
Vetulicolia is a phylum of animals encompassing several extinct species belonging to the Cambrian Period. The phylum was created by Degan Shu and his research team in 2001, and named after Vetulicola cuneata, the first species of the phylum described in 1987. The vetulicolian body comprises two parts: a voluminous anterior forebody, tipped with an anteriorly positioned mouth and lined with a row of five round to oval-shaped features on each lateral side, which have been interpreted as gills ; and a posterior section that primitively comprises seven segments and functions as a tail. All vetulicolians lack preserved appendages of any kind, having no legs, feelers or even eyes. The area where the anterior and posterior parts join is constricted.

Hallucigenia is a genus of lobopodian, known from Cambrian aged fossils in Burgess Shale-type deposits in Canada and China, and from isolated spines around the world. The generic name reflects the type species' unusual appearance and eccentric history of study; when it was erected as a genus, H. sparsa was reconstructed as an enigmatic animal upside down and back to front. Lobopodians are a grade of Paleozoic panarthropods from which the velvet worms, water bears, and arthropods arose.

The Maotianshan Shales are a series of Early Cambrian sedimentary deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.

Parapeytoia is a genus of extinct arthropod that lived over 530 million years ago in the Maotianshan shales of prehistoric China. It was interpreted as an anomalocaridid (radiodont) with legs, but later studies reveal it was a megacheiran, a group of arthropods which are no longer thought to be closely related to the radiodonts.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.
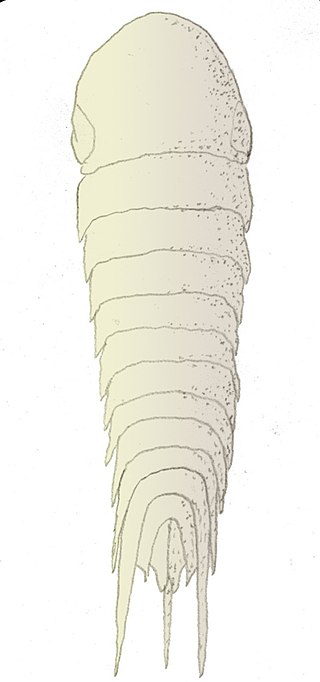
Acanthomeridion is an extinct arthropod found in the Chengjiang fauna deposits of China. In 1997, it was placed in its own, monotypic family, Acanthomeridiidae. It is known from eight specimens, all found in China.

Megacheira is an extinct class of predatory arthropods defined by their possession of spined "great appendages". Their taxonomic position is controversial, with studies either considering them stem-group euarthropods, or stem-group chelicerates. The homology of the great appendages to the cephalic appendages of other arthropods is also controversial. Uncontested members of the group were present in marine environments worldwide from the lower to middle Cambrian.

Kunmingella is genus of Cambrian bradoriid from the Chengjiang biota, containing the single species K. douvillei. Kunmingella had 12 appendages, including a pair of antennae as well pairs of biramous limbs, including four anterior pairs of appendages bearing double rows of endites on their endopods, and a posterior 5 with only a single row of endites, as well as two terminal pairs of uniramous limbs. Eggs have been found preserved attached to the posteriormost three pairs of biramous limbs, suggesting it engaged in brood care. Around 50–80 eggs, each around 150–180 μm across were attached in total.
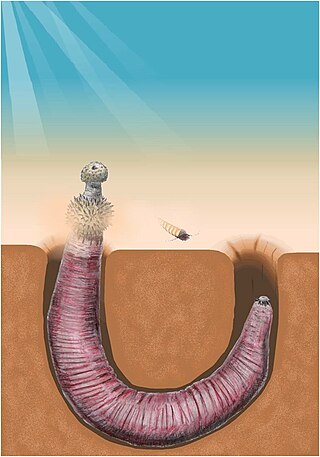
Archaeopriapulida is a group of priapulid-like worms known from Cambrian lagerstätte. The group is closely related to, and very similar to, the modern Priapulids. It is unclear whether it is mono- or polyphyletic. Despite a remarkable morphological similarity to their modern cousins, they fall outside of the priapulid crown group, which is not unambiguously represented in the fossil record until the Carboniferous. In addition to well-preserved body fossils, remains of several archaeopriapulid taxa are known to have been preserved primarily as organic microfossils, such as isolated scalids and pharyngeal teeth. They are probably closely related or paraphyletic to the palaeoscolecids; the relationship between these basal worms is somewhat unresolved.

The palaeoscolecids are a group of extinct ecdysozoan worms resembling armoured priapulids. They are known from the Lower Cambrian to the late Silurian; they are mainly found as disarticulated sclerites, but are also preserved in many of the Cambrian lagerstätten. They take their name from the typifying genus Palaeoscolex. Other genera include Cricocosmia from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang biota. Their taxonomic affinities within Ecdysozoa have been the subject of debate.

Vetulicola cuneata is a species of extinct animal from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China. It was described by Hou Xian-guang in 1987 from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation, and became the first animal under an eponymous phylum Vetulicolia.

Omnidens amplus, meaning "large all-tooth", is an extinct species of large Cambrian animal known only from a series of large mouth apparatus, originally mistaken as the mouthparts of anomalocaridids. When first named, it was interpreted as a giant priapulid, but is now considered a panarthropod. Its mouth apparatus closely resembles that of the smaller gilled lobopodian Pambdelurion, indicating it is likely to have been a close relative of that species, with which it may be synonymous. With a maximum estimated body length of 1.5 metres (4.9 ft), Omnidens is suggested to have been the largest known free-living Cambrian organism. Omnidens fossils are found in the Maotianshan Shales.

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2014.
Archotuba is a genus of elongated conical tubes that were seemingly deposited by colonial organisms. Known from the Chengjiang, its biological affinity is uncertain; it somewhat resembles the tubes of the 'priapulid' Selkirkia, but a cnidarian affinity is also possible. In the absence of soft parts, there really isn't enough data to confirm a biological affiliation.
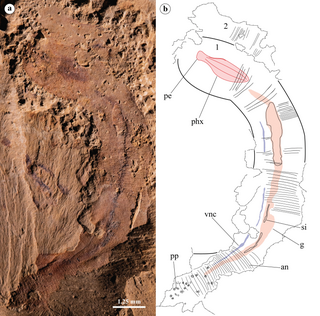
Acosmia is a genus of Chengjiang biota priapulid in the family Acosmiidae. It is represented by a single rare species, Acosmia maotiania. Later studies proposed it is a stem-group ecdysozoan.

Paraselkirkia is a genus of archaeopriapulid known from the Chengjiang biota, resembling Selkirkia.

Iotuba chengjiangensis is a 515 myo Cambrian worm known from the Chengjiang biota. Originally interpreted as a phoronid, the organism is now recognized as an annelid cage worm affiliated with the Flabelligeridae and Acrocirridae, which Zhang et al grouped together in the new superfamily Flabelligeroidea.
Luolishania is an extinct genus of lobopodian panarthropod and known from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation of the Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China. A monotypic genus, it contains one species Luolishania longicruris. It was discovered and described by Hou Xian-Guang and Chen Jun-Yuan in 1989. It is one of the superarmoured Cambrian lobopodians suspected to be either an intermediate form in the origin of velvet worms (Onychophora) or basal to at least Tardigrada and Arthropoda. It is the basis of the family name Luolishaniidae, which also include other related lobopods such as Acinocricus, Collinsium, Facivermis, and Ovatiovermis. Along with Microdictyon, it is the first lobopodian fossil discovered from China.

Lenisambulatrix is a genus of extinct worm belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shale of China. It is represented by a single species L. humboldti. The incomplete fossil was discovered and described by Qiang Ou and Georg Mayer in 2018. Due to its missing parts, its relationship with other lobopodians is not clear. It shares many structural features with another Cambrian lobopodian Diania cactiformis, a fossil of which was found alongside it.
















