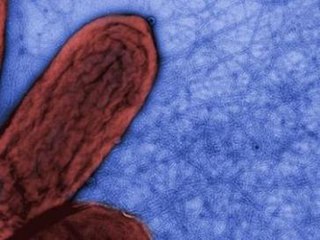
Geobacter sulfurreducens is a gram-negative metal- and sulphur-reducing proteobacterium. It is rod-shaped, aerotolerant anaerobe, non-fermentative, has flagellum and type four pili, and is closely related to Geobacter metallireducens. Geobacter sulfurreducens is an anaerobic species of bacteria that comes from the family of bacteria called Geobacteraceae. Under the genus of Geobacter, G. sulfurreducens is one out of twenty different species. The Geobacter genus was discovered by Derek R. Lovley in 1987. G. sulfurreducens was first isolated in Norman, Oklahoma, USA from materials found around the surface of a contaminated ditch.
Parabacteroides distasonis is a Gram-negative, non-sporeforming, obligately anaerobic, rod-shaped, and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Parabacteroides.
Aciditerrimonas ferrireducens is a Gram-positive, iron-reducing, moderately thermophilic, short rod-shaped, acidophilic and motile bacterium from the genus Aciditerrimonas which has been isolated from soil from a solfataric field in Ōwakudani in Japan.
Propionicimonas is a Gram-positive, non-spore-forming and facultatively anaerobic bacterial genus from the family Propionibacteriaceae.
Carboxydothermus is a genus of thermophilic, anaerobic bacteria from the family of Thermoanaerobacteraceae.
Carboxydothermus ferrireducens is a thermophilic and anaerobic bacterium from the genus of Carboxydothermus.
Carboxydothermus pertinax is a thermophilic and anaerobic bacterium from the genus of Carboxydothermus which has been isolated from a hot spring on the Kyushu Island in Japan.
Carboxydothermus siderophilus is a thermophilic and anaerobic bacterium from the genus of Carboxydothermus which has been isolated from a hot spring in Kamchatka in Russia.
Clostridium disporicum is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped and anaerobic bacterium from the genus Clostridium which has been isolated from the caecum of a rat in England.
Moorella humiferrea is a Gram-positive thermophilic, anaerobic and endospore-forming bacterium from the genus Moorella, which has been isolated from sediments from the Grot geyser, Valley of Geysers, Kamchatka, Russia. This microorganism is able to grow and reduce iron(III) oxide when small amounts of humic acid are available.
Caloranaerobacter is a Gram-negative, thermophilic, anaerobic and chemoorganotrophic bacterial genus from the family of Clostridiaceae.
Caloranaerobacter ferrireducens is a Gram-negative, thermophilic, anaerobic, iron-reducing and motile bacterium from the genus of Caloranaerobacter which has been isolated from hydrothermal sulfide deposits from the East Pacific Rise.
Geoalkalibacter subterraneus is a Fe(III)-reducing, Mn(IV)-reducing, strictly anaerobic, bacterium from the genus of Geoalkalibacter which has been isolated from the water from the Redwash oilfield from Redwash in the United States.
Thermodesulfobium is a Gram-negative, strictly anaerobic, moderately thermophilic, non-spore-forming and non-motile genus of bacteria from the family of Thermodesulfobiaceae.
Geovibrio is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, strictly anaerobic and motile genus of bacteria from the family of Deferribacteraceae.
Geovibrio thiophilus is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming and sulfur-reducing bacterium from the genus of Geovibrio which has been isolated from a drainage ditch in Konstanz in Germany.
Arsenicicoccus is a Gram-positive, non-spore-forming and facultatively anaerobic bacterial genus from the family Dermatophilaceae. The genus was previously in the family Intrasporangiaceae, but was reclassified in 2018.
Sinirhodobacter ferrireducens is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic and Fe(III) oxide-reducing bacterium from the genus Sinirhodobacter.
Geosporobacter ferrireducens is a heterotrophic, iron-reducing, alkaliphilic and anaerobic bacterium from the genus of Geosporobacter which has been isolated from oil-contaminated soil from Korea.
Natronincola ferrireducens is an anaerobic, obligately alkaliphilic, spore-forming and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Natronincola.
