Notes
| Preceded by | King of the Suevi 457 | Succeeded by Rechimund (not as king) |
Framta, Framtan or Framtane (Latin: Framtanus, Spanish: Frantán; died 457) was one of the kings of the Suevi in Galicia in 457.
After the death of the Suevic king Rechiar, executed by the conquering Visigoths, and the Warnic king Aioulf, executed by his Visigothic masters for insubordination, the Suevi regrouped themselves and "set up" one of their own, Maldras, as king in 456. [1] In 457, however, some of the Suevic people apparently abandoned Maldras and "called" Framta king. [1] In light of the evidence of dynastic kingship among the Sueves, the instance of Maldras and Framta has been taken as indicative that the people retained some right to elect a king of their choosing at the end of a lineage. [2]
Framta and Maldras, as well as their followers, acted independently of one another. While Framta reigned, Maldras led his Sueves into Lusitania. [2] Framta died after a few months and there is debate whether the two Suevic factions were reunited under Maldras at that juncture or not. [2] Framta's followers are soon found under the leadership of Rechimund, who was not king. [2]

The Suebi were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later such as the Alamanni and Bavarians and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian.
Year 585 (DLXXXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 585 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This is a historical timeline of the Iberian Peninsula during the period of the post-Imperial kingdoms.
Hermeric was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
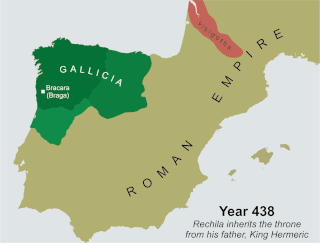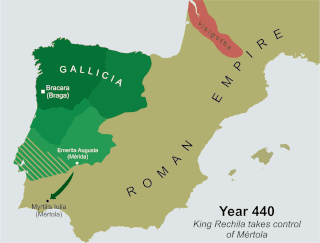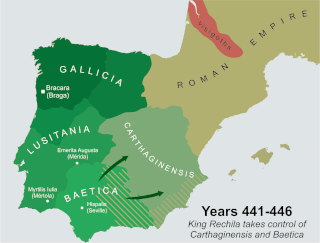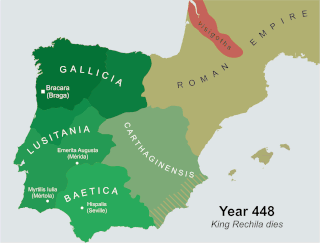
Rechila was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non-Arian) chronicler in Galicia.

Rechiar or Rechiarius was the Suevic king of Gallaecia from 448 until his death. He was the first Chalcedonian Christian (Catholic) Germanic king in Europe and one of the most innovative and belligerent of the Suevi monarchs. Despite his orthodox Christianity, Hydatius, the contemporary bishop and chronicler from Galicia who is the sole contemporary source for biographical details of Rechiar, established his reputation as that of a barbarian with little sense of Roman law, culture, or custom.
Maldras was the Suevic king of Galicia from 456 until his death. After the execution of Rechiar by the victorious Visigoths, the Suevi are said to have established Maldras on the throne. During his reign the Suevic nation became fragmented.

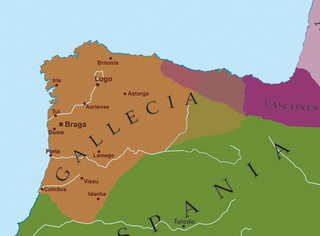
The Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallæcia or Suebi Kingdom of Gallæcia, was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from the Roman Empire. Based in the former Roman provinces of Gallaecia and northern Lusitania, the de facto kingdom was established by the Suebi about 409, and during the 6th century it became a formally declared kingdom identifying with Gallaecia. It maintained its independence until 585, when it was annexed by the Visigoths, and was turned into the sixth province of the Visigothic Kingdom in Hispania.
Aioulf or Ag(r)iwulf was an obscure king of Galicia from 456. In 448, after eight years in captivity, the Roman ambassador Censorius was executed by one Agiulf at Seville (Hispalis). This Agiulf has sometimes been identified with Aioulf.
Richimund or Rechimund was a Suevic leader in Galicia from 457 until about 464. He was not recorded as a king (rex), though Hydatius wrote that inter Frumarium et Rechimundum oritur de regni potestate dissensio. In 457 the Suevi split into two factions, one headed by Maldras raiding Lusitania and another led by Framta remaining in Galicia. After a few months of rule, Framta died and Rechimund appeared as his successor. While it is possible that the Suevi were living under a diarchy, it is more likely that the two factions remained independent of one another. Maldras' eventual successor, Frumar, was also not described as a king, but in 464 or thereabouts the entire Suevic nation was unified under a king named Remismund. Presumably, Rechimund and Frumar had battled for the throne and both had been eliminated, paving the way for Remismund. Some scholars have equated Remismund with Rechimund, but this seems far-fetched.
Frumar was a Suevic warlord who succeeded Maldras, as leader of the Suevic group then raiding Lusitania. He probably competed with Rechimund, the Suevic war leader in Gallaecia, for the throne until his death.
Remismund was the Suevic king of Galicia from c. 464 until his death.

Theodemir or Theodemar was one of the last Suevic kings of Galicia and one of the first Chalcedonian Christians to hold the title. He succeeded Ariamir sometime between the end of May 561 and the year 566 and ruled until his death.

Miro was the Suebian King of Galicia from 570 until his death in 583. His reign was marked by attempts to forge alliances with other Chalcedonian Christian nations with the goal of checking the power of the Arian Visigoths under Leovigild. During his reign relations were established with both Francia and the Byzantine Empire and the kingdom reached its zenith, but it collapsed within three years of his death.

Audeca or Andeca was the last Suevic King of Galicia from 584 until his deposition in 585. He deposed Eboric and usurped the throne by marrying the young king's mother, Siseguntia, the widow of Eboric's father and predecessor, Miro. He consigned Eboric to a monastery.
Censorius was a count (comes) of the Western Roman Empire from 432 until his death. He is mentioned in the Chronicle of Hydatius under the years 432 and 440.

Ariamir was the Suevic King of Galicia, with his capital at Bracara, from 558/9. The bishops of the First Council of Braga recorded Ariamir as the king who summoned them and under whose auspices they deliberated. Because the bishops mention theirs as being the first Nicene synod to be held in Galicia in a long while, Ariamir is sometimes assumed to have been the king who led the conversion of his people from Arianism to orthodoxy and thus to have lifted the ban on Nicene councils.
Heremigarius was a Suevic military leader operating in Lusitania in the early fifth century. He may have been a joint monarch with Hermeric or his successor, but no primary source directly attests it. Writing in the mid-seventh century, Fredegar calls Heremigarius rex Suaevorum, king of the Suevi.
Hermeneric was a Suevic King of Galicia according to a now lost document described by the priest Antonio de Yepes. According to Yepes, the king reigned around 485, which falls within a century-long period (469–c.560) of obscurity during which the Sueves were predominantly Arian Christians. Hermeneric was said to be a destroyer of churches and persecutor of Catholic Christians.
Veremund or Veremundus was a Suevic king of Galicia around 500. His existence is conjectured on the basis of a sixth-century inscription discovered at Salvador de Vairão. The date in the inscription is interpreted as either 485 or 535. Some scholars have dated the inscription to the eighth century, arguing that the Veremundus of the inscription is King Bermudo I of Asturias.