
Rodney Dwight Grams was an American politician and television news anchor who served in both the United States House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate. A local news anchor, Grams became well-known for working at Twin Cities station KMSP-TV from 1982 until 1991. He was a member of the Republican Party.

The Minnesota House of Representatives is the lower house of the U.S. state of Minnesota's legislature. It operates in conjunction with the Minnesota Senate, the state's upper house, to craft and pass legislation, which is then subject to approval by the governor of Minnesota.

Martin Olav Sabo was an American politician who served as United States Representative for Minnesota's fifth district, which includes Minneapolis; the district is one of eight congressional districts in Minnesota.

William Paul Luther is an American politician and lawyer from Minnesota. Luther was a Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party (DFL) member of the United States House of Representatives representing Minnesota's 6th congressional district from January 3, 1995, to January 3, 2003, serving four consecutive terms.

Timothy Joseph Penny is an American author, musician, and former politician from Minnesota. Penny was a Democratic-Farmer-Labor member of the United States House of Representatives, 1983–1995, representing Minnesota's 1st congressional district in the 98th, 99th, 100th, 101st, 102nd and 103rd congresses.
Minnesota's 1st congressional district extends across southern Minnesota from the border with South Dakota to the border with Wisconsin. It is a primarily rural district built on a strong history of agriculture, though this is changing rapidly due to strong population growth in the Rochester combined statistical area. The district is also home to several of Minnesota's major mid-sized cities, including Rochester, Mankato, Winona, Austin, Owatonna, Albert Lea, Red Wing, New Ulm, Worthington, and Lake City. It is represented by Republican Brad Finstad.

Minnesota is known for a politically active citizenry, with populism being a longstanding force among the state's political parties. Minnesota has consistently high voter turnout; in the 2008 U.S. presidential election, 77.8% of eligible Minnesotans voted – the highest percentage of any U.S. state or territory – versus the national average of 61.7%. This was due in part to its same-day voter registration laws; previously unregistered voters can register on election day, at their polls, with evidence of residency.

The 2008 Minnesota U.S. House of Representatives elections took place on November 4, 2008. All 8 congressional seats that make up the state's delegation were contested. Representatives were elected for two-year terms; those elected served in the 111th United States Congress from January 4, 2009 until January 3, 2011.

The 2010 Minnesota U.S. House of Representatives elections took place on November 2, 2010. All eight congressional seats that make up the state's delegation were contested. Representatives are elected for two-year terms; those elected will serve in the 112th United States Congress from January 3, 2011, until January 3, 2013.

The 2000 congressional elections in Minnesota were held on November 7, 2000 to determine who would represent the state of Minnesota in the United States House of Representatives.
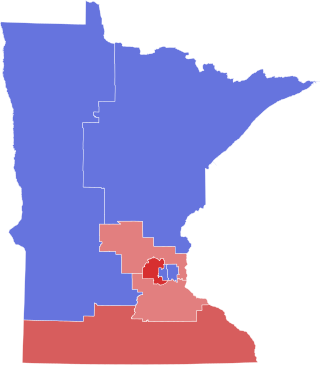
The 2002 congressional elections in Minnesota, were held on November 5, 2002 to determine who would represent the state, in the United States House of Representative.

The 2006 congressional elections in Minnesota were held on November 7, 2006 to determine who would represent the state of Minnesota in the United States House of Representatives.

The 2014 United States House of Representatives elections in Minnesota took place in the U.S. state of Minnesota on November 4, 2014, to elect Minnesota's eight representatives in the United States House of Representatives for two-year terms, one from each of Minnesota's eight congressional districts. Primary elections were held on August 12, 2014.

The 2004 congressional elections in Minnesota were held on November 2, 2004, to determine who would represent the state of Minnesota in the United States House of Representatives.

The 2018 United States House of Representatives elections in Minnesota were held on November 6, 2018, to elect the eight U.S. representatives from the state of Minnesota, one from each of the state's eight congressional districts. The elections coincided with an open gubernatorial election, a U.S. Senate election, a special U.S. Senate election, State House elections, and other elections.
The 2024 United States Senate election in Minnesota will be held on November 5, 2024, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the state of Minnesota. Incumbent Democratic Senator Amy Klobuchar was re-elected with 60.3% of the vote in 2018 and is running for re-election to a fourth term. Primary elections will take place on August 13, 2024.

The 2020 United States House of Representatives elections in Minnesota were held on November 3, 2020, to elect the eight U.S. representatives from the state of Minnesota, one from each of its congressional districts. Primary elections were held in six districts on August 11. The elections coincided with the 2020 United States presidential election as well as other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate and other state and local elections.

The 2022 Minnesota's 1st congressional district special election was a special election held on August 9, 2022. The seat became vacant when incumbent Republican representative Jim Hagedorn died on February 17, 2022, from kidney cancer.

Bradley Howard Finstad is an American politician, farmer, and agricultural consultant serving as the U.S. representative for Minnesota's 1st congressional district since 2022. Finstad represents a large section of southern Minnesota situated along the border with Iowa. A member of the Republican Party, Finstad served in the Minnesota House of Representatives from 2003 until 2009.
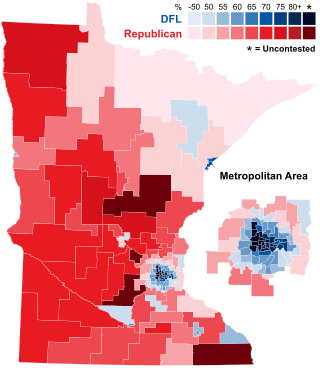
The 2022 Minnesota House of Representatives election was held in the U.S. state of Minnesota on November 8, 2022, to elect members to the House of Representatives of the 93rd Minnesota Legislature. A primary election was held in several districts on August 9, 2022. The election coincided with the election of the other chamber of the Legislature, the Senate.

















