The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as the environment's maximal load, which in population ecology corresponds to the population equilibrium, when the number of deaths in a population equals the number of births. Carrying capacity of the environment implies that the resources extraction is not above the rate of regeneration of the resources and the wastes generated are within the assimilating capacity of the environment. The effect of carrying capacity on population dynamics is modelled with a logistic function. Carrying capacity is applied to the maximum population an environment can support in ecology, agriculture and fisheries. The term carrying capacity has been applied to a few different processes in the past before finally being applied to population limits in the 1950s. The notion of carrying capacity for humans is covered by the notion of sustainable population.
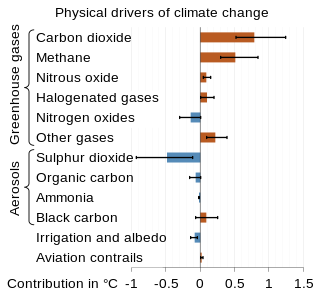
Radiative forcing is a concept used in climate science to quantify the change in energy balance in Earth's atmosphere. Various factors contribute to this change in energy balance, such as concentrations of greenhouse gases and aerosols, and changes in surface albedo and solar irradiance. In more technical terms, it is defined as "the change in the net, downward minus upward, radiative flux due to a change in an external driver of climate change." These external drivers are distinguished from feedbacks and variability that are internal to the climate system, and that further influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the top of the stratosphere. It is quantified in units of watts per square meter, and often summarized as an average over the total surface area of the globe.

The Journal of Geophysical Research is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It is the flagship journal of the American Geophysical Union. It contains original research on the physical, chemical, and biological processes that contribute to the understanding of the Earth, Sun, and Solar System. It has seven sections: A, B, C (Oceans), D (Atmospheres), E (Planets), F, and G (Biogeosciences). All current and back issues are available online for subscribers.

Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences is an annual peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Annual Reviews, which broadly covers Earth and planetary sciences, including geology, atmospheric sciences, climate, geophysics, environmental science, geological hazards, geodynamics, planet formation, and solar system origins. The co-editors are Katherine H. Freeman and Raymond Jeanloz. As of 2023, Journal Citation Reports gives the journal a 2022 impact factor of 14.9. As of 2023, it is being published as open access, under the Subscribe to Open model.
Meteoritics & Planetary Science is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Meteoritical Society. It specialises in the fields of meteoritics and planetary science.

Environmental issues are disruptions in the usual function of ecosystems. Further, these issues can be caused by humans or they can be natural. These issues are considered serious when the ecosystem cannot recover in the present situation, and catastrophic if the ecosystem is projected to certainly collapse.

Planetary boundaries are a framework to describe limits to the impacts of human activities on the Earth system. Beyond these limits, the environment may not be able to self-regulate anymore. This would mean the Earth system would leave the period of stability of the Holocene, in which human society developed. The framework is based on scientific evidence that human actions, especially those of industrialized societies since the Industrial Revolution, have become the main driver of global environmental change. According to the framework, "transgressing one or more planetary boundaries may be deleterious or even catastrophic due to the risk of crossing thresholds that will trigger non-linear, abrupt environmental change within continental-scale to planetary-scale systems."

Earth and Planetary Science Letters (EPSL) is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on physical, chemical and mechanical processes of the Earth and other planets, including extrasolar ones. Topics covered range from deep planetary interiors to atmospheres. The journal was established in 1966 and is published by Elsevier. The co-editors-in-chief are J. Adkins, J.P. Avouac, R. Bendick, L. Derry, M. Ishii, T.A. Mather, W.B. McKinnon, F. Moynier, Chiara Maria Petrone, Hans Thybo, Alexander Webb.
Planetary management is intentional global-scale management of Earth's biological, chemical and physical processes and cycles. Planetary management also includes managing humanity’s influence on planetary-scale processes. Effective planetary management aims to prevent destabilisation of Earth's climate, protect biodiversity and maintain or improve human well-being. More specifically, it aims to benefit society and the global economy, and safeguard the ecosystem services upon which humanity depends – global climate, freshwater supply, food, energy, clean air, fertile soil, pollinators, and so on.

Planetary and Space Science (P&SS), published 15 times per year, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1959. It publishes original research articles along with short communications (letters). The main topic is Solar System processes which encompasses multiple areas of the natural sciences. Numerical simulations of solar system processes are also conducted at ground-based facilities or on-board space platforms. The editor-in-chief is Maria Cristina De Sanctis. It is published by Elsevier.

Advances in Space Research is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published 24 times per year by Elsevier. It was established in 1981 and is the official journal of the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR). The editor-in-chief is Pascal Willis.

Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. It was established in 1950 and is sponsored by the Geochemical Society and the Meteoritical Society. The editor-in-chief is Jeffrey Catalano. The journal covers topics in Earth geochemistry, planetary geochemistry, cosmochemistry and meteoritics.

Astronomy & Geophysics (A&G) is a scientific journal and trade magazine published on behalf of the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS) by Oxford University Press. It is distributed bimonthly to members of the RAS.

Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, established in October 1967, is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. The co-editors are A. Ferreira, K. Hirose, D. Jault, and C. Michaut.
The Journal of Earth System Science is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering Earth system science. It was established in 1978 and is published by Springer Science+Business Media on behalf of the Indian Academy of Sciences. The editor-in-chief is Prof. Somnath Dasgupta.
Planetary health is a multi- and transdisciplinary research paradigm, a new science for exceptional action, and a global movement. Planetary health refers to "the health of human civilization and the state of the natural systems on which it depends". In 2015, the Rockefeller Foundation–Lancet Commission on Planetary Health launched the concept which is currently being developed towards a new health science with over 25 areas of expertise.

Clarivate Plc is a British-American publicly traded analytics company that operates a collection of subscription-based services, in the areas of bibliometrics and scientometrics; business / market intelligence, and competitive profiling for pharmacy and biotech, patents, and regulatory compliance; trademark protection, and domain and brand protection. In the academy and the scientific community, Clarivate is known for being the company that calculates the impact factor, using data from its Web of Science product family, that also includes services/applications such as Publons, EndNote, EndNote Click, and ScholarOne. Its other product families are Cortellis, DRG, CPA Global, Derwent, MarkMonitor, CompuMark, and Darts-ip, and also the various ProQuest products and services.

Dimorphos is a natural satellite or moon of the near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a binary system. The moon was discovered on 20 November 2003 by Petr Pravec in collaboration with other astronomers worldwide. Dimorphos has a diameter of 177 meters (581 ft) across its longest extent and it was the target of the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), a NASA space mission that deliberately collided a spacecraft with the moon on 26 September 2022 to alter its orbit around Didymos. Before the impact by DART, Dimorphos had a shape of an oblate spheroid with a surface covered in boulders but virtually no craters. The moon is thought to have formed when Didymos shed its mass due to its rapid rotation, which formed an orbiting ring of debris that conglomerated into a low-density rubble pile that became Dimorphos today.
Trude Storelvmo is a Norwegian meteorologist who is a professor at the University of Oslo. She specializes in atmospheric science and studies the impact of aerosols and clouds on the climate of the Earth. She was awarded a European Research Council Starting Grant in 2018. She serves as editor-in-chief of Global and Planetary Change.
The Toarcian extinction event, also called the Pliensbachian-Toarcian extinction event, the Early Toarcian mass extinction, the Early Toarcian palaeoenvironmental crisis, or the Jenkyns Event, was an extinction event that occurred during the early part of the Toarcian age, approximately 183 million years ago, during the Early Jurassic. The extinction event had two main pulses, the first being the Pliensbachian-Toarcian boundary event (PTo-E). The second, larger pulse, the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (TOAE), was a global oceanic anoxic event, representing possibly the most extreme case of widespread ocean deoxygenation in the entire Phanerozoic eon. In addition to the PTo-E and TOAE, there were multiple other, smaller extinction pulses within this span of time.












