
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae, a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.

Oxytetracycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic, the second of the group to be discovered.
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.

Cattleya is a genus of orchids from Costa Rica south to Argentina. The genus is abbreviated C in trade journals.

Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin.

The Streptomycetaceae are a family of Actinomycetota, making up the monotypic order Streptomycetales. It includes the important genus Streptomyces. This was the original source of many antibiotics, namely streptomycin, the first antibiotic against tuberculosis.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.

4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (4-HPPA) is an intermediate in the metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. The aromatic side chain of phenylalanine is hydroxylated by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase to form tyrosine. The conversion from tyrosine to 4-HPPA is in turn catalyzed by tyrosine aminotransferase. Additionally, 4-HPPA can be converted to homogentisic acid which is one of the precursors to ochronotic pigment.
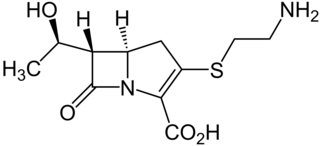
Thienamycin is one of the most potent naturally produced antibiotics known thus far, discovered in Streptomyces cattleya in 1976. Thienamycin has excellent activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is resistant to bacterial β-lactamase enzymes. Thienamycin is a zwitterion at pH 7.

Oleandomycin is a macrolide antibiotic. It is synthesized from strains of Streptomyces antibioticus. It is weaker than erythromycin.
In enzymology, a fluoroacetaldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.69) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a fluorothreonine transaldolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The fluorinase enzyme catalyzes the reaction between fluoride ion and the co-factor S-adenosyl-L-methionine to generate L-methionine and 5'-fluoro-5'-deoxyadenosine, the first committed product of the fluorometabolite biosynthesis pathway. The fluorinase was originally isolated from the soil bacterium Streptomyces cattleya, but homologues have since been identified in a number of other bacterial species, including Streptomyces sp. MA37, Nocardia brasiliensis and Actinoplanes sp. N902-109. This is the only known enzyme capable of catalysing the formation of a carbon-fluorine bond, the strongest single bond in organic chemistry.

The term grex, derived from the Latin noun grex, gregis, meaning 'flock', has been expanded in botanical nomenclature to describe hybrids of orchids, based solely on their parentage. Grex names are one of the three categories of plant names governed by the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants; within a grex the cultivar group category can be used to refer to plants by their shared characteristics, and individual orchid plants can be selected and named as cultivars.
Streptomyces isolates have yielded the majority of human, animal, and agricultural antibiotics, as well as a number of fundamental chemotherapy medicines. Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus of Actinomycetota, producing chemotherapy, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic drugs, and immunosuppressants. Streptomyces isolates are typically initiated with the aerial hyphal formation from the mycelium.
Streptomyces cattleya is a Gram-positive bacterium which makes cephamycin, penicillin and thienamycin. The bacterium expresses a fluorinase enzyme, and the organism has been used to understand the biosynthesis of fluoroacetate and the antibacterial 4-fluoro-L-threonine. The γ-Glu-βes pathway to biosynthesis of non-traditional amino acids β-ethynylserine (βes) and L-propargylglycine (Pra) was first characterized in this species.

4-Fluoro-l-threonine is an antibacterial produced by Streptomyces cattleya. It is formed by the fluorothreonine transaldolase catalysed transfer of fluoroacetaldehyde onto threonine.
Streptomyces nigrescens is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces nigrescens produces 5-alkyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines and the antibiotics phoslactomycin A - F.
Butyrolactol A is an organic chemical compound of interest for its potential use as an antifungal antibiotic.

Prescopranone is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of scopranones. Prescopranone is the precursor to scopranone A, scopranone B, and scopranone C, which are produced by Streptomyces sp. BYK-11038.











