
Urology, also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary system and the reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs.
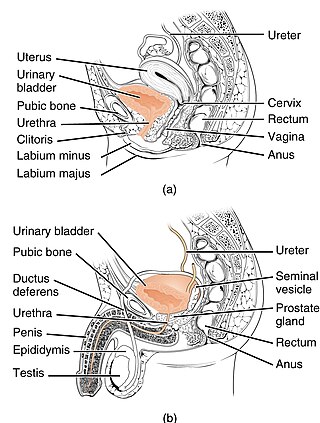
The urethra is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which placental mammals urinate and ejaculate. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the urethra also transports semen but is separate from the urinary tract.

The bladder is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.

The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.
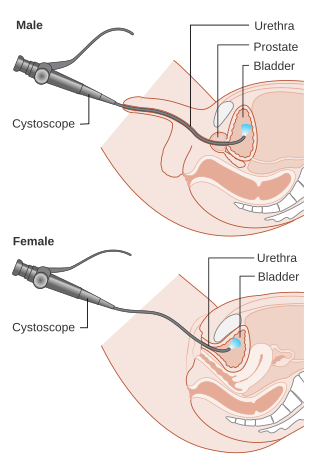
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.

Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women and has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis. UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others.

In urinary catheterization, a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used for treatment or diagnosis of bladder conditions. A clinician, often a nurse, usually performs the procedure, but self-catheterization is also possible. A catheter may be in place for long periods of time or removed after each use.

A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra, the tube connected to the bladder that allows urination. The narrowing reduces the flow of urine and makes it more difficult or even painful to empty the bladder.

Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. "Gross hematuria" occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstick test for hematuria. A urine dipstick test may also give an incorrect positive result for hematuria if there are other substances in the urine such as myoglobin, a protein excreted into urine during rhabdomyolysis. A positive urine dipstick test should be confirmed with microscopy, where hematuria is defined by three or more red blood cells per high power field. When hematuria is detected, a thorough history and physical examination with appropriate further evaluation can help determine the underlying cause.

Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections.

In urology, a Foley catheter is one of many types of urinary catheters (UC). The Foley UC was named after Frederic Foley, who produced the original design in 1929. Foleys are indwelling UC, often referred to as an IDCs. This differs from in/out catheters. The UC is a flexible tube if it is indwelling and stays put, or rigid if it is in/out, that a clinician, or the client themselves, often in the case of in/out UC, passes it through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine.

Hydronephrosis describes hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dilation of the entire upper urinary tract.

The Mitrofanoff procedure, also known as the Mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy, is a surgical procedure in which the appendix is used to create a conduit, or channel, between the skin surface and the urinary bladder. The small opening on the skin surface, or the stoma, is typically located either in the navel or nearby the navel on the right lower side of the abdomen. Originally developed by Professor Paul Mitrofanoff in 1980, the procedure represents an alternative to urethral catheterization and is sometimes used by people with urethral damage or by those with severe autonomic dysreflexia. An intermittent catheter, or a catheter that is inserted and then removed after use, is typically passed through the channel every 3–4 hours and the urine is drained into a toilet or a bottle. As the bladder fills, rising pressure compresses the channel against the bladder wall, creating a one-way valve that prevents leakage of urine between catheterizations.

A suprapubic cystostomy or suprapubic catheter (SPC) is a surgically created connection between the urinary bladder and the skin used to drain urine from the bladder in individuals with obstruction of normal urinary flow. The connection does not go through the abdominal cavity.

Posterior urethral valve (PUV) disorder is an obstructive developmental anomaly in the urethra and genitourinary system of male newborns. A posterior urethral valve is an obstructing membrane in the posterior male urethra as a result of abnormal in utero development. It is the most common cause of bladder outlet obstruction in male newborns. The disorder varies in degree, with mild cases presenting late due to milder symptoms. More severe cases can have renal and respiratory failure from lung underdevelopment as result of low amniotic fluid volumes, requiring intensive care and close monitoring. It occurs in about one in 8,000 babies.
In urology, voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) is a frequently performed technique for visualizing a person's urethra and urinary bladder while the person urinates (voids). It is used in the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux, among other disorders. The technique consists of catheterizing the person in order to fill the bladder with a radiocontrast agent, typically diatrizoic acid. Under fluoroscopy the radiologist watches the contrast enter the bladder and looks at the anatomy of the patient. If the contrast moves into the ureters and back into the kidneys, the radiologist makes the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux, and gives the degree of severity a score. The exam ends when the person voids while the radiologist is watching under fluoroscopy. Consumption of fluid promotes excretion of contrast media after the procedure. It is important to watch the contrast during voiding, because this is when the bladder has the most pressure, and it is most likely this is when reflux will occur. Despite this detailed description of the procedure, at least as of 2016 the technique had not been standardized across practices.
Urethroplasty is the surgical repair of an injury or defect within the walls of the urethra. Trauma, iatrogenic injury and infections are the most common causes of urethral injury/defect requiring repair. Urethroplasty is regarded as the gold standard treatment for urethral strictures and offers better outcomes in terms of recurrence rates than dilatations and urethrotomies. It is probably the only useful modality of treatment for long and complex strictures though recurrence rates are higher for this difficult treatment group.
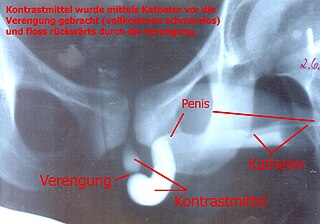
A retrograde urethrography is a routine radiologic procedure used to image the integrity of the urethra. Hence a retrograde urethrogram is essential for diagnosis of urethral injury, or urethral stricture.
Urologic diseases or conditions include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control problems, and prostate problems, among others. Some urologic conditions do not affect a person for that long and some are lifetime conditions. Kidney diseases are normally investigated and treated by nephrologists, while the specialty of urology deals with problems in the other organs. Gynecologists may deal with problems of incontinence in women.
Suprapubic aspiration is a procedure to take a urine sample. It involves putting a needle through the skin just above the pubic bone into the bladder. It is typically used as a method to collect urine in child less than 2 years of age who is not yet toilet trained in an effort to diagnose a urinary tract infection.













