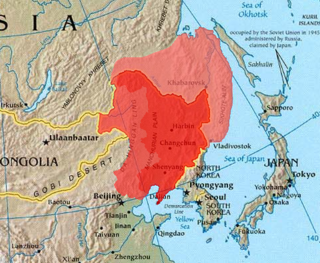
Manchuria is a term that refers to a region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China, and historically parts of the modern-day Russian Far East, often referred to as Outer Manchuria. Its definition may refer to varying geographical extents as follows: in the narrow sense, the area constituted by three Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning but broadly also including the eastern Inner Mongolian prefectures of Hulunbuir, Hinggan, Tongliao, and Chifeng, collectively known as Northeast China; in a broader sense, the area of historical Manchuria includes the aforementioned regions plus the Amur river basin, parts of which were ceded to the Russian Empire by the Manchu-led Qing dynasty during the Amur Annexation of 1858–1860. The parts of Manchuria ceded to Russia are collectively known as Outer Manchuria or Russian Manchuria, which include present-day Amur Oblast, Primorsky Krai, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, the southern part of Khabarovsk Krai, and the eastern edge of Zabaykalsky Krai.

Amur Oblast is a federal subject of Russia, located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya rivers in the Russian Far East. The oblast borders Heilongjiang province of the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the south.

Manchuria is a region in East Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria can refer either to a region falling entirely within present-day China, or to a larger region today divided between Northeast China and the Russian Far East. To differentiate between the two parts following the latter definition, the Russian part is also known as Outer Manchuria, while the Chinese part is known as Northeast China.

The Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China after the defeat of Russia by Qing China at the Siege of Albazin in 1686. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River and Lake Baikal. This border along the Argun River and Stanovoy Range lasted until the Amur Annexation via the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Convention of Peking in 1860. It opened markets for Russian goods in China, and gave Russians access to Chinese supplies and luxuries.

The Argun or Ergune is a 1,620-kilometre (1,010 mi) long river that forms part of the eastern China–Russia border, together with the Amur. Its upper reaches are known as the Hailar River (海拉尔河) in China. The Argun marks the border between Russia and China for about 944 kilometres (587 mi), until it meets the Amur.

Primorskaya Oblast was an administrative division of the Russian Empire and the early Russian SFSR, created on October 31, 1856 by the Governing Senate. The name of the region literally means "Maritime" or "Coastal." The region was established upon a Russian conquest of Daur people that used to live along Amur River. Before the Russian conquest of Russian Manchuria, the territory belonged to the Chinese region of Manchuria.

Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia, or Dauria is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" (trans-) Lake Baikal in Far Eastern Russia.

Prior to the 17th century, China and Russia were on opposite ends of Siberia, which was populated by independent nomads. By about 1640 Russian settlers had traversed most of Siberia and founded settlements in the Amur River basin. From 1652 to 1689, China's armies drove the Russian settlers out, but after 1689, China and Russia made peace and established trade agreements.

Tungusic peoples are an ethnolinguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages. They are native to Siberia, China, and Mongolia.

Albazino is a village (selo) in Skovorodinsky District of Amur Oblast, Russia, noted as the site of Albazin (Албазин), the first Russian settlement on the Amur River.

The Russian conquest of Siberia took place during 1581–1778, when the Khanate of Sibir became a loose political structure of vassalages that were being undermined by the activities of Russian explorers. Although outnumbered, the Russians pressured the various family-based tribes into changing their loyalties and establishing distant forts from which they conducted raids. It is traditionally considered that Yermak Timofeyevich's campaign against the Siberian Khanate began in 1581. The annexation of Siberia and the Far East to Russia was resisted by local residents and took place against the backdrop of fierce battles between the Indigenous peoples of Siberia and the Russian Cossacks, who often committed atrocities against Indigenous Siberians.

The Sino-Russian border conflicts (1652–1689) were a series of intermittent skirmishes between the Qing dynasty of China, with assistance from the Joseon dynasty of Korea, and the Tsardom of Russia by the Cossacks in which the latter tried and failed to gain the land north of the Amur River with disputes over the Amur region. The hostilities culminated in the Qing siege of the Cossack fort of Albazin in 1686 and resulted in the Treaty of Nerchinsk in 1689 which gave the land to China.
Yishiha was a Jurchen eunuch of the Ming dynasty of China. He served the Ming emperors who commissioned several expeditions down the Songhua and Amur Rivers during the period of Ming rule of Manchuria, and is credited with the construction of the only two Ming dynasty Buddhist temples ever built on the territory of present-day Russia.

The House of Gantimurov is a Russian princely family of Evenks.
Dular Bombogor was an Evenk chief, leader of the Evenk federation. His power base laid on the basin of the Amur river.

Jaxa was a 17th-century microstate in North Asia with its capital in Albazino existing between 1665 and 1674. It was located on the border of the Tsardom of Russia and Qing China, by the Amur river. Its population was made up of Polish and Ukrainian refugees from the Tsardom of Russia, and the indigenous Evenks and Daurs. It was established from the territory of the Tsardom of Russia in 1665 by Nikifor Chernigovsky and his men, who fled Russia, and existed until 1674 when it was incorporated back to that country.
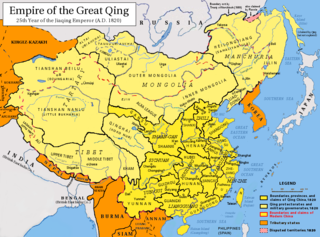
The Qing dynasty in Inner Asia was the expansion of the Qing dynasty's realm in Inner Asia in the 17th and the 18th century AD, including both Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia, both Manchuria and Outer Manchuria, Tibet, Qinghai and Xinjiang.
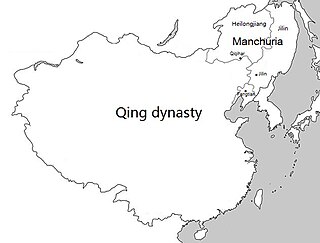
Manchuria under Qing rule was the rule of the Qing dynasty of China over the greater region of Manchuria, including today's Northeast China and Outer Manchuria, although Outer Manchuria was lost to the Russian Empire after the Amur Annexation. The Qing dynasty itself was established by the Manchus, a Tungusic people from Manchuria, who later replaced the Ming dynasty as the ruling dynasty of China. Thus, the region is often seen to have had a special status during the Qing and was not governed as regular provinces until the late Qing dynasty, although the name "Manchuria" itself is an exonym of Japanese origin and was not used by the Qing dynasty in Chinese or Manchu.

The siege of Albazin was a military conflict between the Tsardom of Russia and Qing China from 1685 to 1686. It ultimately ended in the surrender of Albazin to Qing China and Russian abandonment of the Amur River area in return for trading privileges in Beijing.
Events from the year 1667 in China.

















