
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. The amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. Reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. Complications may include dehydration or seizures.

In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mild dehydration can also be caused by immersion diuresis, which may increase risk of decompression sickness in divers.
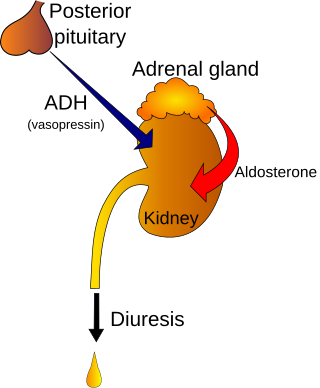
Polyuria is excessive or an abnormally large production or passage of urine. Increased production and passage of urine may also be termed as diuresis. Polyuria often appears in conjunction with polydipsia, though it is possible to have one without the other, and the latter may be a cause or an effect. Primary polydipsia may lead to polyuria. Polyuria is usually viewed as a symptom or sign of another disorder, but it can be classed as a disorder, at least when its underlying causes are not clear.

Thirst is the craving for potable fluids, resulting in the basic instinct of animals to drink. It is an essential mechanism involved in fluid balance. It arises from a lack of fluids or an increase in the concentration of certain osmolites, such as sodium. If the water volume of the body falls below a certain threshold or the osmolite concentration becomes too high, structures in the brain detect changes in blood constituents and signal thirst.
Polydipsia is excessive thirst or excess drinking. The word derives from Greek πολυδίψιος (poludípsios) 'very thirsty', which is derived from Ancient Greek πολύς (polús) 'much, many' and δίψα (dípsa) 'thirst'. Polydipsia is a nonspecific symptom in various medical disorders. It also occurs as an abnormal behaviour in some non-human animals, such as in birds.
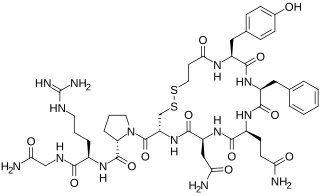
Desmopressin, sold under the trade name DDAVP among others, is a medication used to treat diabetes insipidus, bedwetting, hemophilia A, von Willebrand disease, and high blood urea levels. In hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease, it should only be used for mild to moderate cases. It may be given in the nose, by injection into a vein, by mouth, or under the tongue.

Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid–base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by consuming too little or too much electrolyte as well as excreting too little or too much electrolyte. Examples of electrolytes include calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium.
Hypernatremia, also spelled hypernatraemia, is a high concentration of sodium in the blood. Early symptoms may include a strong feeling of thirst, weakness, nausea, and loss of appetite. Severe symptoms include confusion, muscle twitching, and bleeding in or around the brain. Normal serum sodium levels are 135–145 mmol/L. Hypernatremia is generally defined as a serum sodium level of more than 145 mmol/L. Severe symptoms typically only occur when levels are above 160 mmol/L.
The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), also known as the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD), is characterized by a physiologically inappropriate release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) either from the posterior pituitary gland, or an abnormal non-pituitary source. Unsuppressed ADH causes a physiologically inappropriate increase in solute-free water being reabsorbed by the tubules of the kidney to the venous circulation leading to hypotonic hyponatremia.

Water intoxication, also known as water poisoning, hyperhydration, overhydration, or water toxemia, is a potentially fatal disturbance in brain functions that can result when the normal balance of electrolytes in the body is pushed outside safe limits by excessive water intake.
Fluid balance is an aspect of the homeostasis of organisms in which the amount of water in the organism needs to be controlled, via osmoregulation and behavior, such that the concentrations of electrolytes in the various body fluids are kept within healthy ranges. The core principle of fluid balance is that the amount of water lost from the body must equal the amount of water taken in; for example, in humans, the output must equal the input. Euvolemia is the state of normal body fluid volume, including blood volume, interstitial fluid volume, and intracellular fluid volume; hypovolemia and hypervolemia are imbalances. Water is necessary for all life on Earth. Humans can survive for 4 to 6 weeks without food but only for a few days without water.
Nocturia is defined by the International Continence Society (ICS) as "the complaint that the individual has to wake at night one or more times for voiding ". The term is derived from Latin nox – "night", and Greek [τα] ούρα – "urine". Causes are varied and can be difficult to discern. Although not every patient needs treatment, most people seek treatment for severe nocturia, waking up to void more than 2 or 3 times per night.
Plasma osmolality measures the body's electrolyte–water balance. There are several methods for arriving at this quantity through measurement or calculation.
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, recently renamed arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R) and previously known as renal diabetes insipidus, is a form of diabetes insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. This is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of vasopressin. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an improper response of the kidney to vasopressin, leading to a decrease in the ability of the kidney to concentrate the urine by removing free water.

Primary polydipsia and psychogenic polydipsia are forms of polydipsia characterised by excessive fluid intake in the absence of physiological stimuli to drink. Psychogenic polydipsia caused by psychiatric disorders—oftentimes schizophrenia—is frequently accompanied by the sensation of dry mouth. Some conditions with polydipsia as a symptom are non-psychogenic. Primary polydipsia is a diagnosis of exclusion.

Specific gravity, in the context of clinical pathology, is a urinalysis parameter commonly used in the evaluation of kidney function and can aid in the diagnosis of various renal diseases.
Urine osmolality is a measure of urine concentration, in which large values indicate concentrated urine and small values indicate diluted urine. Consumption of water affects the osmolality of urine.
Central diabetes insipidus, recently renamed arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D), is a form of diabetes insipidus that is due to a lack of vasopressin (ADH) production in the brain. Vasopressin acts to increase the volume of blood (intravascularly), and decrease the volume of urine produced. Therefore, a lack of it causes increased urine production and volume depletion.

The condition known today as diabetes is thought to have been described in the Ebers Papyrus. Ayurvedic physicians first noted the sweet taste of diabetic urine, and called the condition madhumeha. The term diabetes traces back to Demetrius of Apamea. For a long time, the condition was described and treated in traditional Chinese medicine asxiāo kě. Physicians of the medieval Islamic world, including Avicenna, have also written on diabetes. Early accounts often referred to diabetes as a disease of the kidneys. In 1674, Thomas Willis suggested that diabetes may be a disease of the blood. Johann Peter Frank is credited with distinguishing diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus in 1794.

Adipsia, also known as hypodipsia, is a symptom of inappropriately decreased or absent feelings of thirst. It involves an increased osmolality or concentration of solute in the urine, which stimulates secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the hypothalamus to the kidneys. This causes the person to retain water and ultimately become unable to feel thirst. Due to its rarity, the disorder has not been the subject of many research studies.










