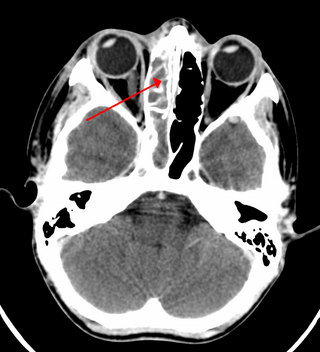
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, headaches, a poor sense of smell, sore throat, a feeling that phlegm is oozing out from the back of the nose to the throat along with a necessity to clear the throat frequently and frequent attacks of cough.

Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior.
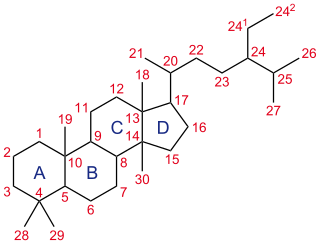
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
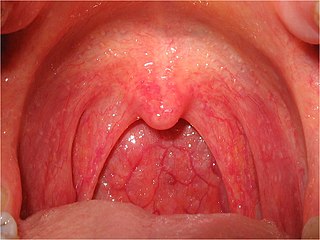
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last 3–5 days, but can be longer depending on cause. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is a type of upper respiratory tract infection.
Saponins, also selectively referred to as triterpene glycosides, are bitter-tasting usually toxic plant-derived organic chemicals that have a foamy quality when agitated in water. They are widely distributed but found particularly in soapwort, a flowering plant, the soapbark tree and soybeans. They are used in soaps, medicines, fire extinguishers, speciously as dietary supplements, for synthesis of steroids, and in carbonated beverages. Saponins are both water and fat soluble, which gives them their useful soap properties. Some examples of these chemicals are glycyrrhizin and quillaia, a bark extract used in beverages.

Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpene with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as Squalus is a genus of sharks). An estimated 12% of bodily squalene in humans is found in sebum. Squalene has a role in topical skin lubrication and protection.

Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune pruritic skin disease that typically occurs in people aged over 60, that may involve the formation of blisters (bullae) in the space between the epidermal and dermal skin layers. It is classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction, which involves formation of anti-hemidesmosome antibodies, causing a loss of keratinocytes to basement membrane adhesion.
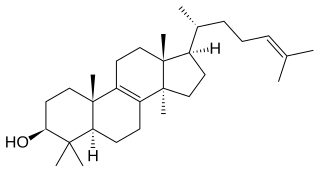
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.

Ceragenins, or cationic steroid antimicrobials (CSAs), are synthetically-produced, small-molecule chemical compounds consisting of a sterol backbone with amino acids and other chemical groups attached to them. These compounds have a net positive charge that is electrostatically attracted to the negative-charged cell membranes of certain viruses, fungi and bacteria. CSAs have a high binding affinity for such membranes and are able to rapidly disrupt the target membranes leading to rapid cell death. While CSAs have a mechanism of action that is also seen in antimicrobial peptides, which form part of the body's innate immune systum, they avoid many of the difficulties associated with their use as medicines.

Benzydamine, available as the hydrochloride salt, is a locally acting nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with local anaesthetic and analgesic properties for pain relief and anti-inflammatory treatment of inflammatory conditions of the mouth and throat. It falls under class of chemicals known as indazole.
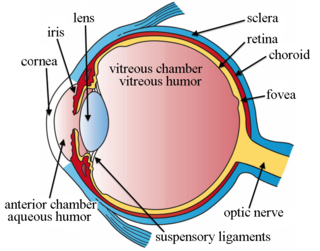
Intravitreal is a route of administration of a drug, or other substance, in which the substance is delivered into the vitreous humor of the eye. "Intravitreal" literally means "inside an eye". Intravitreal injections were first introduced in 1911 when Ohm gave an injection of air into the vitreous humor to repair a detached retina. In the mid-1940s, intravitreal injections became a standard way to administer drugs to treat endophthalmitis and cytomegalovirus retinitis.

Triterpenes are a class of terpenes composed of six isoprene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of three terpene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squalene, the precursor to all steroids.

Betulin is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees. It forms up to 30% of the dry weight of silver birch bark. It is also found in birch sap. Inonotus obliquus contains betulin.

Maslinic acid is a compound derived from dry olive-pomace oil which is a byproduct of olive oil extraction. It is a member of the group of triterpenes known as oleananes.
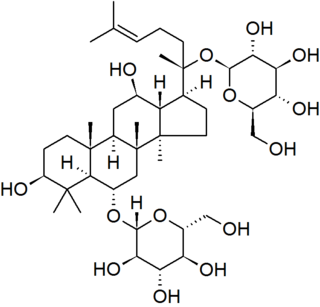
Ginsenosides or panaxosides are a class of natural product steroid glycosides and triterpene saponins. Compounds in this family are found almost exclusively in the plant genus Panax (ginseng), which has a long history of use in traditional medicine that has led to the study of pharmacological effects of ginseng compounds. As a class, ginsenosides exhibit a large variety of subtle and difficult-to-characterize biological effects when studied in isolation.

Lanostane or 4,4,14α-trimethylcholestane is a tetracyclic chemical compound with formula C
30H
54. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, specifically a triterpene. It is an isomer of cucurbitane.

Ergostane is a tetracyclic triterpene, also known as 24S-methylcholestane. The compound itself has no known uses; however various functionalized analogues are produced by plants and animals. The most important of these are the heavily derivatised withanolides. However simpler forms do exist, such as the sterane campestane (24R-methylcholestane). Along with cholestane and stigmastane, this sterane is used as a biomarker for early eukaryotes.

Inocoterone acetate is a steroid-like nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) that was developed for topical administration to treat acne but was never marketed. It is the acetate ester of inocoterone, which is less potent in comparison. Inocoterone acetate is actually not a silent antagonist of the androgen receptor but rather a weak partial agonist, similarly to steroidal antiandrogens like cyproterone acetate.

Protostane is a tetracyclic triterpene, its natural distribution is primarily limited to the genus Alisma. It is so named because it is considered to be the "prototype" of steroids.
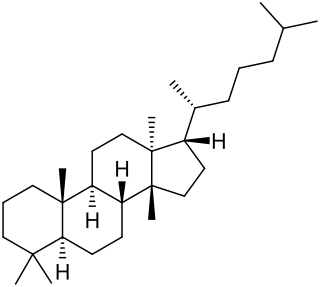
Euphane is a tetracyclic triterpene that is the 13α,14β-stereoisomer of lanostane. Its derivatives are widely distributed in many plants.





















