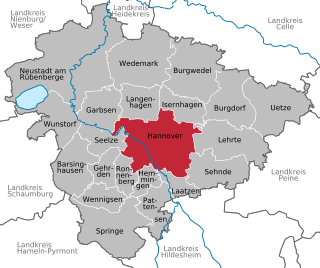
Hanover is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,061 (2017) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the third-largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg and Bremen. Hanover's urban area comprises the towns of Garbsen, Langenhagen and Laatzen and has a population of about 791,000 (2018). The Hanover Region has approximately 1.16 million inhabitants (2019).

A carillon is a pitched percussion idiophone that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 cast bronze bells in fixed suspension and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoniously together. Housed in bell towers, carillons are usually owned by churches, universities, or municipalities. The bells are struck with clappers, which are connected to a keyboard of wooden batons played with the hands and pedals played with the feet. Often, carillons include an automatic system through which the time is announced and simple tunes are played throughout the day.
Campanology is the study of bells. It encompasses the technology of bells – how they are cast, tuned, rung, and sounded – as well as the history, methods, and traditions of bell-ringing as an art.

St. Mary's Church, or formally the Basilica of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary, is a Brick Gothic Catholic church located in central Gdańsk, Poland. With its volume between 185,000 m3 and 190,000 m3 it is currently one of the two or three largest brick churches in the world. Only San Petronio Basilica in Bologna, comprising 258,000 m3 is larger, Munich Frauenkirche and Ulm Minster also comprise 185,000 to 190,000 m3.

A bell is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be made by an internal "clapper" or "uvula", an external hammer, or—in small bells—by a small loose sphere enclosed within the body of the bell.

The Peter and Paul Cathedral is a Russian Orthodox cathedral located inside the Peter and Paul Fortress in St. Petersburg, Russia. It is the first and oldest landmark in St. Petersburg, built between 1712 and 1733 on Hare Island along the Neva River. Both the cathedral and the fortress were originally built under Peter the Great and designed by Domenico Trezzini. The cathedral's bell tower is the world's tallest Orthodox bell tower. Since the belfry is not standalone, but an integral part of the main building, the cathedral is sometimes considered the highest Orthodox Church in the world. There is another Cathedral of Saints Peter and Paul Church in St. Petersburg, located in Petergof.

The Bristol Harbour Railway was a standard-gauge industrial railway that served the wharves and docks of Bristol, England. The line, which had a network of approximately 5 mi (8.0 km) of track, connected the Floating Harbour to the GWR mainline at Bristol Temple Meads. Freight could be transported directly by waggons to Paddington Station in London. The railway officially closed in 1964.

Herrenberg is a town in the middle of Baden-Württemberg, about 30 km south of Stuttgart and 20 km from Tübingen. After Sindelfingen, Böblingen, and Leonberg, it is the fourth largest town in the district of Böblingen.

Hoover Tower is a 285 feet (87 m) structure on the campus of Stanford University in Stanford, California. The tower houses the Hoover Institution Library and Archives, an archive collection founded by Herbert Hoover before he became President of the United States. Hoover had amassed a large collection of materials related to early 20th century history; he donated them to Stanford, his alma mater, to found a "library of war, revolution and peace". Hoover Tower also houses the Hoover Institution research center and think tank.

The Palace of Culture is an edifice located in Iași, Romania. The building served as Administrative and Justice Palace until 1955, when its destination was changed, being assigned to the four museums nowadays united under the name of Moldavia National Museum Complex. Also, the building houses the Cultural Heritage Conservation-Restoration Centre, and hosts various exhibitions and other events.

Gillett & Johnston was a clockmaker and bell foundry based in Croydon, England from 1844 until 1957. Between 1844 and 1950, over 14,000 tower clocks were made at the works. The company's most successful and prominent period of activity as a bellfounder was in the 1920s and 1930s, when it was responsible for supplying many important bells and carillons for sites across Britain and around the world.

A structure relocation is the process of moving a structure from one location to another. There are two main ways for a structure to be moved: disassembling and then reassembling it at the required destination, or transporting it whole. For the latter, the building is first raised and then may be pushed on temporary rails or dollies if the distance is short. Otherwise, wheels, such as flatbed trucks, are used. These moves can be complicated and require the removal of protruding parts of the building, such as the chimney, as well as obstacles along the journey, such as overhead cables and trees.
Jerg Ratgeb, also Jörg Ratgeb, was a German painter during the Renaissance, and a contemporary of Albrecht Dürer.

Rapperswil Castle is a castle, built in the early 13th century AD by the House of Rapperswil in the former independent city of Rapperswil.

Stadtpfarrkirche St. Johann is a Roman Catholic parish church in the city of Rapperswil, canton of St. Gallen, Switzerland.

Veronese bellringing art is a style of ringing church bells that developed around Verona, Italy from the eighteenth century. The bells are rung full circle, being held up by a rope and wheel until a note is required.
Bell Museum may refer to:

Lindenhof in Rapperswil is a moraine hill and a public square being the historic center of Rapperswil, Switzerland.






















