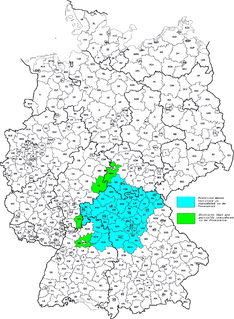
Franconia is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect.
Ansbach is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It surrounds – but does not include – the town of Ansbach; nonetheless the administrative seat of the district is located in Ansbach. It is the district with the largest area in Bavaria.
Schwäbisch Hall is a Landkreis (district) in the northeast of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Neighboring districts are Main-Tauber, the Bavarian district Ansbach, Ostalbkreis, Rems-Murr, and Hohenlohe.

Crailsheim is a town in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Incorporated in 1338, it lies 32 kilometres east of Schwäbisch Hall and 40 km (25 mi) southwest of Ansbach in the Schwäbisch Hall district. The city's main attractions include two Evangelical churches, a Catholic church, and the 67 metre tower of its town hall.

Öhringen is the largest town in Hohenlohe (district) in the state of Baden-Württemberg, in southwest Germany, near Heilbronn. Öhringen is on the railline to Schwäbisch Hall and Crailsheim.

Casimirof Brandenburg-Bayreuth was Margrave of Bayreuth or Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach from 1515 to 1527.

Feuchtwangen is a city in Ansbach district in the administrative region of Middle Franconia in Bavaria, Germany with around 12.000 citizens and 137km² of landmass making it the biggest city in the Ansbach district by Population and Landmass. In the year 2019 Feuchtwangen celebrated its 1200th jubilee based on the first mention of its Benedictine monastery.
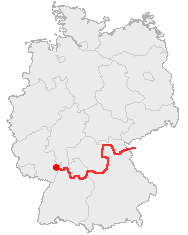
The Castle Road is a theme route in southern Germany and a small portion in the Czech Republic, between Mannheim and Prague.

Satteldorf is a municipality in the district of Schwäbisch Hall in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.

The Gäu Plateaus form the largest natural region in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Not surprisingly, the individual geographical units of this large region show considerable variations in climate and soil types. A common feature of the region, however, is its landscape of flat-topped hills of Muschelkalk, gently rolling tracts of loess and plateaus in which the layers of Muschelkalk have been covered by sediments of Gipskeuper and Lettenkeuper.

The South German Scarplands is a geological and geomorphological natural region or landscape in Switzerland and the south German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The landscape is characterised by escarpments.

Heilbronn-Franken is a region in northeastern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, in the Stuttgart subdivision (Regierungsbezirk). It consists of the former Free imperial city of Heilbronn, Heilbronn district and the districts of Hohenlohe, Main-Tauber and Schwäbisch Hall.
The Swabian Keuper-Lias Plains is a major natural region in southwest Germany and includes the southwesternmost part of the Keuper Uplands, which is bordered immediately to the north by the Swabian Jura.
The Franconian Keuper-Lias Plains or Franconian Keuper-Lias Lands are a major natural region in the South German Scarplands in Upper Franconia and to a lesser extent in the north, in the Thuringian district of Hildburghausen. As the name indicates, the term embraces both the Keuper landscapes and lias landscapes in Franconia. In addition, the fore-land of the Franconian Jura, in which part of the Brown Jurassic occurs, as well as parts of the former volcanic region of Heldburger Gangschar belong to this region.

The Franconian Heights Nature Park is a nature park in Germany that covers an area of approximately 1,100 square kilometres. It is located northeast of the town of Rothenburg ob der Tauber in Bavaria and covers most of the hill ridge known as the Franconian Heights, as well as areas to the west and up to the Sulzach. The nature park is in one of the sunniest areas of southern Germany and offers a very varied landscape with mixed forests, rivers, vineyards and dry habitats.

The Swabian-Franconian Forest is a mainly forested, deeply incised upland region, 1,187 km² in area and up to 586.4 m above sea level (NHN), in the northeast of Baden-Württemberg. It forms natural region major unit number 108 within the Swabian Keuper-Lias Land. Its name is derived from the fact that, in medieval times, the border between the duchies of Franconia and Swabia ran through this forested region. In addition, the Swabian dialect in the south transitions to the East Franconian dialect in the north here.
The Keuper Uplands are part of the South German Scarplands and cover an area of about 3,200 square kilometres.

The Virngrund is a historical landscape in the counties of Ostalbkreis and Schwäbisch Hall in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. it is forested in many places and up to 580 m above sea level (NHN).

The Löwenstein Hills are a hill range up to 561 m above sea level (NHN), in the counties of Heilbronn, Ludwigsburg, Rems-Murr-Kreis and Hohenlohekreis in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. They are named after the town of Löwenstein.

The Waldenburg Hills are a forested hill range, up to 522.8 m above sea level (NHN), in the counties of Schwäbisch Hall and Hohenlohe in the south German state of Baden-Württemberg.












