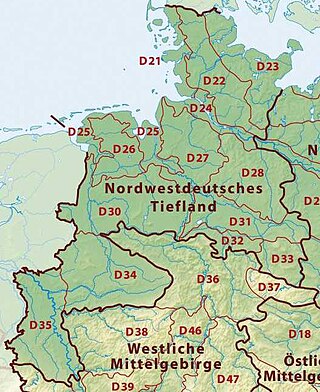
The Westphalian Lowland, also known as the Westphalian Basin is a flat landscape that mainly lies within the German region of Westphalia, although small areas also fall within North Rhine and in Lower Saxony. Together with the neighbouring Lower Rhine Plain to the west, it represents the second most southerly region of the North German Plain, after the Cologne Bight. It is variously known in German as the Westfälische Bucht, the Münsterländer or Westfälische Tieflands- or Flachlandsbucht.

A Naturschutzgebiet is a category of protected area within Germany's Federal Nature Conservation Act . Although often translated as 'Nature Reserve' in English, the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN) refers to them as 'Nature Conservation Areas'. It meets the criteria of an IUCN Category IV Habitat and Species Management Area.

The Federal Maritime and Hydrographic Agency of Germany is a German federal authority based in Hamburg and Rostock. With some 800 employees, the agency's tasks include maritime safety, hydrographic survey, maritime pollution monitoring, and approvals of offshore installations.

The Kingdom of Denmark has existed with its current territory since 1920, although the last territorial dispute with Canada was only settled on 14 June 2022. The only land border of Denmark (proper) is that with Germany, with a length of 68 km (42 mi). Greenland, an autonomous country of the Danish Realm, also shares a border with Canada splitting Hans Island in half in which the border is 1.28 km long. The border along the territorial waters with Sweden runs along the Øresund for a length of about 115 km (71 mi).

The exclusive economic zone of North Korea stretches 200 nautical miles from its basepoints in both the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. The exclusive economic zone (EEZ) was declared in 1977 after North Korea had contested the validity of the Northern Limit Lines (NLL) set up after the Korean War as maritime borders. The EEZ has not been codified in law and North Korea has never specified its coordinates, making it difficult to determine its specific scope.
Malaysia claims an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 334,671 km2 (129,217 sq mi) with 200 nautical miles from its shores. The EEZ includes much of the southern area of the South China Sea. Malaysia has the 29th longest coastline of 4,675 km (2,905 mi). The coastline comprises two distinct parts of Malaysia. The Peninsular Malaysia's coastline to the west is 2,068 km (1,285 mi) and East Malaysia's coastline is 2,607 km (1,620 mi). They are separated by the South China Sea. The total land area, including inland bodies of water, of Malaysia is 330,803 km2 (127,724 sq mi). Peninsular Malaysia borders Thailand in the north, while East Malaysia borders Brunei and Indonesia on the island of Borneo.

The United Kingdom's exclusive economic zone is the fifth largest in the world at 6,805,586 km2 (2,627,651 sq mi). It comprises the exclusive economic zones surrounding the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies, and the British Overseas Territories. The figure does not include the EEZ of the British Antarctic Territory.

India has the 18th-largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ) with a total size of 2,305,143 km2 (890,021 sq mi). It includes the Lakshadweep island group in the Laccadive Sea off the southwestern coast of India and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. India's EEZ is bordered to the west by Pakistan, to the south by the Maldives and Sri Lanka and to the east by Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia. Based on new scientific data, India has petitioned United Nations to extend its EEZ from 200 Nautical miles to 500 miles.
The United States has the world's second-largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ). The total size is 11,351,000 km2 (4,383,000 sq mi)2. Areas of its EEZ are located in three oceans, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea. Most notable areas are Alaska, Hawaii, the East Coast, West Coast and Gulf Coast of the United States.
Spain's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) is the 30th largest in the world with 1,039,233 km2 (401,250 sq mi). It is mostly in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. This is approximately double the entire Spanish land area. Together the land and sea surface would account for approximately 0.3% of the world's land surface.
Greece has claimed an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) with a total size of 505,572 km2 (195,202 sq mi), which is the 53rd largest in the world.

Italy has the world's 48th largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ), with an area of 541,915 km2 (209,235 sq mi). It claims an EEZ of 200 nmi from its shores, which has long coastlines with the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west, the Ionian Sea to the south and the Adriatic Sea to the east. Its EEZ is limited by maritime boundaries with neighboring countries to the north-west, east and southeast.

Inner German relations, also known as the FRG-GDR relations, East Germany-West Germanyrelations or German-German relations, were the political, diplomatic, economic, cultural and personal contacts between the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, at the period of the West-East division in German history from the founding of East Germany on 7 October 1949 to Germany's reunification on 3 October 1990.