BeanShell is a small, free, embeddable Java source interpreter with object scripting language features, written in Java. It runs in the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), dynamically executes standard Java syntax and extends it with common scripting conveniences such as loose types, commands, and method closures, like those in Perl and JavaScript.
JSON is an open standard file format and data interchange format that uses human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of name–value pairs and arrays. It is a commonly used data format with diverse uses in electronic data interchange, including that of web applications with servers.

Douglas Crockford is an American computer programmer who is involved in the development of the JavaScript language. He specified the data format JSON, and has developed various JavaScript related tools such as the static code analyzer JSLint and minifier JSMin. He wrote the book JavaScript: The Good Parts, published in 2008, followed by How JavaScript Works in 2018. He was a senior JavaScript architect at PayPal until 2019, and is also a writer and speaker on JavaScript, JSON, and related web technologies.
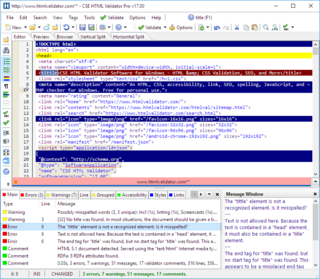
CSS HTML Validator is an HTML editor and CSS editor for Windows that helps web developers create syntactically correct and accessible HTML/HTML5, XHTML, and CSS documents by locating errors, potential problems like browser compatibility issues, and common mistakes. It is also able to check links, check spelling, suggest improvements, alert developers to deprecated, obsolete, or proprietary tags, attributes, and CSS properties, and find issues that can affect search engine optimization.

JSLint is a static code analysis tool used in software development for checking if JavaScript source code complies with coding rules. It is provided primarily as a browser-based web application accessible through the domain jslint.com, but there are also command-line adaptations. It was created in 2002 by Douglas Crockford.
Jenkins is an open source automation server. It helps automate the parts of software development related to building, testing, and deploying, facilitating continuous integration, and continuous delivery. It is a server-based system that runs in servlet containers such as Apache Tomcat. It supports version control tools, including AccuRev, CVS, Subversion, Git, Mercurial, Perforce, ClearCase, and RTC, and can execute Apache Ant, Apache Maven, and sbt based projects as well as arbitrary shell scripts and Windows batch commands.

npm is a package manager for the JavaScript programming language maintained by npm, Inc., a subsidiary of GitHub. npm is the default package manager for the JavaScript runtime environment Node.js and is included as a recommended feature in the Node.js installer.

Opa is a programming language for developing scalable web applications. It is free and open-source software released under a GNU Affero General Public License (AGPLv3), and an MIT License.

Amber Smalltalk, formerly named Jtalk, is an implementation of the programming language Smalltalk-80, that runs on the JavaScript runtime of a web browser. It is designed to enable client-side development using Smalltalk. The programming environment in Amber is named Helios.

Brackets is a source code editor with a primary focus on web development. Created by Adobe Inc., it is free and open-source software licensed under the MIT License, and is currently maintained on GitHub by open-source developers. It is written in JavaScript, HTML and CSS. Brackets is cross-platform, available for macOS, Windows, and most Linux distributions. The main purpose of Brackets is its live HTML, CSS and JavaScript editing functionality.

Gatling is a load- and performance-testing framework based on Scala, Akka and Netty. The first stable release was published on January 13, 2012. In 2015, Gatling's founder, Stéphane Landelle, created a company, dedicated to the development of the open-source project. According to Gatling Corp's official website, Gatling was downloaded more than 20,000,000 times (2024). In June 2016, Gatling officially presented Gatling FrontLine, Gatling's Enterprise Version with additional features.
JetBrains s.r.o. is a Czech software development private limited company which makes tools for software developers and project managers. The company has its headquarters in Prague, and has offices in China, Europe, and the United States.
Grunt is a JavaScript task runner, a tool used to automatically perform frequent tasks such as minification, compilation, unit testing, and linting. It uses a command-line interface to run custom tasks defined in a file. Grunt was created by Ben Alman and is written in Node.js. It is distributed via npm. As of October 2022, there were more than 6,000 plugins available in the Grunt ecosystem.
Metasfresh is an open-source, free ERP software designed and developed for SMEs. Metasfresh is an actively maintained fork of ADempiere and can be used and distributed freely. It does not require a contributor license agreement from partners or contributors. While numerous open-source ERP projects exist, Metasfresh was included in the Top 9 Open Source ERPs to Consider by opensource.com.

DBeaver is a SQL client software application and a database administration tool. For relational databases it uses the JDBC application programming interface (API) to interact with databases via a JDBC driver. For other databases (NoSQL) it uses proprietary database drivers. It provides an editor that supports code completion and syntax highlighting. It provides a plug-in architecture that allows users to modify much of the application's behavior to provide database-specific functionality or features that are database-independent. It is written in Java and based on the Eclipse platform.
This is a list of articles related to the JavaScript programming language.

ESLint is a static code analysis tool for identifying problematic patterns found in JavaScript code. It was created by Nicholas C. Zakas in 2013. Rules in ESLint are configurable, and customized rules can be defined and loaded. ESLint covers both code quality and coding style issues. ESLint supports current standards of ECMAScript, and experimental syntax from drafts for future standards. Code using JSX or TypeScript can also be processed when a plugin or transpiler is used.

Babel is a free and open-source JavaScript transcompiler that is mainly used to convert ECMAScript 2015+ (ES6+) code into backwards-compatible JavaScript code that can be run by older JavaScript engines. It allows web developers to take advantage of the newest features of the language.
Semgrep, Inc. is a cybersecurity company based in San Francisco. The company develops the Semgrep AppSec Platform and actively maintains the open-source static code analysis tool semgrep OSS.










