Lint is the computer science term for a static code analysis tool used to flag programming errors, bugs, stylistic errors and suspicious constructs. The term originates from a Unix utility that examined C language source code. A program which performs this function is also known as a "linter".

A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
A software bug is a bug in computer software.
In computing, DLL Hell is a term for the complications that arise when one works with dynamic-link libraries (DLLs) used with Microsoft Windows operating systems, particularly legacy 16-bit editions, which all run in a single memory space.
In computer science, program analysis is the process of automatically analyzing the behavior of computer programs regarding a property such as correctness, robustness, safety and liveness. Program analysis focuses on two major areas: program optimization and program correctness. The first focuses on improving the program’s performance while reducing the resource usage while the latter focuses on ensuring that the program does what it is supposed to do.

A race condition or race hazard is the condition of an electronics, software, or other system where the system's substantive behavior is dependent on the sequence or timing of other uncontrollable events, leading to unexpected or inconsistent results. It becomes a bug when one or more of the possible behaviors is undesirable.

PMD is an open source static source code analyzer that reports on issues found within application code. PMD includes built-in rule sets and supports the ability to write custom rules. PMD does not report compilation errors, as it only can process well-formed source files. Rather, PMD is designed to detect inefficient code or bad programming habits, which can reduce the performance and maintainability of the program if they accumulate. It can analyze files written in Java, JavaScript, Apex and Visualforce, PLSQL, Apache Velocity, XML, and XSL.
In software engineering, profiling is a form of dynamic program analysis that measures, for example, the space (memory) or time complexity of a program, the usage of particular instructions, or the frequency and duration of function calls. Most commonly, profiling information serves to aid program optimization, and more specifically, performance engineering.
Application security includes all tasks that introduce a secure software development life cycle to development teams. Its final goal is to improve security practices and, through that, to find, fix and preferably prevent security issues within applications. It encompasses the whole application life cycle from requirements analysis, design, implementation, verification as well as maintenance.
Software assurance (SwA) is a critical process in software development that ensures the reliability, safety, and security of software products. It involves a variety of activities, including requirements analysis, design reviews, code inspections, testing, and formal verification. One crucial component of software assurance is secure coding practices, which follow industry-accepted standards and best practices, such as those outlined by the Software Engineering Institute (SEI) in their CERT Secure Coding Standards (SCS).
Automated code review software checks source code for compliance with a predefined set of rules or best practices. The use of analytical methods to inspect and review source code to detect bugs or security issues has been a standard development practice in both Open Source and commercial software domains. This process can be accomplished both manually and in an automated fashion. With automation, software tools provide assistance with the code review and inspection process. The review program or tool typically displays a list of warnings. A review program can also provide an automated or a programmer-assisted way to correct the issues found. This is a component for mastering easily software. This is contributing to the Software Intelligence practice. This process is usually called "linting" since one of the first tools for static code analysis was called Lint.
Dynamic program analysis is the act of analyzing software that involves executing a program – as opposed to static program analysis, which does not execute it.
Microsoft Phoenix was an SDK available from Microsoft Connect for creating compilers, optimize code, and perform code analysis. Microsoft described it in the past tense on 2008-07-01.
StyleCop is an open-source static code analysis tool from Microsoft that checks C# code for conformance to StyleCop's recommended coding styles and a subset of Microsoft's .NET Framework Design Guidelines. StyleCop analyses the source code, allowing it to enforce a different set of rules from FxCop. The rules are classified into the following categories:
Polyspace is a static code analysis tool for large-scale analysis by abstract interpretation to detect, or prove the absence of, certain run-time errors in source code for the C, C++, and Ada programming languages. The tool also checks source code for adherence to appropriate code standards.
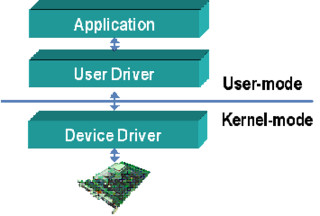
Device drivers are programs which allow software or higher-level computer programs to interact with a hardware device. These software components act as a link between the devices and the operating systems, communicating with each of these systems and executing commands. They provide an abstraction layer for the software above and also mediate the communication between the operating system kernel and the devices below.
Parasoft C/C++test is an integrated set of tools for testing C and C++ source code that software developers use to analyze, test, find defects, and measure the quality and security of their applications. It supports software development practices that are part of development testing, including static code analysis, dynamic code analysis, unit test case generation and execution, code coverage analysis, regression testing, runtime error detection, requirements traceability, and code review. It's a commercial tool that supports operation on Linux, Windows, and Solaris platforms as well as support for on-target embedded testing and cross compilers.

SourceMeter is a source code analyzer tool, which can perform deep static program analysis of the source code of complex programs in C, C++, Java, Python, C#, and RPG (AS/400). FrontEndART has developed SourceMeter based on the Columbus technology researched and developed at the Department of Software Engineering of the University of Szeged.
Visual Expert is a static code analysis tool, extracting design and technical information from software source code by reverse-engineering, used by programmers for software maintenance, modernization or optimization.





