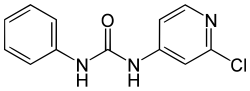
Regulatory assessment
Forchlorfenuron is manufactured to a minimum purity of 97.8% and is marketed in the European Union as the 10 grammes/litre emulsifiable concentrate "SITOFEX EC". The 2017 European Food Safety Authority renewal review considered field-spray applications on kiwifruit and table grapes and found that, when used according to good agricultural practice, the substance provides consistent fruit-size enhancement with no critical efficacy issues identified. [5]
Safety tests showed that forchlorfenuron is quickly absorbed by the body (over 80% in animal studies), spreads throughout the body, is eliminated rapidly, and has low immediate toxicity; target‐organ effects in sub-chronic studies were limited to the liver, kidneys and blood parameters. It is classified as 'Carcinogen Category 2' (meaning it may possibly cause cancer, but evidence is limited) but is neither a reproductive toxicant nor an endocrine disruptor on current evidence. Reference values agreed during the renewal include an acceptable daily intake of 0.05 milligrams per kilogram of body weight per day (a very small amount – for a 70 kg adult, this equals about 3.5 milligrams daily). The acute reference dose (ARfD) – the safe amount someone can consume in one day – was set at 0.5 mg per kg of bodyweight. The acceptable operator exposure level (AOEL) for agricultural workers and pesticide applicators was established at 0.16 mg per kg of body weight per day over their working lifetime. Operator, worker and by-stander exposures estimated with standard EU models were all below the AOEL without special protective equipment. [5]
In the environment, the active substance shows moderate-to-very-high persistence in aerobic soils and sediments, breaking down into a compound called 4-amino-2-chloropyridine, yet both compounds show low-to-slight soil mobility. Modelling indicated little potential for groundwater contamination (no more than 0.1 micrograms per litre – an extremely small amount) and predicted surface-water residues remained well below EU drinking-water limits, even in small edge-of-field water bodies. Ecotoxicological assessments concluded a low acute and chronic risk to birds, mammals, fish and aquatic invertebrates, with remaining data gaps confined to algal diversity testing and honey-bee larval exposure via guttation water. [5]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.