Related Research Articles
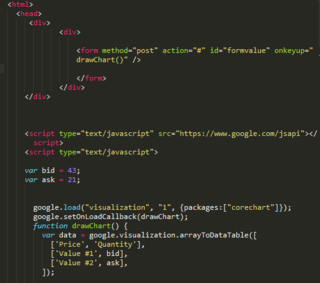
JavaScript, often abbreviated JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Over 97% of websites use JavaScript on the client side for web page behavior, often incorporating third-party libraries. All major web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine to execute the code on users' devices.
VBScript is an Active Scripting language developed by Microsoft that is modeled on Visual Basic. It allows Microsoft Windows system administrators to generate powerful tools for managing computers with error handling, subroutines, and other advanced programming constructs. It can give the user complete control over many aspects of their computing environment.

A debugger or debugging tool is a computer program used to test and debug other programs. The main use of a debugger is to run the target program under controlled conditions that permit the programmer to track its operations in progress and monitor changes in computer resources that may indicate malfunctioning code. Typical debugging facilities include the ability to run or halt the target program at specific points, display the contents of memory, CPU registers or storage devices, and modify memory or register contents in order to enter selected test data that might be a cause of faulty program execution.
AppleScript is a scripting language created by Apple Inc. that facilitates automated control over scriptable Mac applications. First introduced in System 7, it is currently included in all versions of macOS as part of a package of system automation tools. The term "AppleScript" may refer to the language itself, to an individual script written in the language, or, informally, to the macOS Open Scripting Architecture that underlies the language.
JScript is Microsoft's legacy dialect of the ECMAScript standard that is used in Microsoft's Internet Explorer 11 and older, that has multiple security bugs "exploited by nation-state actors", leading Microsoft to add an option to disable it.
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97. The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.
CodeView is a standalone debugger created by David Norris at Microsoft in 1985 as part of its development toolset. It originally shipped with Microsoft C 4.0 and later. It also shipped with Visual Basic for MS-DOS, Microsoft BASIC PDS, and a number of other Microsoft language products. It was one of the first debuggers for MS-DOS to be full-screen oriented, rather than line-oriented.
JScript .NET is a .NET programming language developed by Microsoft.

Microsoft Visual Studio Express is a set of integrated development environments (IDEs) that Microsoft developed and released free of charge. They are function-limited version of the non-free Visual Studio and require mandatory registration. Express editions started with Visual Studio 2005.
In computing, a shell is a computer program which exposes an operating system's services to a human user or other programs. In general, operating system shells use either a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI), depending on a computer's role and particular operation. It is named a shell because it is the outermost layer around the operating system.
As the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000, as well as the successor to Windows Me, Windows XP introduced many new features but it also removed some others.

Process Explorer is a freeware task manager and system monitor for Microsoft Windows created by SysInternals, which has been acquired by Microsoft and re-branded as Windows Sysinternals. It provides the functionality of Windows Task Manager along with a rich set of features for collecting information about processes running on the user's system. It can be used as the first step in debugging software or system problems.
An HTML Application (HTA) is a Microsoft Windows program whose source code consists of HTML, Dynamic HTML, and one or more scripting languages supported by Internet Explorer, such as VBScript or JScript. The HTML is used to generate the user interface, and the scripting language is used for the program logic. An HTA executes without the constraints of the internet browser security model; in fact, it executes as a "fully trusted" application.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
Firebug was a discontinued free and open-source web browser extension for Mozilla Firefox that facilitated the live debugging, editing, and monitoring of any website's CSS, HTML, DOM, XHR, and JavaScript. It is now inbuilt in Firefox.

PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management program from Microsoft, consisting of a command-line shell and the associated scripting language. Initially a Windows component only, known as Windows PowerShell, it was made open-source and cross-platform on 18 August 2016 with the introduction of PowerShell Core. The former is built on the .NET Framework, the latter on .NET Core.

Web development tools allow web developers to test and debug their code. They are different from website builders and integrated development environments (IDEs) in that they do not assist in the direct creation of a webpage, rather they are tools used for testing the user interface of a website or web application.

A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. Operating systems implement a command-line interface in a shell for interactive access to operating system functions or services. Such access was first provided by computer terminals starting in the mid-1960s. This provided an interactive environment not available with punched cards or other input methods.

Visual Studio Code, also commonly referred to as VS Code, is a source-code editor made by Microsoft for Windows, Linux and macOS. Features include support for debugging, syntax highlighting, intelligent code completion, snippets, code refactoring, and embedded Git. Users can change the theme, keyboard shortcuts, preferences, and install extensions that add additional functionality.
References
- ↑ "Discovering Internet Explorer Developer Tools". Microsoft. Retrieved 2009-08-08.
- 1 2 "Introduction to Microsoft Script Debugger for Internet Explorer". Microsoft. Retrieved 2009-09-08.[ dead link ]
- ↑ "Contents of Script Debugger Release Notes". Microsoft. June 23, 2005. Retrieved 2009-09-08.[ dead link ] Alternative web page