Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyquinol (1,2,4-benzenetriol) and pyrogallol (1,2,3-benzenetriol). Phloroglucinol, and its benzenetriol isomers, are still defined as "phenols" according to the IUPAC official nomenclature rules of chemical compounds. Many such monophenolics are often termed "polyphenols" by the cosmetic and parapharmaceutical industries, which does not match the scientifically accepted definition.

Phenanthrenoids are chemical compounds formed with a phenanthrene backbone. Those compound are naturally occurring in plants, although they can also be synthetized.
Neoflavonoids are a class of polyphenolic compounds. While flavonoids have the 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone, neoflavonoids have the 4-phenylchromen backbone with no hydroxyl group substitution at position 2.

Perrottetinene is a naturally occurring cannabinoid compound found in liverworts from the genus Radula native to Japan, New Zealand and Costa Rica, namely Radula perrottetii, Radula marginata and Radula laxiramea, along with a number of similar compounds. Its chemical structure closely resembles that of THC, the main active component of marijuana. The absolute configuration of perrottetinene was established in 2008 by an enantioselective total synthesis. In 2018, a study showed that perrottetinene is moderately psychoactive through activation of the cannabinoid receptor 1. The same study also reported reduced prostaglandin D2 and E2 brain concentrations in mice after perrottetinene administration.

Astragalin is a chemical compound. It can be isolated from Phytolacca americana or in the methanolic extract of fronds of the fern Phegopteris connectilis. It is also found in wine.

Daidzin is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as isoflavones. Daidzin can be found in Japanese plant kudzu and from soybean leaves.

Ergosterol peroxide (5α,8α-epidioxy-22E-ergosta-6,22-dien-3β-ol) is a steroid derivative. It has been isolated from a variety of fungi, yeast, lichens and sponges, and has been reported to exhibit immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, trypanocidal and antitumor activities in vitro.

Eupatolitin is a chemical compound. It is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. Eupatolitin can be found in Brickellia veronicaefolia and in Ipomopsis aggregata.
Flavonolignans are natural phenols composed of a part flavonoid and a part lignan.

Mearnsetin is an O-methylated flavonol. It can be found in Eucalyptus globulus and in Elaeocarpus lanceofolius. The compound has antioxidative properties.

Barbigerone is one of a few pyranoisoflavones among several groups of isoflavones. It was first isolated from the seed of a leguminous plant Tephrosia barbigera; hence the name "barbigerone". Members of the genus Millettia are now known to be rich in barbigerone, including M. dielsiena, M. ferruginea, M. usaramensis, and M. pachycarpa. It has also been isolated from the medicinal plant Sarcolobus globosus. Barbigerone from S. globosus is validated to have significant antioxidant property. Barbigerone exhibits profound antiplasmodial activity against the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. It is also demonstrated that it has anti-cancer potential as it causes apoptosis of murine lung-cancer cells.

Quercus salicina is an oak species found in Japan, South Korea and Taiwan.

Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.

The pomegranate ellagitannins, which include punicalagin isomers, are ellagitannins found in the fruit, rind (peel), bark or heartwood of pomegranates.
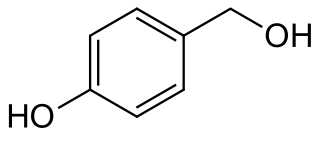
Gastrodigenin is a phenolic compound found in the rhizome of Gastrodia elata.

Dihydrostilbenoids (bibenzyls) are natural phenols formed from the dihydrostilbene (bibenzyl) backbone.
Ecklonia stolonifera is a brown alga species in the genus Ecklonia found in the Sea of Japan. It is an edible species traditionally eaten in Japan.

Dryopteris crassirhizoma is a fern species in the genus Dryopteris. It is an element of the Yupingfeng Asian soup formulation derivative.

Mallotus japonicus, known as East Asian mallotus, the food wrapper plant or Akamegashiwa in Japanese, is a plant species in the genus Mallotus native to China. It is also found in Japan and Korea.
Short chain ω-phenylalkanoic acids have long been known to occur in natural products. Phenylacetic, 3-phenylpropanoic and 3-phenylpropenoic (cinnamic) acids are found in propolis, mammalian exocrine secretions or plant fragrances. During a systematic study of the lipids from seeds of the plant Araceae, the presence of 13-phenyltridecanoic acid as a major component was discovered. Other similar compounds but with 11 and 15 carbon chain lengths and saturated or unsaturated were shown to be also present but in lower amounts. At the same time, the even carbon chain ω-phenylalkanoic acids of C10 up to C16 were discovered in halophilic bacteria.






















