Related Research Articles

Nucleotides are organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver.
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HNO3. It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% HNO3, it is referred to as fuming nitric acid. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%.
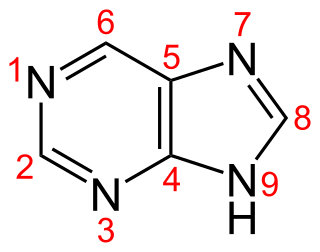
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature.

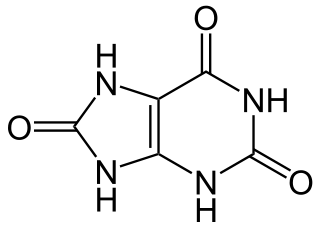
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones.

Adenine is a purine nucleobase. It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acids of DNA, the other three being guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Adenine derivatives have various roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and Coenzyme A. It also has functions in protein synthesis and as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. The shape of adenine is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.
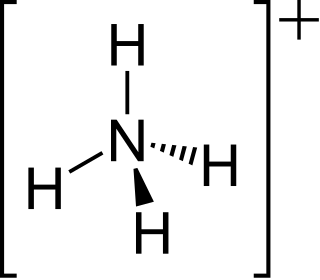
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NH+4 or [NH4]+. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia. Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged (protonated) substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations, where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic or other groups.
Hyperuricaemia or hyperuricemia is an abnormally high level of uric acid in the blood. In the pH conditions of body fluid, uric acid exists largely as urate, the ion form. Serum uric acid concentrations greater than 6 mg/dL for females, 7 mg/dL for men, and 5.5 mg/dL for youth are defined as hyperuricemia. The amount of urate in the body depends on the balance between the amount of purines eaten in food, the amount of urate synthesised within the body, and the amount of urate that is excreted in urine or through the gastrointestinal tract. Hyperuricemia may be the result of increased production of uric acid, decreased excretion of uric acid, or both increased production and reduced excretion.
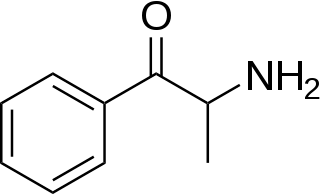
Cathinone is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis (khat) and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine, methcathinone and other amphetamines. It is probably the main contributor to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis, also known as khat. Cathinone differs from many other amphetamines in that it has a ketone functional group. Other phenethylamines that share this structure include the stimulants methcathinone, MDPV, mephedrone and the antidepressant bupropion.

Hermann Emil Louis Fischer was a German chemist and 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fischer projection, a symbolic way of drawing asymmetric carbon atoms. He also hypothesized lock and key mechanism of enzyme action. He never used his first given name, and was known throughout his life simply as Emil Fischer.

Allantoin is a chemical compound with formula C4H6N4O3. It is also called 5-ureidohydantoin or glyoxyldiureide. It is a diureide of glyoxylic acid. Allantoin is a major metabolic intermediate in most organisms including animals, plants and bacteria. It is produced from uric acid, which itself is a degradation product of nucleic acids, by action of urate oxidase (uricase). The occurs as a natural mineral compound (IMA symbol Aan).

Lesch–Nyhan syndrome (LNS) is a rare inherited disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). This deficiency occurs due to mutations in the HPRT1 gene located on the X chromosome. LNS affects about 1 in 380,000 live births. The disorder was first recognized and clinically characterized by American medical student Michael Lesch and his mentor, pediatrician William Nyhan, at Johns Hopkins.
Classical qualitative inorganic analysis is a method of analytical chemistry which seeks to find the elemental composition of inorganic compounds. It is mainly focused on detecting ions in an aqueous solution, therefore materials in other forms may need to be brought to this state before using standard methods. The solution is then treated with various reagents to test for reactions characteristic of certain ions, which may cause color change, precipitation and other visible changes.

Alloxan, sometimes referred to as alloxan hydrate, is an organic compound with the formula OC(N(H)CO)2C(OH)2. It is classified as a derivative of pyrimidine. The anhydrous derivative OC(N(H)CO)2CO is also known, as well as a dimeric derivative. These are some of the earliest known organic compounds. They exhibit a variety of biological activities.

Bladder stones or uroliths are a common occurrence in animals, especially in domestic animals such as dogs and cats. Occurrence in other species, including tortoises, has been reported as well. The stones form in the urinary bladder in varying size and numbers secondary to infection, dietary influences, and genetics. Stones can form in any part of the urinary tract in dogs and cats, but unlike in humans, stones of the kidney are less common and do not often cause significant disease, although they can contribute to pyelonephritis and chronic kidney disease. Types of stones include struvite, calcium oxalate, urate, cystine, calcium phosphate, and silicate. Struvite and calcium oxalate stones are by far the most common. Bladder stones are not the same as bladder crystals but if the crystals coalesce unchecked in the bladder they can become stones.
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.
Free base is a descriptor for the neutral form of an amine commonly used in reference to illicit drugs. The amine is often an alkaloid, such as nicotine, cocaine, morphine, and ephedrine, or derivatives thereof. Freebasing is a more efficient method of self-administering alkaloids via the smoking route.

Alstonia constricta, commonly known as quinine bush or bitterbark, is an endemic Australian endemic shrub or small tree of the family Apocynaceae.
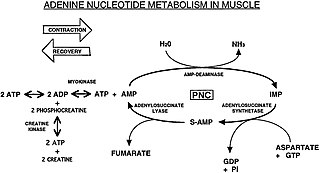
The Purine Nucleotide Cycle is a metabolic pathway in protein metabolism requiring the amino acids aspartate and glutamate. The cycle is used to regulate the levels of adenine nucleotides, in which ammonia and fumarate are generated. AMP converts into IMP and the byproduct ammonia. IMP converts to S-AMP (adenylosuccinate), which then converts to AMP and the byproduct fumarate. The fumarate goes on to produce ATP (energy) via oxidative phosphorylation as it enters the Krebs cycle and then the electron transport chain. Lowenstein first described this pathway and outlined its importance in processes including amino acid catabolism and regulation of flux through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.

Dragendorff's reagent is a color reagent to detect alkaloids in a test sample or as a stain for chromatography plates. Alkaloids, if present in the solution of sample, will react with Dragendorff's reagent and produce an orange or orange-red precipitate. This reagent was invented by the German pharmacologist, Johann Georg Dragendorff (1836–1898) at the University of Dorpat.
Alexander Haig was a Scottish physician, dietitian and vegetarianism activist. He was best known for pioneering the uric-acid free diet.
References
- ↑ Agarwal O.P. Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry (26th ed.). Meerut, India: GOEL Publishing House. p. 53.
- ↑ Nayeem AA, Khatun A, Rahman MS, Rahman M (2011). "Evaluation of phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Mikania cordata (Asteraceae) leaves". Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy. 3 (8): 118–123.
- ↑ Sharma DC; Sharma. Riyat. Practical Medical Biochemistry. BI Publications Pvt Ltd. p. 36.