
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

A ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled bump associated with a joint or tendon sheath. It most often occurs at the back of the wrist, followed by the front of the wrist.

A Bartholin's cyst occurs when a Bartholin's gland within the labia becomes blocked. Small cysts may result in minimal or no symptoms. Larger cysts may result in swelling on one side of the vaginal opening, as well as pain during sex or walking. If the cyst becomes infected, an abscess can occur, which is typically red and very painful. If there are no symptoms, no treatment is needed. Bartholin's cysts affect about 2% of women at some point in their life. They most commonly occur during childbearing years.
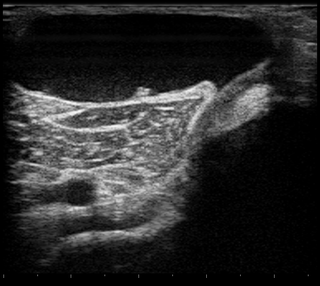
A Baker's cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a type of fluid collection behind the knee. Often there are no symptoms. If symptoms do occur these may include swelling and pain behind the knee, or knee stiffness. If the cyst breaks open, pain may significantly increase with swelling of the calf. Rarely complications such as deep vein thrombosis, peripheral neuropathy, ischemia, or compartment syndrome may occur.

Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters the organ's normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pain or malabsorption. It is a disease process characterized by irreversible damage to the pancreas as distinct from reversible changes in acute pancreatitis. Tobacco smoke and alcohol misuse are two of the most frequently implicated causes, and the two risk factors are thought to have a synergistic effect with regards to the development of chronic pancreatitis. Chronic pancreatitis is a risk factor for the development of pancreatic cancer.

Spermatocele is a fluid-filled cyst that develops in the epididymis. The fluid is usually a clear or milky white color and may contain sperm. Spermatoceles are typically filled with spermatozoa and they can vary in size from several millimeters to many centimeters. Small spermatoceles are relatively common, occurring in an estimated 30 percent of males. They are generally not painful. However, some people may experience discomfort such as a dull pain in the scrotum from larger spermatoceles. They are not cancerous, nor do they cause an increased risk of testicular cancer. Additionally, unlike varicoceles, they do not reduce fertility.

A pancreatic pseudocyst is a circumscribed collection of fluid rich in pancreatic enzymes, blood, and non-necrotic tissue, typically located in the lesser sac of the abdomen. Pancreatic pseudocysts are usually complications of pancreatitis, although in children they frequently occur following abdominal trauma. Pancreatic pseudocysts account for approximately 75% of all pancreatic masses.

Lymphangiomas are malformations of the lymphatic system characterized by lesions that are thin-walled cysts; these cysts can be macroscopic, as in a cystic hygroma, or microscopic. The lymphatic system is the network of vessels responsible for returning to the venous system excess fluid from tissues as well as the lymph nodes that filter this fluid for signs of pathogens. These malformations can occur at any age and may involve any part of the body, but 90% occur in children less than 2 years of age and involve the head and neck. These malformations are either congenital or acquired. Congenital lymphangiomas are often associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as Turner syndrome, although they can also exist in isolation. Lymphangiomas are commonly diagnosed before birth using fetal ultrasonography. Acquired lymphangiomas may result from trauma, inflammation, or lymphatic obstruction.

Pericoronitis is inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth, including the gingiva (gums) and the dental follicle. The soft tissue covering a partially erupted tooth is known as an operculum, an area which can be difficult to access with normal oral hygiene methods. The hyponym operculitis technically refers to inflammation of the operculum alone.

Pelvic pain is pain in the area of the pelvis. Acute pain is more common than chronic pain. If the pain lasts for more than six months, it is deemed to be chronic pelvic pain. It can affect both the male and female pelvis.
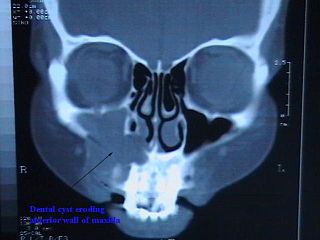
Commonly known as a dental cyst, the periapical cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. It may develop rapidly from a periapical granuloma, as a consequence of untreated chronic periapical periodontitis.
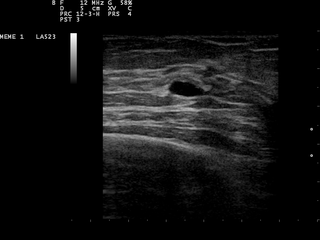
A breast cyst is a cyst, a fluid-filled sac, within the breast. One breast can have one or more cysts. They are often described as round or oval lumps with distinct edges. In texture, a breast cyst usually feels like a soft grape or a water-filled balloon, but sometimes a breast cyst feels firm.

Endometrioma is the presence of tissue similar to, but distinct from, the endometrium in and sometimes on the ovary. It is the most common form of endometriosis. Endometrioma is found in 17–44% patients with endometriosis.

A breast mass, also known as a breast lump, is a localized swelling that feels different from the surrounding tissue. Breast pain, nipple discharge, or skin changes may be present. Concerning findings include masses that are hard, do not move easily, are of an irregular shape, or are firmly attached to surrounding tissue.

Tarlov cysts, are type II innervated meningeal cysts, cerebrospinal-fluid-filled (CSF) sacs most frequently located in the spinal canal of the sacral region of the spinal cord (S1–S5) and much less often in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine. They can be distinguished from other meningeal cysts by their nerve-fiber-filled walls. Tarlov cysts are defined as cysts formed within the nerve-root sheath at the dorsal root ganglion. The etiology of these cysts is not well understood; some current theories explaining this phenomenon have not yet been tested or challenged but include increased pressure in CSF, filling of congenital cysts with one-way valves, and/or inflammation in response to trauma and disease. They are named for American neurosurgeon Isadore Tarlov, who described them in 1938.
The hand is a very complex organ with multiple joints, different types of ligament, tendons and nerves. Hand disease injuries are common in society and can result from excessive use, degenerative disorders or trauma.
Theca lutein cyst is a type of bilateral functional ovarian cyst filled with clear, straw-colored fluid. These cysts result from exaggerated physiological stimulation due to elevated levels of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) or hypersensitivity to beta-hCG. On ultrasound and MRI, theca lutein cysts appear in multiples on ovaries that are enlarged.

Endosalpingiosis is a condition in which fallopian tube-like epithelium is found outside the fallopian tube. It is unknown what causes this condition. It is generally accepted that the condition develops from transformation of coelomic tissue. It is often an incidental finding and is not usually associated with any pathology.

Pelvic congestion syndrome, also known as pelvic vein incompetence, is a long-term condition believed to be due to enlarged veins in the lower abdomen. The condition may cause chronic pain, such as a constant dull ache, which can be worsened by standing or sex. Pain in the legs or lower back may also occur.
Periapical granuloma, also sometimes referred to as a radicular granuloma or apical granuloma, is an inflammation at the tip of a dead (nonvital) tooth. It is a lesion or mass that typically starts out as an epithelial lined cyst, and undergoes an inward curvature that results in inflammation of granulation tissue at the root tips of a dead tooth. This is usually due to dental caries or a bacterial infection of the dental pulp. Periapical granuloma is an infrequent disorder that has an occurrence rate between 9.3 to 87.1 percent. Periapical granuloma is not a true granuloma due to the fact that it does not contain granulomatous inflammation; however, periapical granuloma is a common term used.

















