
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. It is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

Rattus is a genus of muroid rodents, all typically called rats. However, the term rat can also be applied to rodent species outside of this genus.

Bougainville, officially the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, is an autonomous region in Papua New Guinea. The largest island is Bougainville Island, while the region also includes Buka Island and a number of outlying islands and atolls. The interim capital is Buka, though it is expected that major government services and buildings will be moved to Arawa, following reconstruction.

The Bismarck Archipelago is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.

The Papuan languages are the non-Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan peoples as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892.

German New Guinea consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, became a German protectorate in 1884. Other island groups were added subsequently. The Bismarck Archipelago, and the North Solomon Islands were declared a German protectorate in 1885; in the same year the Marshall Islands were bought from Spain for $4.5 million by the Hispano-German Protocol of Rome; Nauru was annexed to the Marshall Islands protectorate in 1888, and finally the Caroline Islands, Palau, and the Mariana Islands were bought from Spain in 1899. German Samoa, though part of the German colonial empire, was not part of German New Guinea.

The flag of Papua New Guinea was adopted on 1 July 1971. In the hoist, it depicts the Southern Cross; in the fly, a raggiana bird-of-paradise is silhouetted. The design was chosen through a nationwide design competition in early 1971. The winning designer was Susan Karike, who was 15 at the time.

The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the annexation but in 1884 a Protectorate was proclaimed over the territory, then called "British New Guinea". There is a certain ambiguity about the exact date on which the entire territory was annexed by the British. The Papua Act 1905 recites that this happened "on or about" 4 September 1888. On 18 March 1902, the Territory was placed under the authority of the Commonwealth of Australia. Resolutions of acceptance were passed by the Commonwealth Parliament, who accepted the territory under the name of Papua.

The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian-administered territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the name of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. That administrative union was renamed as Papua New Guinea in 1971. Notwithstanding that it was part of an administrative union, the Territory of New Guinea at all times retained a distinct legal status and identity until the advent of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.

The states and territories are federated administrative divisions in Australia, ruled by regional governments that constitute the second level of governance between the federal government and local governments. States are self-governing regions with their own constitutions, legislatures, departments, and certain civil authorities that administer and deliver most public policies and programmes. Territories administer local policies and programmes much like the states, but are constitutionally and financially subordinate to the federal government.
Mailu, or Magi (Magɨ), is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea.

Nukumanu, formerly Tasman Islands, is an atoll of Papua New Guinea, located in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean, 4 degrees south of the equator.

The Territory of Papua and New Guinea was established by an administrative union between the Australian-administered territories of Papua and New Guinea in 1949. In December 1971, the name of the Territory changed to "Papua New Guinea" and in 1975 it became the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.

Elseya branderhorsti is a species of freshwater turtle in the family Chelidae. The species is endemic to southern New Guinea, in West Papua Indonesia and Western Province of Papua New Guinea. Until recently it has been a confusing species due to its lost holotype and its sympatry with another, undescribed, species. E. branderhorsti is currently listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN RedList in part due to its vulnerability to the Asian turtle trade.
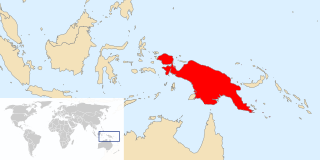
New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, and with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), the largest island in the Southern Hemisphere. Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, it is separated by the 150 km wide Torres Strait from Australia. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea or West Papua, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua and West Papua.
Japanese settlement in the Territory of Papua and German New Guinea dates back to the early 20th century when migrants from Japan established copra plantations and trading businesses in the islands, specifically Rabaul. The Japanese community remained small throughout the first half of the 20th century, although there were Japanese migrating in and out of New Guinea in different years from 1901 to 1945, it generally never exceeded more than 100 as a whole community. Some Japanese stayed for short terms while others stayed longer periods depending on their roles. Most Japanese in Papua were businessmen and plantation managers, although a few became fishermen. As almost all the migrants were men, many of them married local Papuan wives and raised mixed-race Japanese-Papuan families while other Japanese men staying only for short periods also had sexual cohabitations with local Papuan women, but in most cases without marrying. Many of them did produced offspring but they were generally abandoned by their Japanese fathers and raised by their single Papuan mothers or sent to the orphanage. These abandoned mixed-race children's were recorded as ethnic Papuans in the census as the ethnicity of their fathers was unknown.

Batocera is a genus of the family Cerambycidae, subfamily Lamiinae, close to the genus Rosenbergia.

Lesticus is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following species:

Glenea is a genus of longhorn beetles belonging to the family Cerambycidae, subfamily Lamiinae.

Glenea lefebvrei is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville in 1831, originally under the genus Saperda. It is known from Papua New Guinea and Indonesia.


















