Related Research Articles

The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm in June 1972. Its mandate is to provide leadership, deliver science and develop solutions on a wide range of issues, including climate change, the management of marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and green economic development. The organization also develops international environmental agreements; publishes and promotes environmental science and helps national governments achieve environmental targets.

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable".

The Global Environment Facility (GEF) is a multilateral environmental fund that provides grants and blended finance for projects related to biodiversity, climate change, international waters, land degradation, persistent organic pollutants (POPs), mercury, sustainable forest management, food security, and sustainable cities in developing countries and countries with economies in transition. It is the largest source of multilateral funding for biodiversity globally and distributes more than $1 billion a year on average to address inter-related environmental challenges.

Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, groups and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where it is possible, to repair damage and reverse trends.
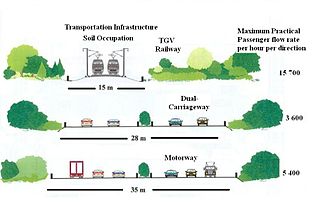
Sustainable urban infrastructure expands on the concept of urban infrastructure by adding the sustainability element with the expectation of improved and more resilient urban development. In the construction and physical and organizational structures that enable cities to function, sustainability also aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the capabilities of the future generations.
The Earth Institute is a research institute at Columbia University created in 1995 for addressing complex issues facing the planet and its inhabitants, with a focus on sustainable development. With an interdisciplinary approach, this includes research in climate change, geology, global health, economics, management, agriculture, ecosystems, urbanization, energy, hazards, and water. The Earth Institute's activities are guided by the idea that science and technological tools that already exist could be applied to greatly improve conditions for the world's poor, while preserving the natural systems that support life on Earth.

The Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Partnership (REEEP) is a Vienna-based Quasi-International Organisation that advances markets for renewable energy and energy efficiency with a particular emphasis on the emerging markets and developing countries.

A green-collar worker is a worker who is employed in an environmental sector of the economy. Environmental green-collar workers satisfy the demand for green development. Generally, they implement environmentally conscious design, policy, and technology to improve conservation and sustainability. Formal environmental regulations as well as informal social expectations are pushing many firms to seek professionals with expertise with environmental, energy efficiency, and clean renewable energy issues. They often seek to make their output more sustainable, and thus more favorable to public opinion, governmental regulation, and the Earth's ecology.

Deforestation in Cambodia has increased in recent years. Cambodia is one of the world's most forest endowed countries, that was not historically widely deforested. However, massive deforestation for economic development threatens its forests and ecosystems. As of 2015, the country has one of the highest rates of deforestation in the world.
The Korea Federation for Environmental Movements (KFEM) is a non-profit organization in South Korea that focuses on environmentalism.
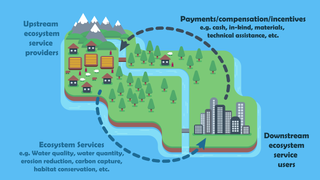
Payments for ecosystem services (PES), also known as payments for environmental services, are incentives offered to farmers or landowners in exchange for managing their land to provide some sort of ecological service. They have been defined as "a transparent system for the additional provision of environmental services through conditional payments to voluntary providers". These programmes promote the conservation of natural resources in the marketplace.
Conservation finance is the practice of raising and managing capital to support land, water, and resource conservation. Conservation financing options vary by source from public, private, and nonprofit funders; by type from loans, to grants, to tax incentives, to market mechanisms; and by scale ranging from federal to state, national to local.
Environmental governance (EG) consists of a system of laws, norms, rules, policies and practices that dictate how the board members of an environment related regulatory body should manage and oversee the affairs of any environment related regulatory body which is responsible for ensuring sustainability (sustainable development) and manage all human activities—political, social and economic. Environmental governance includes government, business and civil society, and emphasizes whole system management. To capture this diverse range of elements, environmental governance often employs alternative systems of governance, for example watershed-based management.

ECODES "huft" Foundation Ecology and Development is an independent non-profit organization that works towards sustainable and environmentally friendly development, founded on 10 March 1992.
A sustainability organization is (1) an organized group of people that aims to advance sustainability and/or (2) those actions of organizing something sustainably. Unlike many business organizations, sustainability organizations are not limited to implementing sustainability strategies which provide them with economic and cultural benefits attained through environmental responsibility. For sustainability organizations, sustainability can also be an end in itself without further justifications.

The Asia Network for Sustainable Agriculture and Bioresources (ANSAB) is a non-governmental organization, headquartered in Kathmandu, Nepal. It was established in 1992. ANSAB is committed to enterprise oriented solutions to biodiversity conservation and sustainable community development.

Forest Trends is a non-profit organization founded in 1998 and based in Washington, DC, that connects with economic tools and incentives for maintaining ecosystems. Its mission is four-fold: to expand the value of forests to society, to promote sustainable forest management and conservation by creating and capturing market values for ecosystem services, to support innovative projects and companies that are developing these markets and to enhance the livelihoods of local communities living in and around those forests.

CLASP is an international nonprofit organization which provides technical and policy support to governments worldwide and works to implement energy efficiency standards and labels (S&L) for appliances, lighting, and equipment. It specializes in publishing studies and analyses with relevance to S&L practitioners.

Environment and Ecology Bureau is a policy bureau of the Government of Hong Kong. The agency was established on 1 July 2022. The current Secretary for Environment and Ecology is Tse Chin-wan.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "北京市朝阳区永续全球环境研究所 – GEI".
- ↑ Fallows, James (June 1, 2008). "China's Silver Lining". The Atlantic.
- ↑ Broder, John M.; Ansfield, Jonathan (June 7, 2009). "China and U.S. Seek a Truce on Greenhouse Gases". The New York Times– via NYTimes.com.
- ↑ "加州州长全球气候峰会". lvse.sohu.com.
- ↑ "Little thaw over warming". Los Angeles Times. July 29, 2009.
- ↑ "Conservation incentive agreements: An approach to linking conservation and economic development on Indigenous lands in Ecuador" (PDF). Retrieved 2001-06-17.
- ↑ "Training". Archived from the original on 2011-06-29. Retrieved 2011-02-23.
- ↑ Madame Jiaman JIN, Executive Director of China's Global Environmental Institute on YouTube
- ↑ "Encouraging communities in China to protect local ecologies". 2013-03-06. Archived from the original on 2014-09-21. Retrieved 2011-02-23.
- ↑ "China Watch". Worldwatch Institute. Archived from the original on 2019-05-31. Retrieved 2019-05-31.