The Isthmus of Chignecto is an isthmus bordering the Maritime provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia that connects the Nova Scotia peninsula with North America.

Michael Francklin or Franklin served as Nova Scotia's Lieutenant Governor from 1766 to 1772. He is buried in the crypt of St. Paul's Church (Halifax).
Economy is an unincorporated rural community situated along the north shore of the Minas Basin/Cobequid Bay, at approximately 45°23'N, 63°54'W, in Colchester County, Nova Scotia. In the late 19th century, it was known for its shipbuilding industry.

Fort Lawrence was a British fort built during Father Le Loutre's War and located on the Isthmus of Chignecto.

Spencer's Island is a rural community in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, located at the western end of Greville Bay on the Bay of Fundy. The community is named after a small island 45°19′50″N64°41′30″W of the same name located offshore from nearby Cape Spencer. According to local oral history, the island, cape and community trace their name to a man named Spencer who is buried on the island. However the name more likely comes from Lord Spencer, a British statesman at the time the community was settled.

The Missaguash River is a small Canadian river that forms the southern portion of the inter-provincial boundary between Nova Scotia and New Brunswick on the Isthmus of Chignecto. It had historic significance in the 18th century as the de facto border between French and English-controlled territories.
Fort Lawrence is a Canadian rural community located on the Isthmus of Chignecto in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, which is named after Fort Lawrence.

The Cornwallis River is in Kings County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It has a meander length of approximately 48 kilometres (30 mi) through eastern Kings County, from its source on the North Mountain at Grafton to its mouth near Wolfville on the Minas Basin. The lower portion of the river beginning at Kentville is tidal and there are extensive tidal marshes in the lower reaches. In its upper watershed at Berwick, the river draws on the Caribou Bog while a longer branch continues to the official source, a stream on the North Mountain at Grafton.

Cape Chignecto is a headland located on the Bay of Fundy coast of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

The St. Croix River is a river in Nova Scotia entirely contained in Hants and Halifax Counties. Its headwaters are Panuke Lake. The river has been exploited for water power. There were water mills in the nineteenth century and in the 1930s three hydroelectric dams were built; they still operate.
Avonport is a community in the province of Nova Scotia, Canada, located in Kings County between the mouths of the Avon River and the Gaspereau River. Early settlers included the Fillis and Reid families. It was part of the Horton Township settlement and was known as Horton Point until its name was changed to Avonport in 1864.
Maccan is a small community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in Cumberland County 10 minutes away from Amherst, Nova Scotia on Route 302.

Apple River is a community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in Cumberland County.

The Raid on Lunenburg occurred during the French and Indian War when Mi'kmaq and Maliseet fighters attacked a British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on May 8, 1756. The native militia raided two islands on the northern outskirts of the fortified Township of Lunenburg, Rous Island, and Payzant Island. According to French reports, the Raiding party killed twenty settlers and took five prisoners. This raid was the first of nine the Natives and Acadians would conduct against the peninsula over a three-year period during the war. The Wabanaki Confederacy took John Payzant and Lewis Payzant prisoner, both of whom left written account of their experiences.
Glooscap 35 is a Mi'kmaq reserve located in Kings County, Nova Scotia.
Paqtnkek Mi’kmaw Nation is a Mi'kmaq Band in northeastern Nova Scotia. Its populated reserve is Paqtnkek-Niktuek 23. As of December 2019 the total registered population was 598. It is a member of the Confederacy of Mainland Mi'kmaq. The name Paqtnkek means “by the bay” or "Above the water ". The area has long been important to Mi'kmaq for the fishing of eel and other species.
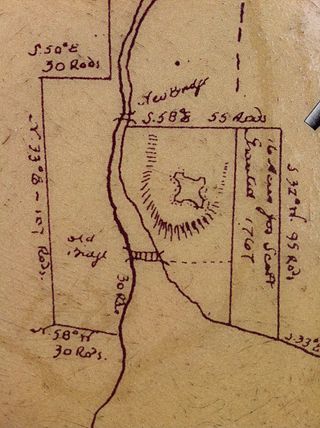
Fort Sackville was a British fort in present-day Bedford, Nova Scotia. It was built during Father Le Loutre's War by British adjacent to present-day Scott Manor House, on a hill overlooking the Sackville River to help prevent French, Acadian and Mi'kmaq attacks on Halifax. The fort consisted of a blockhouse, a guard house, a barracks that housed 50 soldiers, and outbuildings, all encompassed by a palisade. Not far from the fort was a rifle range. The fort was named after George Germain, 1st Viscount Sackville.

Fort Ellis was a British fort or blockhouse built during the French and Indian War, located at the junction of the Shubenacadie and Stewiacke Rivers, close to Stewiacke, Nova Scotia, Canada. The location was labelled Ville Pierre Hebert by Charles Morris. The 14 Acadian families in the area vacated with the Acadian Exodus. Charles Morris recommended a Fort on the Shubenacadie River in 1753. Governor Lawrence first considered the fort in 1754 as a means to protect Halifax from Mi'kmaq raids. Lawrence decided the fort would not be effective until after the Battle of Fort Beauséjour. The fort was completed on October 18, 1761, shortly after the Halifax Treaties were signed. The fort was to guard the new road built to connect Truro and Halifax against Mi'kmaq raids. The fort was called Fort Ellis after Governor Henry Ellis, who was appointed governor weeks after the forts completion. The fort was never garrisoned and eventually abandoned in 1767. Fort Belcher, named after Governor Jonathan Belcher, was built on Salmon River in Lower Onslow, Nova Scotia (1761–67). Fort Franklin was built at Tatamagouche in 1768, named after Michael Francklin and lasted only a year. Fort Morris was named after Charles Morris.

The military history of the Mi'kmaq consisted primarily of Mi'kmaq warriors (smáknisk) who participated in wars against the English independently as well as in coordination with the Acadian militia and French royal forces. The Mi'kmaq militias remained an effective force for over 75 years before the Halifax Treaties were signed (1760–1761). In the nineteenth century, the Mi'kmaq "boasted" that, in their contest with the British, the Mi'kmaq "killed more men than they lost". In 1753, Charles Morris stated that the Mi'kmaq have the advantage of "no settlement or place of abode, but wandering from place to place in unknown and, therefore, inaccessible woods, is so great that it has hitherto rendered all attempts to surprise them ineffectual". Leadership on both sides of the conflict employed standard colonial warfare, which included scalping non-combatants. After some engagements against the British during the American Revolutionary War, the militias were dormant throughout the nineteenth century, while the Mi'kmaq people used diplomatic efforts to have the local authorities honour the treaties. After confederation, Mi'kmaq warriors eventually joined Canada's war efforts in World War I and World War II. The most well-known colonial leaders of these militias were Chief (Sakamaw) Jean-Baptiste Cope and Chief Étienne Bâtard.

A township in Nova Scotia, Canada, was an early form of land division and local administration during British colonial settlement in the 18th century. They were created as a means of populating the colony with people loyal to British rule. They were typically rural or wilderness areas of around 100,000 acres (400 km2) that would eventually include several villages or towns. Some townships, but not all, returned a member to the General Assembly of Nova Scotia; others were represented by the members from the county. Townships became obsolete by 1879 by which time towns and counties had become incorporated.