
Hair color is the pigmentation of hair follicles due to two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Generally, if more melanin is present, the color of the hair is darker; if less melanin is present, the hair is lighter. The tone of the hair is dependent on the ratio of black or brown eumelanin to yellow or red pheomelanin. Levels of melanin can vary over time causing a person's hair color to change, and it is possible to have hair follicles of more than one color on the same person. Some hair colors are associated with some ethnic groups due to observed higher frequency of particular hair color within their geographical region, e.g. straight dark hair amongst East Asians, a large variety of dark, fair, curly, wavy and bushy hair amongst Europeans, curly, dark, and uniquely helical hair with Africans, whilst gray, white or "silver" hair is often associated with age and wisdom.
In computing, on the X Window System, X11 color names are represented in a simple text file, which maps certain strings to RGB color values. It was traditionally shipped with every X11 installation, hence the name, and is usually located in <X11root>/lib/X11/rgb.txt. The web colors list is descended from it but differs for certain color names.

Complementary colors are pairs of colors which, when combined or mixed, cancel each other out by producing a grayscale color like white or black. When placed next to each other, they create the strongest contrast for those two colors. Complementary colors may also be called "opposite colors".

Grey or gray is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed of black and white. It is the color of a cloud-covered sky, of ash and of lead.

Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic character determined by two distinct factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris.

Olive is a dark yellowish-green color, like that of unripe or green olives.

A gray horse has a coat color characterized by progressive depigmentation of the colored hairs of the coat. Most gray horses have black skin and dark eyes; unlike some equine dilution genes and some other genes that lead to depigmentation, gray does not affect skin or eye color. Gray horses may be born any base color, depending on other color genes present. White hairs begin to appear at or shortly after birth and become progressively more prevalent as the horse ages as white hairs become intermingled with hairs of other colors. Graying can occur at different rates—very quickly on one horse and very slowly on another. As adults, most gray horses eventually become completely white, though some retain intermixed light and dark hairs.
In many languages, the colors described in English as "blue" and "green" are colexified, i.e. expressed using a single cover term. To describe this English lexical gap, linguists use the portmanteau word grue, from green and blue, a term coined by the philosopher Nelson Goodman—with a rather different meaning—in his 1955 Fact, Fiction, and Forecast to illustrate his "new riddle of induction". The alternative, bleen, is not really used.
Taupe is a dark gray-brown color. The word derives from the French noun taupe meaning "mole". The name originally referred only to the average color of the French mole, but beginning in the 1940s, its usage expanded to encompass a wider range of shades.

Black squirrels are a melanistic subgroup of squirrels with black coloration on their fur. The phenomenon occurs with several species of squirrels, although it is most frequent with the eastern gray squirrel and the fox squirrel. Black morphs of the eastern gray and fox squirrels are the result of an abnormal pigment gene. Several theories have surfaced as to why the black morph occurs, with some suggesting that the black morph is a selective advantage for squirrels inhabiting the northern ranges of the species, with the black-fur providing a thermal advantage over its non-melanistic counterpart.

The first recorded use of "light blue" as a color term in English is in the year 1915.

Horses exhibit a diverse array of coat colors and distinctive markings. A specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe them.
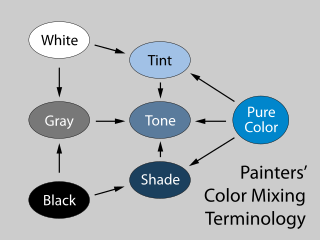
In color theory, a tint is a mixture of a color with white, which increases lightness, while a shade is a mixture with black, which increases darkness. Both processes affect the resulting color mixture's relative saturation. A tone is produced either by mixing a color with gray, or by both tinting and shading. Mixing a color with any neutral color reduces the chroma, or colorfulness, while the hue remains unchanged.

The ColorMonitor IIe, later renamed AppleColor Composite Monitor IIe is a CRT-based color or gray monochrome (selectable) 13-inch monitor manufactured by Apple Computer for the Apple II personal computer family. This monitor is designed to fit into the grooves on the top of the Apple II, II+, and IIe computers. This monitor has no swiveling option.
Blue-gray or blue-grey is a medium bluish-gray color. Another name for this color is livid; this color name comes from the Latin color term lividus meaning "'a dull leaden-blue color', and also used to describe the color of contused flesh, leading to the English expression 'black and blue'".

Variations of gray or grey include achromatic grayscale shades, which lie exactly between white and black, and nearby colors with low colorfulness. A selection of a number of these various colors is shown below.

Shades of brown can be produced by combining red, yellow, and black pigments, or by a combination of orange and black—illustrated in the color box. The RGB color model, that generates all colors on computer and television screens, makes brown by combining red and green light at different intensities. Brown color names are often imprecise, and some shades, such as beige, can refer to lighter rather than darker shades of yellow and red. Such colors are less saturated than colors perceived to be orange. Browns are usually described as light or dark, reddish, yellowish, or gray-brown. There are no standardized names for shades of brown; the same shade may have different names on different color lists, and sometimes one name can refer to several very different colors. The X11 color list of web colors has seventeen different shades of brown, but the complete list of browns is much longer.

Shades of black are colors that differ only slightly from pure black. These colors have a low lightness. From a photometric point of view, a color which differs slightly from black always has low relative luminance. Variations of black include what are commonly termed off-black colors, which may be considered part of a neutral color scheme, usually in interior design as a part of a background for brighter colors. Black and dark gray colors are powerful accent colors that suggest weight, dignity, formality, and solemnity.










