Related Research Articles
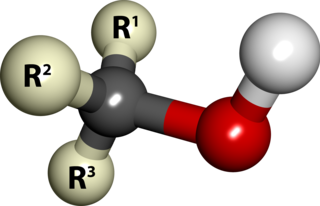
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of hydrocarbons, conferring hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur.
Marquis reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of formaldehyde and concentrated sulfuric acid, which is dripped onto the substance being tested. The United States Department of Justice method for producing the reagent is the addition of 100 mL of concentrated (95–98%) sulfuric acid to 5 mL of 40% formaldehyde. Different compounds produce different color reactions. Methanol may be added to slow down the reaction process to allow better observation of the colour change.
Chromic acid is jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide.

Potassium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KMnO4. It is a purplish-black crystalline salt, that dissolves in water as K+ and MnO−
4, an intensely pink to purple solution.

Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula C4H10O, (CH3CH2)2O or (C2H5)2O, sometimes abbreviated as Et2O. It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling, extremely flammable liquid. It is commonly used as a solvent in laboratories and as a starting fluid for some engines. It was formerly used as a general anesthetic, until non-flammable drugs were developed, such as halothane. It has been used as a recreational drug to cause intoxication.

Molisch's test is a sensitive chemical test, named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch, for the presence of carbohydrates, based on the dehydration of the carbohydrate by sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to produce an aldehyde, which condenses with two molecules of a phenol, resulting in a violet ring.

Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and industrial applications. As with all hexavalent chromium compounds, it is acutely and chronically harmful to health. It is a crystalline ionic solid with a very bright, red-orange color. The salt is popular in laboratories because it is not deliquescent, in contrast to the more industrially relevant salt sodium dichromate.
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH or DNPH) is the organic compound C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2. DNPH is a red to orange solid. It is a substituted hydrazine. The solid is relatively sensitive to shock and friction. For this reason DNPH is usually handled as a wet powder. DNPH is a precursor to the drug Sivifene.

Sulfamic acid, also known as amidosulfonic acid, amidosulfuric acid, aminosulfonic acid, sulphamic acid and sulfamidic acid, is a molecular compound with the formula H3NSO3. This colourless, water-soluble compound finds many applications. Sulfamic acid melts at 205 °C before decomposing at higher temperatures to water, sulfur trioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen.

Reagent testing is one of the processes used to identify substances contained within a pill, usually illicit substances. With the increased prevalence of drugs being available in their pure forms, the terms "drug checking" or "pill testing" may also be used, although these terms usually refer to testing with a wider variety of techniques covered by drug checking.
Ehrlich's reagent or Ehrlich reagent is a reagent containing p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (DMAB) and thus can act as an indicator to presumptively identify indoles and urobilinogen. Several Ehrlich tests use the reagent in a medical test; some are drug tests and others contribute to diagnosis of various diseases or adverse drug reactions. It is named after Nobel Prize winner Paul Ehrlich who used it to distinguish typhoid from simple diarrhoea.
The Liebermann reagent named after Hungarian chemist Leo Liebermann (1852-1926) is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of potassium nitrite and concentrated sulfuric acid. 1 g of potassium nitrite is used for every 10 mL of sulfuric acid. Potassium nitrite may also be substituted by sodium nitrite. It is used to test for cocaine, morphine, PMA and PMMA.
The Mecke reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of selenous acid and concentrated sulfuric acid, which is dripped onto the substance being tested.
The Mandelin reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of ammonium metavanadate and concentrated sulfuric acid. Its primary use is for the detection of ketamine and PMA Unlike the most common reagent test chemicals, it has a deep red colour that changes to yellow if there is no alkaloid, which occurs within about 48 hours of mixing.
Simon's reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It reacts with secondary amines like MDMA and methamphetamine to give a blue solution.
The Froehde reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids, especially opioids, as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of molybdic acid or a molybdate salt dissolved in hot, concentrated sulfuric acid, which is then dripped onto the substance being tested.
The Dille–Koppanyi reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify barbiturates. It is composed of a mixture of two solutions. Part A is 0.1 g of cobalt(II) acetate dihydrate dissolved in 100 ml of methanol mixed with 0.2 ml of glacial acetic acid. Part B made up of is 5% isopropylamine (v/v) in methanol. Two drops of A are dropped onto the substance followed by one drop of B and any change in colour is observed.
Drug precursors, also referred to as precursor chemicals or simply precursors, are substances used to manufacture illicit drugs. Most precursors also have legitimate commercial uses and are legally used in a wide variety of industrial processes and consumer products, such as medicines, flavourings, and fragrances.
The Zimmermann reagent is used as a simple spot-test used in chromatography to presumptively identify alkaloids, especially benzodiazepines, as well as other compounds. It is therefore used in drugs testing.

The Chen-Kao reaction is a chemical method for determining the presence of pseudoephedrine, ephedrine, and similar phenylalkylamines. The reaction is used in spot tests and is also known as Chen-Kao test. The test is often used to distinguish ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, norephedrine, cathinone and methcathinone from amphetamine and methamphetamine, which do not react with Chen’s test reagent.
References
- 1 2 "Colour Tests for Precursor Chemicals of Amphetamine-Type Substances" (PDF). UNODC. December 2007. p. 38. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ↑ Rapid Testing Methods of Drugs of Abuse. Manual for use by national law enforcement and narcotics laboratory personnel (ST/NAR/13/REV.1), United Nations, New York, 1994.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Toole, Kaitlyn E (2012). "Color Tests for the Preliminary Identification of Methcathinone and Analogues of Methcathinone" (PDF). Microgram. 9 (1). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-05-13. Retrieved 2015-12-11.