
Fort Jesus is a fort located on Mombasa Island. Designed by Italian Giovanni Battista Cairati, it was built between 1593 and 1596 by order of King Felipe II of Castille, who also reigned as King Filipe I of Portugal and the Algarves, to guard the Old Port of Mombasa. Fort Jesus was the only fort maintained by the Portuguese on the Swahili coast, and is recognised as a testament to the first successful attempt by a Western power to establish influence over the Indian Ocean trade.

Cidade Velha is a city in the southern part of the island of Santiago, Cape Verde. Founded in 1462, it is the oldest settlement in Cape Verde and its former capital. Once called Ribeira Grande, its name was changed to Cidade Velha in the late 18th century. It is the seat of the Ribeira Grande de Santiago municipality.

Elvas is a Portuguese municipality, former episcopal city and frontier fortress of easternmost central Portugal, located in the district of Portalegre in Alentejo. It is situated about 200 kilometres (120 mi) east of Lisbon, and about 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) west of the Spanish fortress of Badajoz, by the Madrid-Badajoz-Lisbon railway. The municipality population as of 2011 was 23,078, in an area of 631.29 square kilometres (243.74 sq mi). The city itself had a population of 16,640 as of 2011.

The Island of Mozambique lies off northern Mozambique, between the Mozambique Channel and Mossuril Bay, and is part of Nampula Province. Prior to 1898, it was the capital of colonial Portuguese East Africa. With its rich history and sandy beaches, the Island of Mozambique is a UNESCO World Heritage site and one of Mozambique's fastest growing tourist destinations. It has a permanent population of approximately 14,000 people and is served by nearby Lumbo Airport on the Nampula mainland. The name of the country, Mozambique, is derived from the name of this island.

Blaye is a commune and subprefecture in the Gironde department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France. For centuries, Blaye was a particularly convenient crossing point for those who came from the north and went to Bordeaux or further south, to Spain and Portugal. Fortified since antiquity, this eminently strategic site located on the bank of a large river, was not modernized until the end of the 17th century, thanks to Vauban. It is indeed in 1685 that the Commissaire general des fortifications of Louis XIV will propose the construction of a real lock on the Gironde in order to "take control of the river" and to keep Bordeaux in respect in case of a revolt. It is then that the citadel of Blaye will be built, which constitutes the major element of the estuary control system. Dominating the urban landscape, this imposing building has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2008, as part of the network of major sites in Vauban.

Campo Maior is a municipality in the Portalegre District, Alentejo Region, Portugal. The population in 2011 was 8,456, in an area of 247.20 square kilometres (95.44 sq mi). It is bordered by Spain on the North and East, by Elvas Municipality on the Southeast, and by Arronches Municipality on the West.
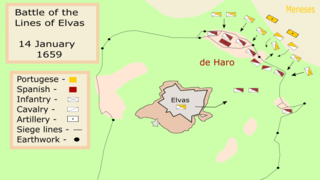
The Battle of the Lines of Elvas, was fought on 14 January 1659, in Elvas, between Portugal and Spain during the Portuguese Restoration War. It ended in a decisive Portuguese victory.

Ojuelos de Jalisco is a colonial town and municipality in the state of Jalisco, Mexico. The town's 1990 population was 7,265, although by the year 2010 it had increased to 11,881.
Castles in Portugal were crucial components of the military throughout its history. The Portuguese learned the art of building fortifications from the Romans and the Moors. The Romans, who ruled and colonized the territory of current-day Portugal for more than four centuries, built forts with high walls and strong towers to defend their populations. The Moors, who invaded the Iberian Peninsula in the year 711 A.D., brought new stonework and heavily fortified gates to the peninsula.

The Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as Vallum Antonini, was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Forth and the Firth of Clyde. Representing the northernmost frontier barrier of the Roman Empire, it spanned approximately 63 kilometres and was about 3 metres high and 5 metres wide. Lidar scans have been carried out to establish the length of the wall and the Roman distance units used. Security was bolstered by a deep ditch on the northern side. It is thought that there was a wooden palisade on top of the turf. The barrier was the second of two "great walls" created by the Romans in Great Britain. Its ruins are less evident than those of the better-known Hadrian's Wall to the south, primarily because the turf and wood wall has largely weathered away, unlike its stone-built southern predecessor.

The fortifications of Kotor are an integrated historical fortification system that protected the medieval town of Kotor containing ramparts, towers, citadels, gates, bastions, forts, cisterns, a castle, and ancillary buildings and structures. They incorporate military architecture mainly of Venice, but also a few of Illyria, Byzantium, and Austria. Together with the old town and its natural surroundings the fortifications were inscribed in the list of World Heritage Sites in 1979 labelled Natural and Culturo-Historical Region of Kotor and represent the only such site of cultural significance in Montenegro.

Galle Fort, in the Bay of Galle on the southwest coast of Sri Lanka, was built first in 1588 by the Portuguese, then extensively fortified by the Dutch during the 17th century from 1649 onwards. It is a historical, archaeological and architectural heritage monument, which even after more than 432 years maintains a polished appearance, due to extensive reconstruction work done by Archaeological Department of Sri Lanka.

The Castle of Alegrete, is a Portuguese medieval castle in the civil parish of Alegrete, in the municipality of Portalegre, in the district of the same name.

Forte Real de São Filipe is a 16th century fortress in the city of Cidade Velha in the south of the island of Santiago, Cape Verde. It is located on a plateau above the town centre, 120 meters above sea level. The historic centre of Cidade Velha is an UNESCO World Heritage site since June 2009. The fort was part of a system of defence for the city, which also included six smaller forts on the coast and a wall along the port.

The Nossa Senhora da Graça Fort, officially Conde de Lippe Fort and known historically as La Lippe, is a fort in the village of Alcáçova, about 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) north of the town of Elvas in the Portalegre District of Portugal.

Forte de São Lourenço is a fort located in Itaparica, Bahia in Brazil. It sits on a strategic point at the north of Itaparica Island on a site used for whaling in the early 17th century. The Dutch constructed a small earthwork fortification on the site during the Dutch occupation of Brazil (1630–1654); it was reconstructed by the Portuguese in its present form in the early 18th century. The fort was used by Brazilian forces during the Brazilian struggle for independence in 1823; the Brazilian Navy has owned the fort since the same year. The Forte de São Lourenço was listed as a federal historic structure in 1938.

Venetian Works of Defence between the 16th and 17th centuries: Stato da Terra – Western Stato da Mar is a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising six bastion forts built by the Republic of Venice on its mainland domains and its Domains of the Sea.


















