
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of natural phenol and antioxidant. It is a plant secondary metabolite. It belongs to the group of flavan-3-ols, part of the chemical family of flavonoids.
Proanthocyanidins are a class of polyphenols found in a variety of plants such as blueberry. Chemically, they are oligomeric flavonoids. Many are oligomers of catechin and epicatechin and their gallic acid esters. More complex polyphenols, having the same polymeric building block, form the group of tannins.

Procyanidins are members of the proanthocyanidin class of flavonoids. They are oligomeric compounds, formed from catechin and epicatechin molecules. They yield cyanidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Cucurbitacin is any of a class of biochemical compounds that some plants — notably members of the pumpkin and gourd family, Cucurbitaceae — produce and which function as a defence against herbivores. Cucurbitacins are chemically classified as triterpenes, formally derived from cucurbitane, a triterpene hydrocarbon – specifically, from the unsaturated variant cucurbit-5-ene, or 19(10→9β)-abeo-10α-lanost-5-ene. They often occur as glycosides. They and their derivatives have been found in many plant families, in some mushrooms and even in some marine mollusks.
Prodelphinidin is a name for the polymeric tannins composed of gallocatechin. It yields delphinidin during depolymerisation under oxidative conditions.

Hyperoside is a chemical compound. It is the 3-O-galactoside of quercetin.

Procyanidin C2 is a B type proanthocyanidin trimer, a type of condensed tannin.

Procyanidin B2 is a B type proanthocyanidin. Its structure is (−)-Epicatechin-(4β→8)-(−)-epicatechin.
A type proanthocyanidins are a specific type of proanthocyanidins, which are a class of flavonoid. Proanthocyanidins fall under a wide range of names in the nutritional and scientific vernacular, including oligomeric proanthocyanidins, flavonoids, polyphenols, condensed tannins, and OPCs. Proanthocyanidins were first popularized by French scientist Jacques Masquelier.
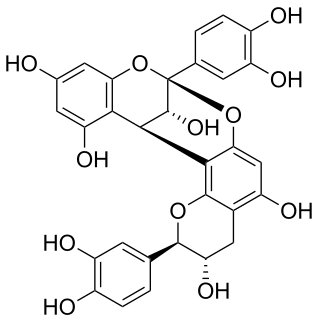
Procyanidin A1 is an A type proanthocyanidin dimer.
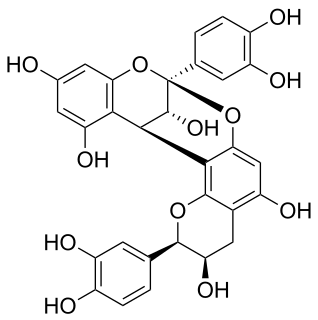
Procyanidin A2 is an A type proanthocyanidin.

Afzelechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Bergenia ligulata. It exists as at least 2 major epimers.

Selliguea feei is a fern belonging to the genus Selliguea in the family Polypodiaceae. This fern can be collected in Indonesia. The species name feei commemorates the botanist Antoine Laurent Apollinaire Fée.

Condensed tannins are polymers formed by the condensation of flavans. They do not contain sugar residues.
B type proanthocyanidins are a specific type of proanthocyanidin, which are a class of flavanoids. They are oligomers of flavan-3-ols.

Catechin-7-O-glucoside is a flavan-3-ol glycoside formed from catechin.
Propelargonidins are a type of condensed tannins formed from epiafzelechin. They yield pelargonidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.
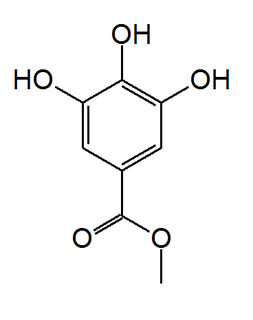
Methyl gallate is a phenolic compound. It is the methyl ester of gallic acid.

Geranin A is an A type proanthocyanidin of the propelargonidin sub type. Its structure is epi-afzelechin-(4β→8, 2β→O→7)-afzelechin.














