Related Research Articles

South Ossetia, officially the Republic of South Ossetia or the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated population of just over 56,500 people (2022), who live in an area of 3,900 square kilometres (1,500 sq mi), with 33,000 living in the capital city, Tskhinvali.
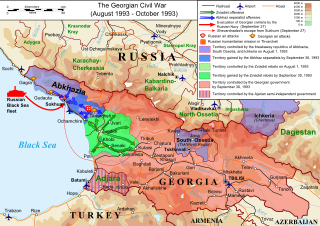
The Georgian Civil War lasted from 1991 to 1993 in the South Caucasian country of Georgia. It consisted of inter-ethnic and international conflicts in the regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, as well as the violent military coup d'état against the first democratically-elected President of Georgia, Zviad Gamsakhurdia, and his subsequent uprising in an attempt to regain power.

The Abkhazia conflict is a territorial dispute over Abkhazia, a region on the eastern coast of the Black Sea in the South Caucasus, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. The conflict involves Georgia, Russian Federation and Russian-backed self-proclaimed Republic of Abkhazia, internationally recognised only by Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria; Georgia and all other United Nations members consider Abkhazia a sovereign territory of Georgia. However, as of 2023, Georgia lacks de facto control over the territory.

The Georgian–Ossetian conflict is an ethno-political conflict over Georgia's former autonomous region of South Ossetia, which evolved in 1989 and developed into a war. Despite a declared ceasefire and numerous peace efforts, the conflict remained unresolved. In August 2008, military tensions and clashes between Georgia and South Ossetian separatists erupted into the Russo-Georgian War. Since then, South Ossetia has been under a de-facto Russian control.
Russia and Georgia have had relations for centuries. The contacts between the two date back to the 15th and 16th centuries, and the most important stage started in the 1580s, when the Georgian kingdom of Kakheti and the Russian Empire signed a treaty of alliance in 1587. Since then, Georgia–Russia relations have been developing vibrantly and culminated in the Treaty of Georgievsk, which established eastern Georgia as a protectorate of Russia. At that time, Georgia saw Russia as a powerful Christian and modernizing neighbor, capable of protecting Georgia from invading Muslim empires and North Caucasian raiders.

The Republic of Abkhazia is a partially recognized state in the South Caucasus which declared independence from Georgia during the War in Abkhazia (1992–1993). At the time, the Soviet Union had recently collapsed (1991).
An international diplomatic crisis between Georgia and Russia began in 2008, when Russia announced that it would no longer participate in the Commonwealth of Independent States economic sanctions imposed on Abkhazia in 1996 and established direct relations with the separatist authorities in Abkhazia and South Ossetia. The crisis was linked to the push for Georgia to receive a NATO Membership Action Plan and, indirectly, the unilateral declaration of independence by Kosovo.

The 2008 Georgian drone shootdowns refer to a series of military incidents involving Georgian unmanned aerial vehicles brought down over the breakaway republic of Abkhazia between March and May 2008. The skirmishes were part of a larger context of tensions between Georgia and Russia, eventually leading up to the Russo-Georgian War.

The 2008 Russo-Georgian War was a war between Russia together with the Russian-backed self-proclaimed republics of South Ossetia and Abkhazia against Georgia. The war took place in August following a diplomatic crisis between Russia and Georgia, both formerly constituent republics of the Soviet Union. The fighting took place in the strategically important South Caucasus region. It is regarded as the first European war of the 21st century.
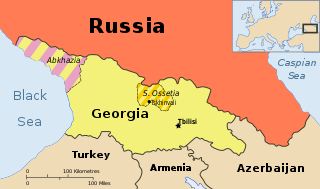
The Russo-Georgian War broke out in August 2008 and involved Georgia, Russian Federation, South Ossetia and Abkhazia.

This article describes the background of the Russo-Georgian War.

Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It covers 8,665 square kilometres (3,346 sq mi) and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi.

Abkhazia and South Ossetia are separatist regions of Georgia in the Caucasus. Most countries recognise them as part of Georgia, while Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria regard them as independent. Russia's initial recognition of the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia occurred in the aftermath of the Russo-Georgian War in 2008. The government of Georgia considers the republics to be Russian-occupied territories.
The Sochi agreement was a ceasefire agreement ostensibly marking the end of both the Georgian–Ossetian and Georgian–Abkhazian conflicts, signed in Sochi on June 24, 1992 between Georgia and Russia, the ceasefire with Abkhazia on July 27, 1993.

The State Ministry for Reconciliation and Civic Equality is a governmental agency within the Cabinet of Georgia in charge of coordination and monitoring of activities undertaken towards Georgian–Ossetian and Georgian–Abkhazian conflict resolution, generating new peace initiatives and reintegrating the conflict regions and their population with the rest of Georgia. The ministry was established in 2008 and it was known as the State Ministry for Reintegration until 2014. Incumbent minister is Tea Akhvlediani.

Russian-occupied territories in Georgia are areas of Georgia that have been occupied by Russia after the Russo-Georgian War in 2008. They consist of the regions of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia and the former South Ossetian Autonomous Region of Soviet Georgia, whose status is a matter of international dispute.
The events in 2010 in Georgia.
South Ossetia is a partially recognised landlocked state, approximately 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) above sea level on the slopes of the Greater Caucasus. Although it declared independence in 2008, only a few countries acknowledge it. The region is inhabited by Ossetians, an Iranian ethnic group. According to Russia, Nicaragua, Venezuela, Syria and Nauru, it is one of the world's newest independent states. All other states and international organisations consider South Ossetia an autonomous region of Georgia, functioning as a de facto state for twenty years after declaring independence and conducting a successful armed rebellion. Its Georgian inhabitants have been displaced. South Ossetia has been a source of tension for a number of years, with Georgia and Russia's political differences impeding peaceful independence and breeding a turbulent series of events which undermine the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.

The Administration of South Ossetia, officially the Administration of the temporary Administrative-Territorial Unit on the Territory of the Former Autonomous Region of South Ossetia, is an administrative division that Georgia regards as the legal government of South Ossetia. The administration was set up by the Georgian government as a transitional measure leading to the settlement of South Ossetia's status. The area lies within the territory of the former South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast which was abolished by the Georgian government in 1990. Since then South Ossetia has no formal autonomous status within Georgia.
Konstantin Kochiev is an Ossetian diplomat and politician from the partially recognized Caucasian Republic of South Ossetia, which most of the United Nations recognizes as part of Georgia, occupied by Russia.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "At Geneva Talks Russia Says Georgia's NATO Integration Poses Security Threat to Region". Civil Georgia. 2 July 2015. Retrieved 8 July 2015.
- 1 2 "Press releases related to the Geneva International Discussions". Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. Retrieved 8 July 2015.
- ↑ "Georgia Makes 'Unilateral Pledge' of Non-Use of Force". Civil Georgia. 23 November 2010. Retrieved 8 July 2015.
- ↑ David X. Noack: »Wir wären gerne Mitglied der Eurasischen Union« (interview with Kan Taniya), junge Welt 09.06.2016. Original source. Free version.
- 1 2 "Konstantin Kochiev told about the results of the 59th round of Geneva discussions". State Information Agency . Retrieved 7 April 2024.