Related Research Articles

Seafood is any form of sea life regarded as food by humans, prominently including fish and shellfish. Shellfish include various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Historically, marine mammals such as cetaceans as well as seals have been eaten as food, though that happens to a lesser extent in modern times. Edible sea plants such as some seaweeds and microalgae are widely eaten as sea vegetables around the world, especially in Asia.
The term hake refers to fish in the:

Hazard analysis and critical control points, or HACCP, is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, and physical hazards in production processes that can cause the finished product to be unsafe and designs measures to reduce these risks to a safe level. In this manner, HACCP attempts to avoid hazards rather than attempting to inspect finished products for the effects of those hazards. The HACCP system can be used at all stages of a food chain, from food production and preparation processes including packaging, distribution, etc. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) require mandatory HACCP programs for juice and meat as an effective approach to food safety and protecting public health. Meat HACCP systems are regulated by the USDA, while seafood and juice are regulated by the FDA. All other food companies in the United States that are required to register with the FDA under the Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002, as well as firms outside the US that export food to the US, are transitioning to mandatory hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls (HARPC) plans.

The fishing industry includes any industry or activity concerned with taking, culturing, processing, preserving, storing, transporting, marketing or selling fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including recreational, subsistence and commercial fishing, and the related harvesting, processing, and marketing sectors. The commercial activity is aimed at the delivery of fish and other seafood products for human consumption or as input factors in other industrial processes. The livelihood of over 500 million people in developing countries depends directly or indirectly on fisheries and aquaculture.
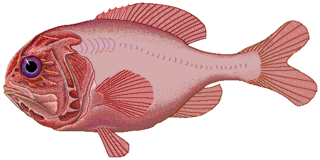
The orange roughy, also known as the red roughy, slimehead and deep sea perch, is a relatively large deep-sea fish belonging to the slimehead family (Trachichthyidae). The UK Marine Conservation Society has categorized orange roughy as "vulnerable to exploitation". It is found in 3 to 9 °C, deep waters of the Western Pacific Ocean, eastern Atlantic Ocean, Indo-Pacific, and in the eastern Pacific off Chile. The orange roughy is notable for its extraordinary lifespan, attaining over 200 years. It is important to commercial deep-trawl fisheries. The fish is a bright, brick-red color, fading to a yellowish-orange after death.

The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) is a non-profit organization which aims to set standards for sustainable fishing. Fisheries that wish to demonstrate they are well-managed and sustainable compared to the MSC's standards are assessed by a team of Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs).
The blue grenadier is a merluccid hake of the family Merlucciidae found around southern Australia and New Zealand, as well as off both the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of South America from Peru to Brazil at depths of between 10 and 1,000 m. It feeds in midwater on small squids, crustaceans, and fish. Its length is between 60 and 120 cm. It is a slender, silvery fish similar in appearance to the gemfish. The meat of the fish is white and almost always sold in fillets; culinarily it is considered a whitefish.
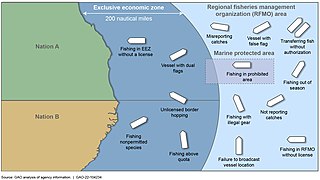
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.
Brim hf. is a fishing and fish processing company in Iceland. Brim's headquarters are in Reykjavík where its office and groundfish production are located. The company also runs fish processing plants in two other towns in Iceland, Akranes and Vopnafjörður.

The term fish processing refers to the processes associated with fish and fish products between the time fish are caught or harvested, and the time the final product is delivered to the customer. Although the term refers specifically to fish, in practice it is extended to cover any aquatic organisms harvested for commercial purposes, whether caught in wild fisheries or harvested from aquaculture or fish farming.

The Alaska pollock or walleye pollock is a marine fish species of the cod genus Gadus and family Gadidae. It is a semi-pelagic schooling fish widely distributed in the North Pacific, with largest concentrations found in the eastern Bering Sea.
Sustainable seafood is seafood that is caught or farmed in ways that consider the long-term vitality of harvested species and the well-being of the oceans, as well as the livelihoods of fisheries-dependent communities. It was first promoted through the sustainable seafood movement which began in the 1990s. This operation highlights overfishing and environmentally destructive fishing methods. Through a number of initiatives, the movement has increased awareness and raised concerns over the way our seafood is obtained.

American Seafoods Group, LLC is an American seafood company. Based in Seattle, Washington, ASC owns and operates six large catcher-processor vessels that harvest and process on board fish caught in the U.S. waters of Alaska and the Pacific Northwest. American Seafoods Company is the largest harvester in the U.S. Bering Sea Alaska Pollock fishery with approximately 45% of the catcher-processor market share.

Canada's fishing industry is a key contributor to the success of the Canadian economy. In 2016, Canada's fishing industry exported $6.6 billion in fish and seafood products and employed approximately 72,000 people in the industry. Aquaculture, which is the farming of fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in fresh or salt water, is the fastest growing food production activity in the world and a growing sector in Canada. In 2015, aquaculture generated over $1 billion in GDP and close to $3 billion in total economic activity. The Department Of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) oversees the management of Canada's aquatic resources and works with fishermen across the country to ensure the sustainability of Canada's oceans and in-land fisheries.
Aker BioMarine is a Norwegian fishing and biotech company providing krill products through a fully documented and secured catch and process chain. Based in Oslo, Aker BioMarine is part of the Aker Group and the company also created Eco-Harvesting.

Friend of the Sea is a project of the World Sustainability Organization for the certification and promotion of seafood from sustainable fisheries and sustainable aquaculture. It is the only certification scheme which, with the same logo, certifies both wild and farmed seafood.
Seafood in Australia comes from local and international commercial fisheries, aquaculture and recreational anglers. It is an economically important sector, and along with agriculture and forestry contributed $24,744 million to Australia's GDP in year 2007–2008, out of a total GDP of $1,084,146 million. Commercial fisheries in Commonwealth waters are managed by the Australian Fisheries Management Authority, while commercial and recreational fishing in state waters is managed by various state-level agencies.
A fish fillet processor processes fish into a fillet. Fish processing starts from the time the fish is caught. Popular species processed include cod, hake, haddock, tuna, herring, mackerel, salmon and pollock.
Norway Pelagic is a producer and exporter of pelagic fish, such as atlantic herring, atlantic mackerel and capelin, caught in the seas close to Norway. Total raw material processed is on annual basis about 50% of total landings of pelagic fish in Norway processed for human consumption. Norway Pelagic ASA is listed on the Oslo Stock Exchange and its head office is in Ålesund, Norway.
The South African Deep-Sea Trawling Industry Association (SADSTIA) represents the trawler owners and operators active in the offshore demersal trawl fishery for hake, the most valuable of South Africa's commercial fisheries, contributing approximately 45 percent of the value of fishery production. Based in Cape Town, South Africa, SADSTIA currently has 32 members that catch, process and market the Cape hakes, Merluccius paradoxus and Merluccius capensis as well as several bycatch species.
References
- ↑ http://www.hyfoma.com/en/content/food-branches-processing-manufacturing/meat-fish-shrimps/fish-processing/fillet/
- ↑ "Seawork: hake H&G; fillet & frozen fish hake fillet skin on". www.seawork.com.na. Archived from the original on 2010-09-02.
- ↑ "Home". msc.org.
- ↑ "Home". friendofthesea.org.