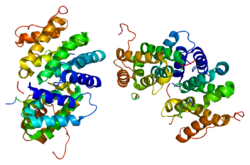
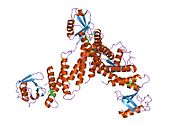
ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) is a member of the ADP ribosylation factor family of GTP-binding proteins. ARF6 has a variety of cellular functions that are frequently involved in trafficking of biological membranes and transmembrane protein cargo. ARF6 has specifically been implicated in endocytosis of plasma membrane proteins and also, to a lesser extent, plasma membrane protein recycling.

ADP-ribosylation factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARF1 gene.

ADP-ribosylation factor-binding protein GGA1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GGA1 gene.

Coatomer subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPB1 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit mu-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1M1 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1G1 gene.
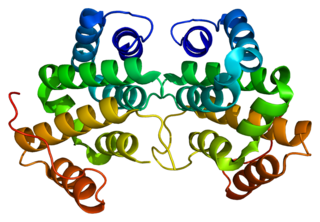
ADP-ribosylation factor-binding protein GGA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GGA2 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1B1 gene.

ADP-ribosylation factor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARF3 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit delta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3D1 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit sigma-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1S1 gene.

Coatomer subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPG2 gene.

ADP-ribosylation factor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARF4 gene.

AP-1 complex subunit gamma-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1G2 gene.

ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARL1 gene.

Synergin gamma also known as AP1 subunit gamma-binding protein 1 (AP1GBP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYNRG gene.

Rab GTPase-binding effector protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RABEP1 gene. It belongs to rabaptin protein family.

Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 3 (LRP-3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRP3 gene.
Clathrin adaptor proteins, also known as adaptins, are vesicular transport adaptor proteins associated with clathrin. These proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes, processed in the endoplasmic reticulum and transported from the Golgi apparatus to the trans-Golgi network, and from there via small carrier vesicles to their final destination compartment. The association between adaptins and clathrin are important for vesicular cargo selection and transporting. Clathrin coats contain both clathrin and adaptor complexes that link clathrin to receptors in coated vesicles. Clathrin-associated protein complexes are believed to interact with the cytoplasmic tails of membrane proteins, leading to their selection and concentration. Therefore, adaptor proteins are responsible for the recruitment of cargo molecules into a growing clathrin-coated pits. The two major types of clathrin adaptor complexes are the heterotetrameric vesicular transport adaptor proteins (AP1-5), and the monomeric GGA adaptors. Adaptins are distantly related to the other main type of vesicular transport proteins, the coatomer subunits, sharing between 16% and 26% of their amino acid sequence.

The C-terminal domain ofBeta2-adaptin is a protein domain is involved in cell trafficking by aiding import and export of substances in and out of the cell.