Related Research Articles
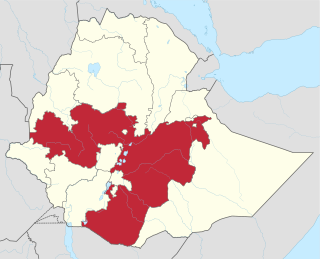
Oromia is a regional state in Ethiopia and the homeland of the Oromo people. Under Article 49 of Ethiopian Constitution, the capital of Oromia is Addis Ababa, also called Finfinne. The provision of the article maintains special interest of Oromia by utilizing social services and natural resources of Addis Ababa.

RasMakonnen Wolde Mikael Wolde Melekot, or simply Ras Makonnen, also known as Abba Qagnew, was an Ethiopian royal from Shewa, a military leader, the governor of Harar, and the father of future Emperor Haile Selassie. Described by Nikolai Gumilev as “one of the greatest leaders of Abyssinia”, he served in the First Italo-Ethiopian War, playing a key role at the Battle of Adwa.

Shewa, formerly romanized as Shua, Shoa, Showa, Shuwa, is a historical region of Ethiopia which was formerly an autonomous kingdom within the Ethiopian Empire. The modern Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa is located at its center.

Sarsa Dengel, also known as Sarsa the Great, was Emperor of Ethiopia, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. His throne name was throne name Malak Sagad I .

The Kingdom of Kaffa was a kingdom located in what is now Ethiopia from 1390 to 1897, with its first capital at Bonga. The Gojeb River formed its northern border, beyond which lay the Gibe kingdoms; to the east the territory of the Konta and Kullo peoples lay between Kaffa and the Omo River; to the south numerous subgroups of the Gimira people, and to the west lay the Majangir people. The native language, also known as Kaffa, is one of the Omotic group of languages.

The Sultanate of Ifat, known as Wafāt or Awfāt in Arabic texts, or the Kingdom of Zeila was a medieval Sunni Muslim state in the eastern regions of the Horn of Africa between the late 13th century and early 15th century. It was formed in present-day Ethiopia around eastern Shewa in Ifat. Led by the Walashma dynasty, the polity stretched from Zequalla to the port city of Zeila. The kingdom ruled over parts of what are now Ethiopia, Djibouti, Somaliland, Somalia.

The Zemene Mesafint was a period in Ethiopian history between the mid-18th and mid-19th centuries when the country was ruled by a class of Oromo elite noblemen who replaced Habesha nobility in their courts, making the emperor merely a figurehead. For the most part, the regional lords were tightly related by marriage and constituted a stable ruling elite that prevailed until the mid-20th century. In short, during the Zemene Mesafint, the emperors from the Solomonic dynasty were reduced to little more than figureheads confined to the capital city of Gondar.

The Warjih, also known as Wargar are an ethnic group inhabiting Ethiopia.
Were Ilu is a town in north-central Ethiopia. Located in the Debub Wollo Zone of the Amhara Region, this town has a latitude and longitude of 10°36′N39°26′E. From the 1870s, Were Ilu had a Thursday market.

Ethiopia is one of the oldest countries in Africa; the emergence of Ethiopian civilization dates back thousands of years. Abyssinia or rather "Ze Etiyopia" was ruled by the Semitic Abyssinians (Habesha) composed mainly of the Amhara, Tigrayans and the Cushitic Agaw. In the Eastern escarpment of the Ethiopian highlands and more so the lowlands were the home of the Harari/Harla that founded Sultanates such as Ifat and Adal and the Afars. In the central and south were found the ancient Sidama and Semitic Gurage, among others.
The Argobba are an ethnic group inhabiting Ethiopia. A Muslim community, they are spread out through isolated village networks and towns in the north-eastern and eastern parts of the country. Group members have typically been astute traders and merchants, and have adjusted to the economic trends in their area. These factors have led to a decline in usage of the Argobba language. Argobba are considered endangered today due to exogamy and destitution as well as ethnic cleansing by the Abyssinian state over the centuries.

FitawrariHabte Giyorgis Dinagde also known by his horse name Abba Mechal was an Ethiopian military commander and government official who, among several other posts, served as President of the Council of Ministers and as Minister of War during the reigns of Menelik II, Zewditu and Haile Selassie. He was also Shum or Governor of Borena, Ibat, and Mecha.

The Oromia Special Zone Surrounding Finfinne is a zone in Oromia Region of Ethiopia that surrounds Addis Ababa. It was created in 2008 from parts of North Shewa Zone, East Shewa Zone, Southwest Shewa zone and West Shewa Zones. The zone was created to support the cooperation and development of the surrounding areas of Addis Ababa, and to control the urban sprawl of the city on the lands of Oromia. The administrative center of this zone is in Addis Ababa (Finfinne). The districts and town in this zone include Akaki, Bereh, Burayu, Dubra, Holeta Town, Koye Feche, Mulo, Sebeta Hawas, Sebeta Town, Sendafa Town, Sululta, Walmara, Laga Xafo Laga Dadhi, Galaan, Sebeta Hawas (Town) and Dukem.

The Oromo expansions or the Oromo invasions, were a series of expansions in the 16th and 17th centuries by the Oromo. Prior to their great expansion in the 16th century, the Oromo inhabited only the area of what is now modern-day southern Ethiopia and northern Kenya. Over the centuries due to many factors, mostly the wars between the Adal Sultanate and the Ethiopian Empire would further encourage the numerous Oromo tribes to expand towards central and eastern modern Ethiopia.
The Sultanate of Arababni was an Oromo Muslim sultanate located in what is now the Arsi Zone of Ethiopia. Founded around the 12th - 16th century, it was the smallest of the Muslim kingdoms described by the Muslim geographers al-Umari and al-Makrizi.
Chercher was a province in Hararghe now part of Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Also known as Ittuu and West Hararghe, Chercher is the name given mainly to the eastern escarpment highland areas of Oromia state's West Hararaghe Zone, where the chains of Checher or higher mountains rise and extend inland from the Great Rift Valley in its northwest. The capital of the former Chercher province was Chiro.

The Arbegnoch were Ethiopian anti-fascist World War II resistance fighters in Italian East Africa from 1936 until 1941 who fought against Fascist Italy's occupation of the Ethiopian Empire.

Fatagar was a historical province that separated Muslim and Christian dominions in the medieval Horn of Africa. In the eleventh century it was part of the Muslim states, then was invaded by the Christian kingdom led by Emperor Amda Seyon I, after which it would serve as central district in, and home of multiple rulers of, the Ethiopian Empire in the 15th century.
A neftenya was the name given to Emperor Menelik II's warriors, who were primarily of Shewan Amhara origin, that collected customs and taxes for the Imperial Ethiopian government. In its literal meaning, neftenya, referred to riflemen in the Imperial Ethiopian Army who were known to have settled in Ethiopia's peripheral regions, including parts of present-day Oromia Region, the SNNPR Region, Gambela Region and the Benishangul-Gumuz Region from the late 19th century onwards. The origin of this term lies from the fact that these soldiers, i.e. "neftenya", were granted land on these newly conquered territories, including the services of the indigenous people on these lands, as rewards for their services.

The relations between Oromia and Addis Ababa has been great controversy as the subject sparked historical revisionism in the linkage of history of Addis Ababa. The area in the present day Addis Ababa called Finfinne where various Oromo pastoralists inhabited the region, and the emergence of Abyssinian expansionism under Emperor Menelik II which renamed the area as Addis Ababa in 1886. Throughout the 20th century, Addis Ababa was governed as the capital city of the Ethiopia under urban influence.
References
- ↑ Braukamper, Ulrich. Islamic History and Culture in Southern Ethiopia. LitVerlag. pp. 47–48.
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Aethiopica: D-Ha pg. 686