
The Globigerinina is a suborder of foraminiferans that are found as marine plankton. They produce hyaline calcareous tests, and are known as fossils from the Jurassic period onwards. The group has included more than 100 genera and over 400 species, of which about 30 species are extant. One of the most important genera is Globigerina; vast areas of the ocean floor are covered with Globigerina ooze, dominated by the shells of planktonic forms.

The Fusulinida is an extinct order within the Foraminifera in which the tests are traditionally considered to have been composed of microgranular calcite. Like all forams, they were single-celled organisms. In advanced forms the test wall was differentiated into two or more layers. Loeblich and Tappan, 1988, gives a range from the Lower Silurian to the Upper Permian, with the fusulinid foraminifera going extinct with the Permian–Triassic extinction event. While the latter is true, a more supported projected timespan is from the Mid-Carboniferous period.

The Rotaliida are an order of Foraminifera, characterized by multilocular tests (shells) composed of bilamellar perforate hyaline lamellar calcite that may be optically radial or granular.
The Endothyracea is a superfamily in the foraminiferal order, Fusulinida known from the upper Devonian to the Lower Permian. Probably ancestral to the Fusulinacea.
The Fusulinidae is a family of fusulinacean foraminifera from the upper Carboniferous to the Upper Permian (Guadalupian), tests of which are fusiform to subcylindrical with walls of two to four layers. Are planispirally coiled throughout or with early whorls at a distinct angle to the later plane of coiling. Septa, flat to well fluted; tunnel, single; chomata variable in development.

Globigerinoidea is a superfamily of free-living, calcareous, planktonic foraminiferal protists that have lived in the open ocean since the Eocene. It is part of the suborder Globigerinina.
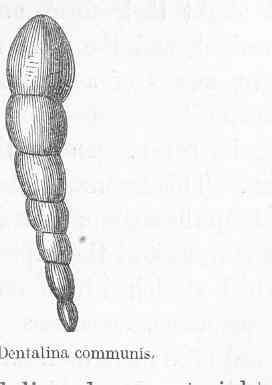
Lagenida is an order of benthic foraminiferal protists in which the tests (shells) are monolamellar, with walls composed of optically and ultra-structurally radiate calcite, with the crystallographic c-axes perpendicular to the surface. Lagenids first appear in the Upper Silurian and continue to the Recent. They are currently divided into two superfamilies, the older Robuloidacea which range from the Upper Silurian to the Lower Cretaceous (Albian) and the younger Nodosariacea, ranging from the Permian to Recent.
Robuloidacea is a superfamily included in the Protista order Lagenida in which the test wall is either not secondarily lamellar or is only slightly so, as in later taxa.

Cibicides is a genus of cosmopolitan benthic foraminifera known from at least as far back as the Paleocene that extends down to the present.
Discorbis is a genus of benthic Foraminifera, that made its first appearance during the Eocene. Its present distribution is cosmopolitan.
Astrononion is a genus of foraminifera in the family Nonionidae, characterized by an evolute planispiral test with radially stellate structures partly covering the sutures on either side. The test is free, bilaterally symmetrical; periphery broadly rounded; chambers distinct, separated by depressed radial sutures, increasing gradually in size, and usually inflated; aperture a low arched opening at the base of the face of the test. The wall is of finely perforate monolamellar granular calcite.
The Cassidulinacea is a superfamily of benthic amoeboid foraminifera in the order Rotaliida that has been extant from the Paleocene down to the present. Tests are composed of secreted, optically radial or granular, perforate calcite with chambers biserially coiled at least in the early part, Apertures are usually an interiomarginal slit, but may become terminal and may have secondary features.
The Schwagerinidae comprise a family of large, generally fusiform, foraminiferans included in the Fusulinacea, a superfamily of fusulinids, locally abundant during the later Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) and most of the Permian.
The Globoroatioidea constitutes a superfamily of Cenozoic plantonic foraminifera. It is part of the suborder Globigerinina. Globoroatioidea have trochospiral tests with rounded to carinate peripheries, the walls of which are of finely lamellar, perforate, of optically radial calcite, with an inner organic lining. The surface of these tests is smooth, lacking spines, but may be covered with pustules or pitted, and may have one or more large pores at the center. There is a single primary aperture that may be bordered by an imperforate lip, as well as possible supplementary apertures.
Sigmoilina is a miliolid genus, referring to the foraminiferal order Miliolida, characterized by an assymmetricall biconvex test formed by strongly overlapping chambers, one-half coil in length, that form a sigmoid (S-shaped) curve in cross section. The strongly overlapping chambers obliterate earlier ones from view resulting in the compressed biloculine appearance, differing from the squat, depressed biloculine form of Pyrgo and Biloculina. The test, as for all Miliolida, is porcelaneous and imperphorate, the terminal aperture, with tooth, the only point of egress and ingress for the animal.

Hauerinidae is a large and diverse family of miliolid forams that includes genera distributed among various subfamilies in the Treatise as well as genera named and described since.
Hemigordiopsidae is a miliolid family included in the Cornuspiracea that has a range extending from the Early Carboniferous (Visean) to the present.
Cornuspiracea comprise a superfamily of miliolid forams in which the test may be free or attached, planispiral or trochospiral, evolute or involute, spreading or discoidal. The proloculus, or initial chamber, is followed by undivided spiral passage or enrolled tubular chamber, later may be irregularly coiled, unicoiled, or show zigzag growth pattern and may be distinctly chambered. The test wall is composed of imperforate porcelaneous calcite, a character of the Miliolida

Rotaliana is a subclass of benthic Foraminifera with multichambered tests of perforate hyaline calcite. Tests may be planospiral, low or high trochospiral, or serial. Interiors may be complex with secondary chambers and interconnecting canal systems. Rotaliana are separate from the planktonic Globigerinana although both have tests of similar composition. The Textulariana, which contains forms that are rather similar, differs in be agglutinated.

Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich was an American micropaleontologist who was a professor of geology at the University of California, Los Angeles, a United States Geological Survey (USGS) biostratigrapher, and a scientific illustrator whose micropaleontology specialty was research on Cretaceous foraminifera.






