Related Research Articles

Genome projects are scientific endeavours that ultimately aim to determine the complete genome sequence of an organism and to annotate protein-coding genes and other important genome-encoded features. The genome sequence of an organism includes the collective DNA sequences of each chromosome in the organism. For a bacterium containing a single chromosome, a genome project will aim to map the sequence of that chromosome. For the human species, whose genome includes 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes, a complete genome sequence will involve 46 separate chromosome sequences.
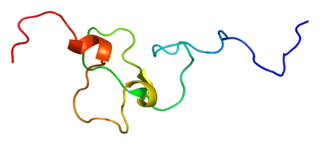
Inhibitor of growth protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ING4 gene.

Brevican core protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCAN gene. Brevican is a member of the lectican protein family.
Yingchengvirus is a genus of double stranded DNA viruses that infect haloarchaea. The genus was previously named Betasphaerolipovirus.
Glaciecola punicea is a psychrophilic bacteria found in Antarctic sea-ice habitats, being the type species of its genus. It is pigmented, psychrophilic, and a strictly aerobic chemoheterotroph. Its type strain is. Its genome has been sequenced.
Rhodococcus opacus is a bacterium species in the genus Rhodococcus. It is moderately chemolithotrophic. Its genome has been sequenced. R. opacus possesses extensive catabolic pathways for both sugars and aromatics and can tolerate inhibitory compounds found in depolymerized biomass
Glaciecola is an aerobic bacteria genus from the family of Alteromonadaceae.
Pelagibacterium is a bacteria genus from the family Hyphomicrobiaceae.
Aliiglaciecola lipolytica is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped and motile from the genus of Aliiglaciecola with a single polar flagellum which has been isolated from seawater in China.
Marivirga is a genus from the phylum Bacteroidota.
Phaeodactylibacter is a genus from the family Lewinellaceae.
Bat coronavirus RaTG13 is a SARS-like betacoronavirus identified in the droppings of the horseshoe bat Rhinolophus affinis. It was discovered in 2013 in bat droppings from a mining cave near the town of Tongguan in Mojiang county in Yunnan, China. In February 2020, it was identified as the closest known relative of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, sharing 96.1% nucleotide identity. However, in 2022, scientists found three closer matches in bats found 530 km south, in Feuang, Laos, designated as BANAL-52, BANAL-103 and BANAL-236.
Cytochrome P450, family 305, also known as CYP305, is an animal cytochrome P450 family found in insect genome. The first gene identified in this family is the CYP305A1 from the Drosophila melanogaster.
RmYN02 is a bat-derived strain of Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus. It was discovered in bat droppings collected between May and October 2019 from sites in Mengla County, Yunnan Province, China. It is the second-closest known relative of SARS-CoV-2, the virus strain that causes COVID-19, sharing 93.3% nucleotide identity at the scale of the complete virus genome. RmYN02 contains an insertion at the S1/S2 cleavage site in the spike protein, similar to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that such insertion events can occur naturally.
RacCS203 is a bat-derived strain of severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus collected in acuminate horseshoe bats from sites in Thailand and sequenced by Lin-Fa Wang's team. It has 91.5% sequence similarity to SARS-CoV-2 and is most related to the RmYN02 strain. Its spike protein is closely related to RmYN02's spike, both highly divergent from SARS-CoV-2's spike.
Bat coronavirus RpYN06 is a SARS-like betacoronavirus that infects the horseshoe bat Rhinolophus pusillus, it is a close relative of SARS-CoV-2 with a 94.48% sequence identity.
The human identical sequence (HIS) is a sequence of RNA elements, 24-27 nucleotides in length, that coronavirus genomes share with the human genome. In pathogenic progression, HIS acts as a NamiRNA (nuclear activating miRNA) through the NamiRNA-enhancer network to activate neighboring host genes. The first HIS elements was identified in the SARS-CoV-2 genome, which has five HIS elements; other human coronaviruses have one to five. It has been suggested that these sequences can be more generally termed "host identical sequences" since similar correlations have been found between the genome of SARS-CoV-2 and multiple potential hosts (bats, pangolins, ferrets, and cats).
References
- ↑ Baik KS, Park YD, Seong CN, Kim EM, Bae KS, Chun J (2006). "Glaciecola nitratireducens sp. nov., isolated from seawater". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 56 (Pt 9): 2185–8. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64330-0 . PMID 16957118.
- ↑ Bian, F.; Qin, Q.-L.; Xie, B.-B.; Shu, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. (2011). "Complete Genome Sequence of Seawater Bacterium Glaciecola nitratireducens FR1064T". Journal of Bacteriology. 193 (24): 7006–7007. doi:10.1128/JB.06296-11. ISSN 0021-9193. PMC 3232840 . PMID 22123761.