
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers write once, run anywhere (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages.

A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally describes what is required in a JVM implementation. Having a specification ensures interoperability of Java programs across different implementations so that program authors using the Java Development Kit (JDK) need not worry about idiosyncrasies of the underlying hardware platform.
In computer programming, operator overloading, sometimes termed operator ad hoc polymorphism, is a specific case of polymorphism, where different operators have different implementations depending on their arguments. Operator overloading is generally defined by a programming language, a programmer, or both.

Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation.
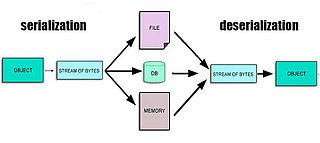
In computing, serialization is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored or transmitted and reconstructed later. When the resulting series of bits is reread according to the serialization format, it can be used to create a semantically identical clone of the original object. For many complex objects, such as those that make extensive use of references, this process is not straightforward. Serialization of objects does not include any of their associated methods with which they were previously linked.
Java and C++ are two prominent object-oriented programming languages. By many language popularity metrics, the two languages have dominated object-oriented and high-performance software development for much of the 21st century, and are often directly compared and contrasted. Java's syntax was based on C/C++.
In computing, Strongtalk is a Smalltalk environment with optional static typing support. Strongtalk can make some compile time checks, and offer stronger type safety guarantees; this is the source of its name. It is non-commercial, though it was originally a commercial project developed by a small startup company named LongView Technologies.
A foreign function interface (FFI) is a mechanism by which a program written in one programming language can call routines or make use of services written or compiled in another one. An FFI is often used in contexts where calls are made into a binary dynamic-link library.

Java is a set of computer software and specifications that provides a software platform for developing application software and deploying it in a cross-platform computing environment. Java is used in a wide variety of computing platforms from embedded devices and mobile phones to enterprise servers and supercomputers. Java applets, which are less common than standalone Java applications, were commonly run in secure, sandboxed environments to provide many features of native applications through being embedded in HTML pages.
Generics are a facility of generic programming that were added to the Java programming language in 2004 within version J2SE 5.0. They were designed to extend Java's type system to allow "a type or method to operate on objects of various types while providing compile-time type safety". The aspect compile-time type safety required that parametrically polymorphic functions are not implemented in the Java virtual machine, since type safety is impossible in this case.
Newspeak is a programming language and platform in the tradition of Smalltalk and Self being developed by a team led by Gilad Bracha. The platform includes an integrated development environment (IDE), a graphical user interface (GUI) library, and standard libraries. Starting in 2006, Cadence Design Systems funded its development and employed the main contributors, but ended funding in January 2009.
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an API specification. A computer system that meets this standard is said to implement or expose an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation.
Dart is a programming language designed by Lars Bak and Kasper Lund and developed by Google. It can be used to develop web and mobile apps as well as server and desktop applications.
Java bytecode is the instruction set of the Java virtual machine (JVM), the language to which Java and other JVM-compatible source code is compiled. Each instruction is represented by a single byte, hence the name bytecode, making it a compact form of data.
Gradual typing is a type system that lies inbetween static typing and in dynamic typing. Some variables and expressions may be given types and the correctness of the typing is checked at compile time and some expressions may be left untyped and eventual type errors are reported at runtime.
In computer programming, several language mechanisms exist for exception handling. The term exception is typically used to denote a data structure storing information about an exceptional condition. One mechanism to transfer control, or raise an exception, is known as a throw; the exception is said to be thrown. Execution is transferred to a catch.





