A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

Xanthine is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids, as well as in other organisms. Several stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.

Fluorescein is an organic compound and dye based on the xanthene tricyclic structural motif, formally belonging to triarylmethine dyes family. It is available as a dark orange/red powder slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is widely used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications.

Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dyes. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine 123, and Rhodamine B. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness for fabric dyeing.
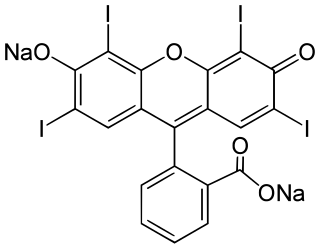
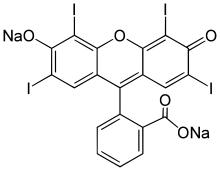
Erythrosine, also known as Red No. 3, is an organoiodine compound, specifically a derivative of fluorone. It is a pink dye which is primarily used for food coloring. It is the disodium salt of 2,4,5,7-tetraiodofluorescein. Its maximum absorbance is at 530 nm in an aqueous solution, and it is subject to photodegradation.

Xanthone is an organic compound with the molecular formula O[C6H4]2CO. It is a white solid.

Rhodamine B is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with fluorometers.

Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.
New methylene blue is an organic compound of the thiazine class of heterocycles. It is used as a stain and as an antimicrobial agent. It is classified as an azine dye, and the chromophore is a cation, the anion is often unspecified.

Thioxanthene is a chemical compound in which the oxygen atom in xanthene is replaced with a sulfur atom. It is also related to phenothiazine. Several of its derivatives are used as typical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychoses.

Xantphos is an organophosphorus compound derived from the heterocycle xanthene. It is used as a bidentate diphosphine ligand and is noteworthy for having a particularly wide bite angle (108°). Such ligands are useful in the hydroformylation of alkenes. Illustrative of its wide bite angle, it forms both cis and trans adducts of platinum(II) chloride. In the latter context, xantphos is classified as a trans-spanning ligand. A related bidentate ligand with a greater bite angle is spanphos.
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes.
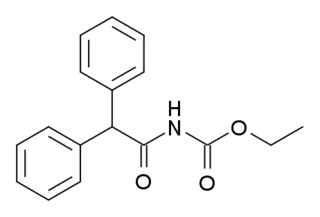
Ro01-6128 is a drug used in scientific research, which acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR1. It was derived by modification of a lead compound found via high-throughput screening, and was further developed to give the improved compound Ro67-4853.

Ro67-4853 is a drug used in scientific research, which acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR1. It was derived by modification of the simpler compound Ro01-6128, and has itself subsequently been used as a lead compound to develop a range of potent and selective mGluR1 positive modulators.
The molecular formula C13H8O2 (molar mass: 196.20 g/mol, exact mass: 196.0524 u) may refer to:
This is an index of articles relating to pesticides.
The molecular formula C13H10O (molar mass: 182.22 g/mol, exact mass: 182.0732 u) may refer to:

Xanthydrol is an organic chemical compound. Its formula is C13H10O2. Its total molecular weight is 198.221 g/mol. Xanthydrol is used to test the levels of urea in the bloodstream.

Gortyna xanthenes, the artichoke moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It was described by Ernst Friedrich Germar in 1842. It is found on the Canary Islands, the Balearic Islands, Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily and Malta as well as in Portugal, Spain, France, Italy and Greece.