Function
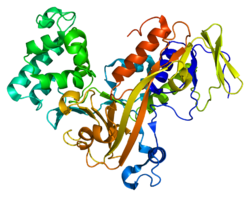
GDP dissociation inhibitors are proteins that regulate the GDP-GTP exchange reaction of members of the rab family, small GTP-binding proteins of the ras superfamily, that are involved in vesicular trafficking of molecules between cellular organelles. GDIs slow the rate of dissociation of GDP from rab proteins and release GDP from membrane-bound rabs. GDI1 is expressed primarily in neural and sensory tissues. Mutations in GDI1 have been linked to X-linked nonspecific mental retardation. [7]
Rab GTPases cycles between the cytosolic compartment, where it is bound to a protein called GDI (GDP Dissociation Inhibitor), and the membrane, where it interacts with a receptor, a nucleotide exchange factor, a GAP (GTPase Activating Protein) and probably other factors that link it to the appropriate SNARE. GDI is non-specific with respect to the rab it binds. However, the exchanger, receptor and GAP, are rab specific.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.